Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments Worksheet Answers
Understanding Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments
Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is considered the father of modern genetics due to his groundbreaking experiments on pea plants in the 1860s. His work laid the foundation for our understanding of genetic inheritance and the laws that govern it. In this article, we will delve into Mendel’s pea plant experiments, explore the key concepts, and provide answers to a worksheet on the topic.
Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments: An Overview
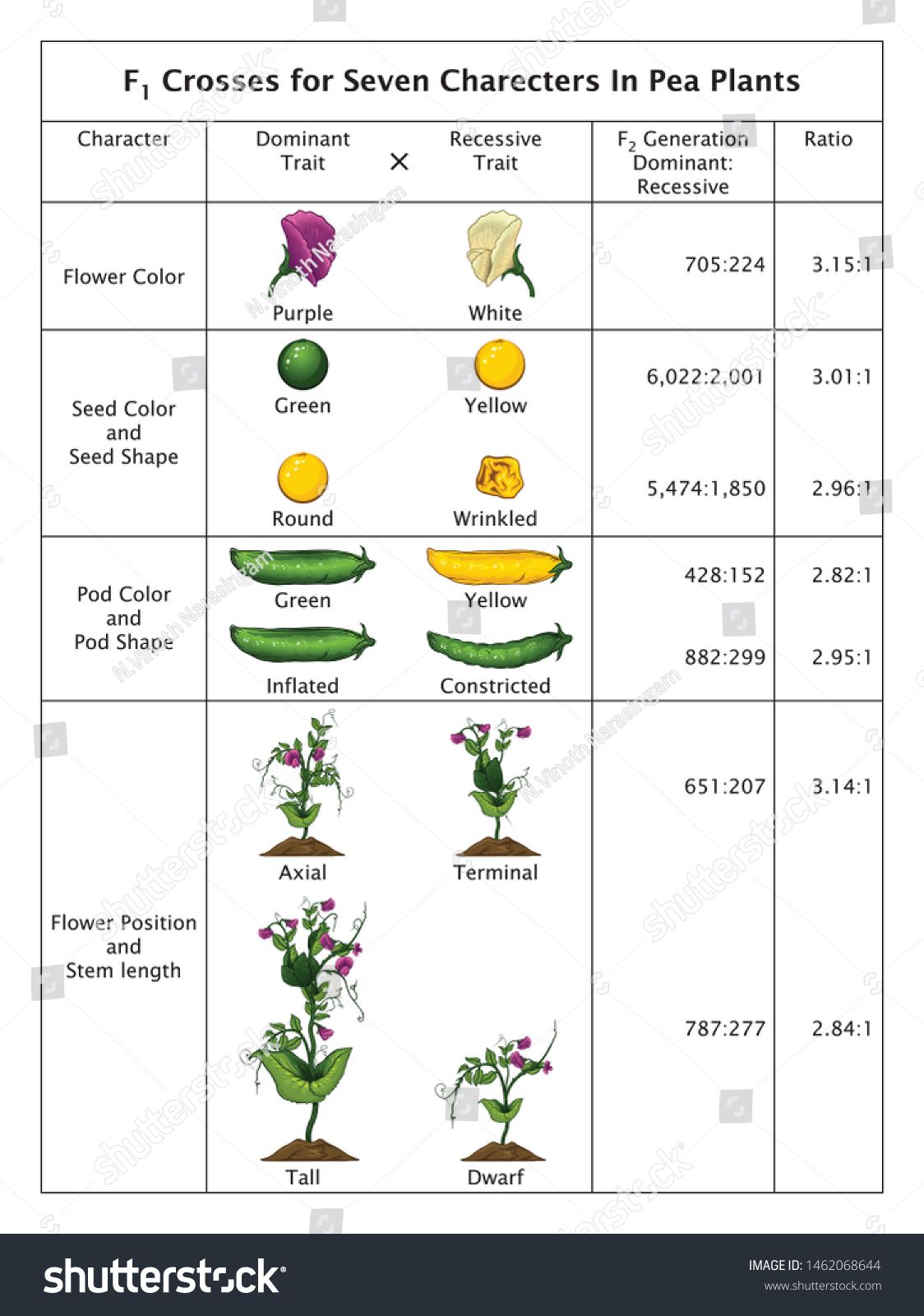
Mendel’s experiments involved crossing different varieties of pea plants to study how traits were passed down from one generation to the next. He chose pea plants because they have distinct characteristics, such as flower color, plant height, and seed shape, that are easily observable. Mendel’s experiments consisted of the following steps:
- Step 1: Mendel selected pea plants with distinct characteristics, such as tall or short stems, green or yellow seeds, and purple or white flowers.
- Step 2: He cross-pollinated the plants to create hybrids, which are offspring that result from the combination of two different parent plants.
- Step 3: Mendel allowed the hybrids to self-pollinate, resulting in the production of seeds.
- Step 4: He then planted the seeds and observed the characteristics of the offspring.
Key Concepts: Mendel's Laws
Mendel’s experiments led to the development of three fundamental laws of inheritance:
- The Law of Segregation: This law states that each pair of alleles (different forms of a gene) separates from each other during gamete formation, resulting in each offspring inheriting one allele from each parent.
- The Law of Independent Assortment: This law states that different genes are sorted independently of each other during gamete formation, resulting in a random combination of alleles in offspring.
- The Law of Dominance: This law states that one allele can be dominant over another allele, resulting in the dominant allele being expressed in the offspring.
Worksheet Answers
What was the main goal of Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
- Answer: To understand how traits are passed down from one generation to the next.
What were some of the characteristics that Mendel studied in his pea plant experiments?
- Answer: Flower color, plant height, seed shape, and seed color.
What is the term for the offspring that result from the combination of two different parent plants?
- Answer: Hybrids.
What is the Law of Segregation?
- Answer: The law that states each pair of alleles separates from each other during gamete formation, resulting in each offspring inheriting one allele from each parent.
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
- Answer: The law that states different genes are sorted independently of each other during gamete formation, resulting in a random combination of alleles in offspring.
What is the Law of Dominance?
- Answer: The law that states one allele can be dominant over another allele, resulting in the dominant allele being expressed in the offspring.
🌱 Note: Mendel's pea plant experiments were a crucial step in understanding genetic inheritance and paved the way for modern genetics.
Conclusion
Mendel’s pea plant experiments were a groundbreaking study that laid the foundation for our understanding of genetic inheritance. By crossing different varieties of pea plants, Mendel was able to identify the fundamental laws that govern how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Understanding these laws is crucial for modern genetics and has far-reaching implications for fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
What were the key findings of Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
+
Mendel’s pea plant experiments led to the discovery of the fundamental laws of inheritance, including the Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, and the Law of Dominance.
What is the significance of Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
+
Mendel’s pea plant experiments laid the foundation for modern genetics and have far-reaching implications for fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
What is the difference between a dominant and recessive allele?
+
A dominant allele is an allele that will be expressed if an individual has one copy of the allele, while a recessive allele is an allele that will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of the allele.
Related Terms:
- Gregor Mendel
- Gregor Mendel news
- Gregor Mendel images
- Gregor Mendel videos
- Mendel pea plant experiment
- Mendel experiment



