Meiosis Review Worksheet Answer Key Secrets Revealed
Unlocking the Secrets of Meiosis: A Comprehensive Review
Meiosis is a complex and crucial process in biology that can be overwhelming for students to grasp. However, with a thorough understanding of the key concepts and processes, anyone can master meiosis. In this article, we will delve into the world of meiosis, exploring its intricacies and providing a comprehensive review of the subject. Whether you’re a student looking to ace your biology exam or a teacher seeking to reinforce your understanding, this article is designed to be your ultimate resource.
What is Meiosis?
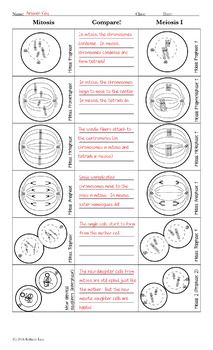
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, resulting in the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for sexual reproduction, allowing for genetic diversity and the creation of unique offspring. Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Meiosis I: The First Round of Cell Division
Meiosis I is the first stage of meiosis, where a diploid cell (containing two sets of chromosomes) divides to form two haploid cells (containing one set of chromosomes). This process involves several key events:
- Prophase I: Chromosomes condense, and homologous pairs come together in a process called synapsis.
- Metaphase I: Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase I: Homologous pairs separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I: Nuclear envelope reforms, and chromosomes uncoil.
🔍 Note: During meiosis I, crossing over and independent assortment occur, increasing genetic diversity.
Meiosis II: The Second Round of Cell Division
Meiosis II is the second stage of meiosis, where the haploid cells produced in meiosis I undergo another round of cell division. This process is similar to mitosis, with the following events:
- Prophase II: Chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II: Nuclear envelope reforms, and chromosomes uncoil.
Key Concepts and Terms
- Genetic recombination: The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.
- Independent assortment: The random separation of homologous pairs during meiosis I.
- Crossing over: The exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during meiosis I.
- Synapsis: The pairing of homologous chromosomes during prophase I.

| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Meiosis | A type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, resulting in the production of gametes. |
| Genetic recombination | The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I. |
| Independent assortment | The random separation of homologous pairs during meiosis I. |
Conclusion
Meiosis is a complex and fascinating process that is essential for sexual reproduction. By understanding the key concepts and processes involved in meiosis, you can unlock the secrets of this intricate process. Whether you’re a student or a teacher, this comprehensive review is designed to provide you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle meiosis with ease.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
+Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, allowing for genetic diversity and the creation of unique offspring.
What is the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
+Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous pairs, while meiosis II involves the separation of sister chromatids.
What is genetic recombination?
+Genetic recombination is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.