Matter Chemistry Worksheet for Students
Understanding the Basics of Matter Chemistry
Matter chemistry is a fundamental concept in science that deals with the study of the composition, properties, and reactions of matter. As a student, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of matter chemistry to excel in your studies and future careers. In this worksheet, we’ll explore the basics of matter chemistry, covering topics such as the definition of matter, types of matter, and the properties of matter.
Definition of Matter
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It’s the substance that makes up all physical objects in the universe, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest galaxies. Matter can exist in various forms, including solid, liquid, gas, and plasma.
Types of Matter
There are several types of matter, including:
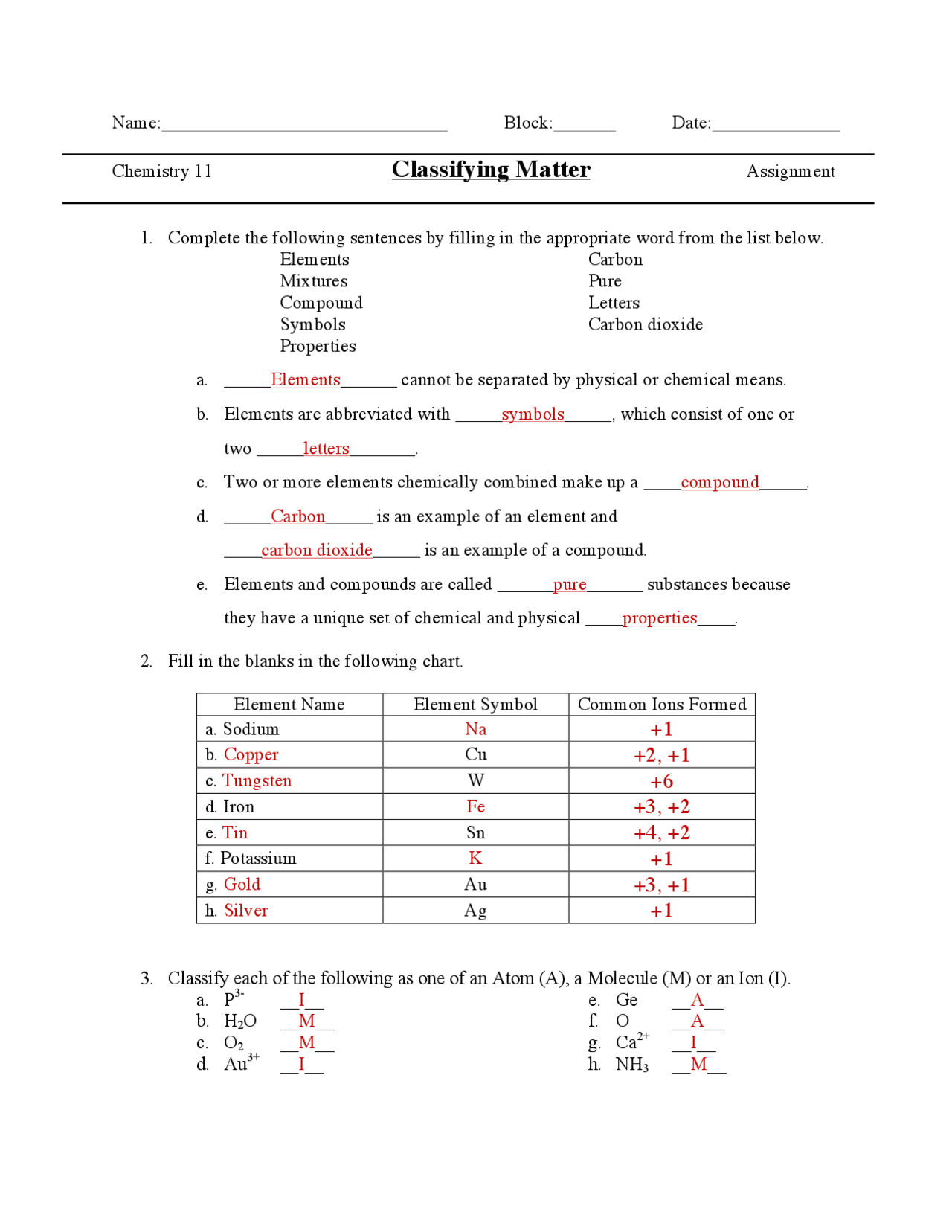
- Elements: Substances consisting of only one type of atom, such as hydrogen (H) or oxygen (O).
- Compounds: Substances formed by the chemical bonding of two or more different elements, such as water (H2O) or carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Mixtures: Physical combinations of two or more substances, such as air (a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases) or soil (a mixture of minerals, organic matter, and water).
Properties of Matter
Matter has several properties that can be measured and observed, including:
- Mass: The amount of matter in an object, typically measured in units such as grams (g) or kilograms (kg).
- Volume: The amount of space occupied by an object, typically measured in units such as milliliters (mL) or liters (L).
- Density: The mass of an object per unit volume, typically measured in units such as grams per milliliter (g/mL) or kilograms per liter (kg/L).
- Boiling Point: The temperature at which a substance changes state from liquid to gas.
- Melting Point: The temperature at which a substance changes state from solid to liquid.
Changes in Matter
Matter can undergo various changes, including:
- Physical Changes: Changes in the physical state of a substance, such as melting, freezing, or evaporating.
- Chemical Changes: Changes in the chemical composition of a substance, such as combustion or oxidation.
Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one substance to another. This means that the total mass of a closed system remains constant over time, even if the matter within the system undergoes chemical or physical changes.
🔍 Note: The law of conservation of mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry and is used to describe the behavior of matter in various chemical reactions and processes.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of one or more substances into new substances. These reactions can be classified into several types, including:
- Synthesis Reactions: Reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance.
- Decomposition Reactions: Reactions in which a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
- Replacement Reactions: Reactions in which one substance is replaced by another substance.
Chemical Formulas and Equations
Chemical formulas and equations are used to describe the composition and behavior of matter in chemical reactions. Chemical formulas represent the composition of a substance using symbols and numbers, while chemical equations represent the reaction itself, including the reactants, products, and any conditions or catalysts involved.
Properties of Elements
Elements have several properties that can be used to identify and describe them, including:
- Atomic Number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s identity.
- Atomic Mass: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s mass.
- Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s energy levels, which determines the element’s chemical properties.
Periodic Table
The periodic table is a tool used to organize and classify elements based on their properties and electron configurations. The periodic table is arranged in a logical and systematic way, with elements that have similar properties and electron configurations grouped together.
What is the definition of matter?
+Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
What are the types of matter?
+There are several types of matter, including elements, compounds, and mixtures.
What is the law of conservation of mass?
+The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one substance to another.
In conclusion, matter chemistry is a fundamental concept in science that deals with the study of the composition, properties, and reactions of matter. Understanding the basics of matter chemistry is essential for students to excel in their studies and future careers. By mastering the concepts of matter chemistry, students can develop a deeper understanding of the world around them and make informed decisions about the world they live in.
Related Terms:
- Atom
- Energi
- Kimia
- Zat kimia
- Materi
- chemistry worksheet: matter #1 pdf