Solving Triangles: Find Missing Angles Made Easy
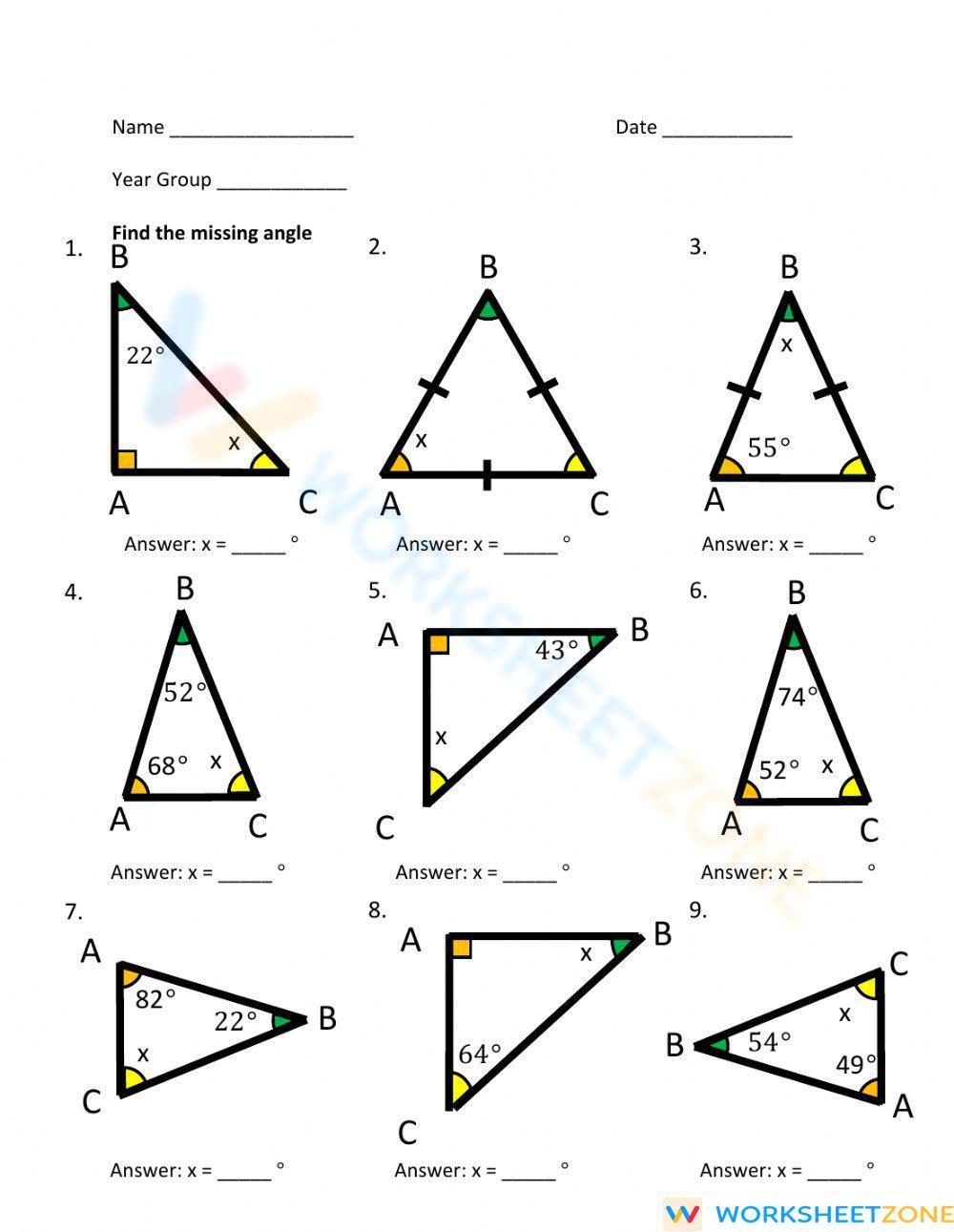
Understanding Triangles and Their Angles
Triangles are one of the most fundamental shapes in geometry, and understanding their properties is crucial for problem-solving in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. One of the most common challenges when dealing with triangles is finding missing angles. In this article, we will explore the concept of triangles, types of angles, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to find missing angles in a triangle.
Types of Angles in a Triangle
A triangle has three angles, and the sum of these angles is always 180 degrees. There are several types of angles in a triangle, including:
- Acute angle: An acute angle is less than 90 degrees.
- Right angle: A right angle is exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse angle: An obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
- Straight angle: A straight angle is exactly 180 degrees.
Types of Triangles
There are several types of triangles, including:
- Equilateral triangle: An equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles.
- Isosceles triangle: An isosceles triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles.
- Scalene triangle: A scalene triangle has three unequal sides and three unequal angles.
- Right triangle: A right triangle has one right angle and two acute angles.
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Missing Angles
Finding missing angles in a triangle can be a straightforward process if you follow these steps:
- Identify the given angles: Start by identifying the angles that are given in the problem.
- Determine the type of triangle: Determine the type of triangle you are dealing with, as this can help you identify the missing angles.
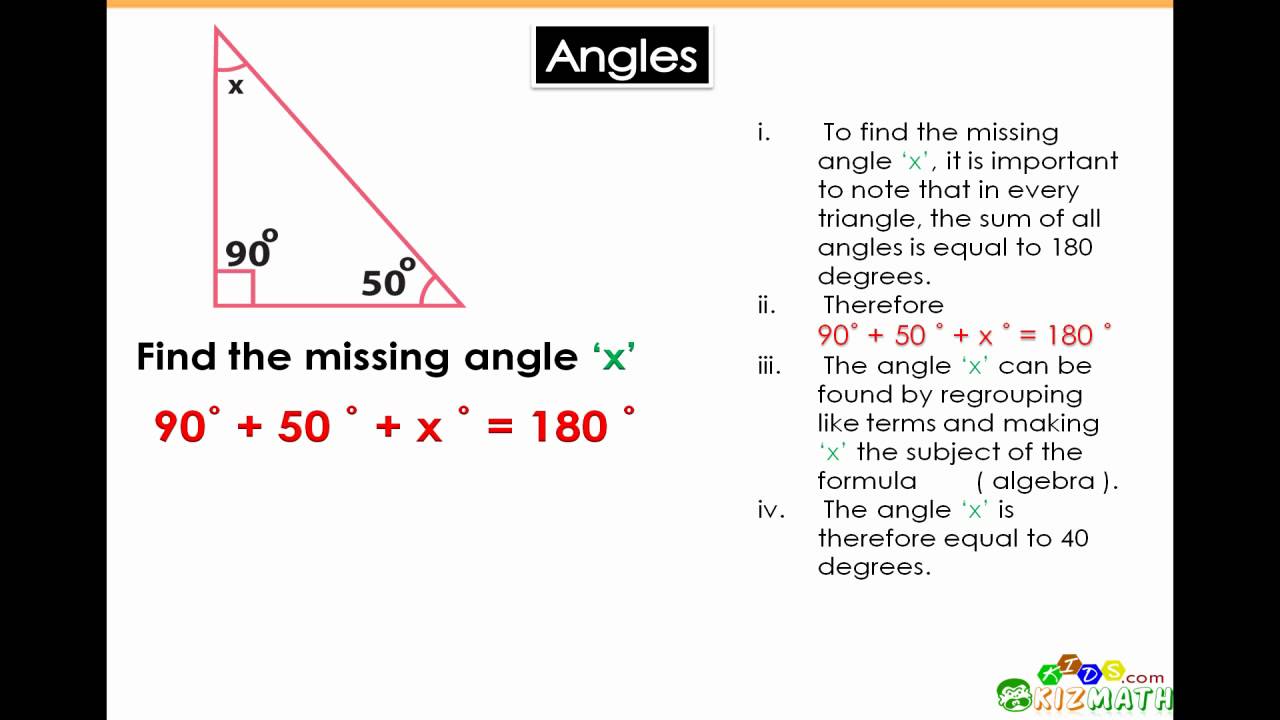
- Use the angle sum property: The sum of the angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees. Use this property to find the missing angles.
- Apply trigonometric ratios: If you know the lengths of the sides of the triangle, you can use trigonometric ratios to find the missing angles.
📝 Note: Make sure to read the problem carefully and identify the given angles and the type of triangle before attempting to find the missing angles.
Example Problems
Let’s consider a few example problems to illustrate the steps:
Example 1: Find the missing angle in an equilateral triangle
Given: ∠A = ∠B = 60°
To find: ∠C
Solution: Since the triangle is equilateral, we know that all three angles are equal. Therefore, ∠C = 60°.
Example 2: Find the missing angle in a right triangle
Given: ∠A = 30°, ∠B = 90°
To find: ∠C
Solution: Since the triangle is a right triangle, we know that one angle is 90°. Using the angle sum property, we can find ∠C: ∠C = 180° - 30° - 90° = 60°.
Using Trigonometric Ratios to Find Missing Angles
If you know the lengths of the sides of the triangle, you can use trigonometric ratios to find the missing angles. The most common trigonometric ratios are:
- Sine: sin(A) = opposite side / hypotenuse
- Cosine: cos(A) = adjacent side / hypotenuse
- Tangent: tan(A) = opposite side / adjacent side
📝 Note: Make sure to use the correct trigonometric ratio for the given problem.
Table of Trigonometric Ratios
| Angle | Sine | Cosine | Tangent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30° | 1⁄2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 |
| 45° | 1/√2 | 1/√2 | 1 |
| 60° | √3/2 | 1⁄2 | √3 |
| 90° | 1 | 0 | undefined |
Conclusion
Finding missing angles in a triangle can be a straightforward process if you follow the steps outlined in this article. Remember to identify the given angles, determine the type of triangle, and use the angle sum property and trigonometric ratios to find the missing angles. With practice, you will become more comfortable and confident in solving triangle problems.
What is the sum of the angles in a triangle?
+The sum of the angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees.
What is the difference between an acute angle and an obtuse angle?
+An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, while an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
How do I use trigonometric ratios to find missing angles in a triangle?
+You can use trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent to find missing angles in a triangle. Make sure to use the correct ratio for the given problem.