Meiosis Phase Worksheet Answer Key Simplified

Understanding Meiosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Meiosis is a fundamental concept in biology, essential for the reproduction of eukaryotic organisms. It is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) with a unique combination of genetic traits. In this article, we will delve into the phases of meiosis, exploring the process step-by-step, and providing a simplified answer key for a meiosis phase worksheet.
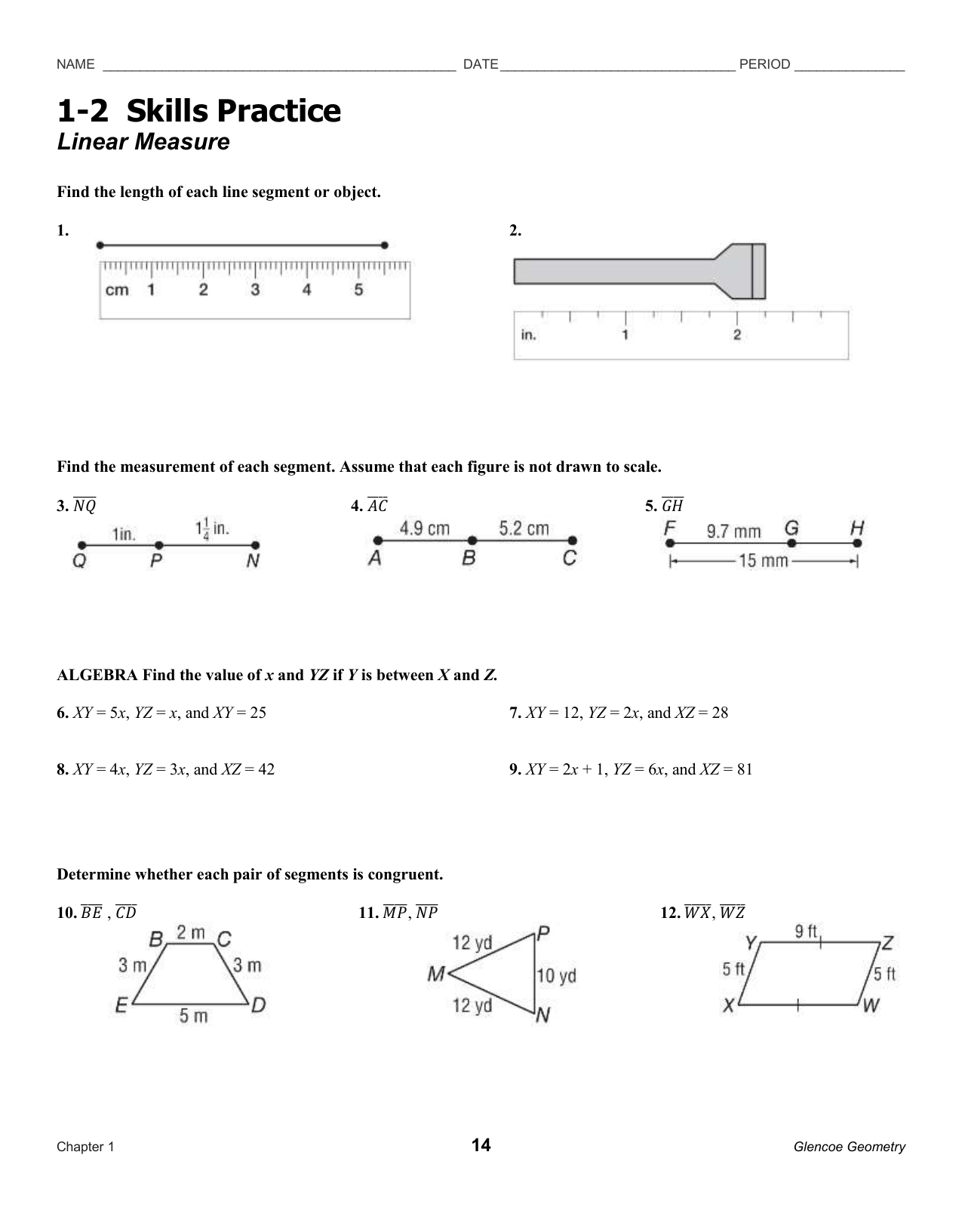
Meiosis Phases Overview
Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. Each division has distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Understanding these phases is crucial for grasping the meiotic process.
Meiosis I
- Prophase I: Chromosomes condense, and homologous pairs come together, forming a tetrad. Crossing over and independent assortment occur during this phase.
- Metaphase I: Tetrads align at the metaphase plate, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I: Nuclear envelope reforms, and chromosomes uncoil.
Meiosis II
- Prophase II: Chromosomes condense again, and a new nuclear envelope forms.
- Metaphase II: Sister chromatids align at the metaphase plate, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II: Nuclear envelope reforms, and chromosomes uncoil, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis Phase Worksheet Answer Key

| Phase | Description | Key Events |
|---|---|---|
| Prophase I | Chromosomes condense, homologous pairs form a tetrad | Crossing over, Independent assortment |
| Metaphase I | Tetrads align at the metaphase plate | Spindle fibers attach |
| Anaphase I | Homologous chromosomes separate | Move to opposite poles |
| Telophase I | Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil | |
| Prophase II | Chromosomes condense, new nuclear envelope forms | |
| Metaphase II | Sister chromatids align at the metaphase plate | Spindle fibers attach |
| Anaphase II | Sister chromatids separate | Move to opposite poles |
| Telophase II | Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil | Four haploid daughter cells |
🔔 Note: The meiosis phase worksheet answer key provides a simplified overview of the key events occurring during each phase.
Key Takeaways
- Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II.
- Each division has distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Crossing over and independent assortment occur during prophase I, increasing genetic diversity.
- Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells with a unique combination of genetic traits.
Final Thoughts
Meiosis is a complex process, but breaking it down into its individual phases can help clarify the steps involved. By understanding meiosis, you’ll gain insight into the fundamental principles of genetics and how eukaryotic organisms reproduce. The meiosis phase worksheet answer key provided above should serve as a useful resource for reinforcing your knowledge of this crucial biological process.
What is the primary purpose of meiosis?
+The primary purpose of meiosis is to reduce the chromosome number by half, resulting in the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) with a unique combination of genetic traits.
What is the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
+Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, while meiosis II involves the separation of sister chromatids.
What is the significance of crossing over and independent assortment in meiosis?
+Crossing over and independent assortment increase genetic diversity by allowing for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
Related Terms:
- Meiosis Worksheet answer key PDF
- Meiosis Practice Worksheet
- Meiosis Worksheet PDF
- Phases of meiosis