5 Ways to Master Long Division With Remainders
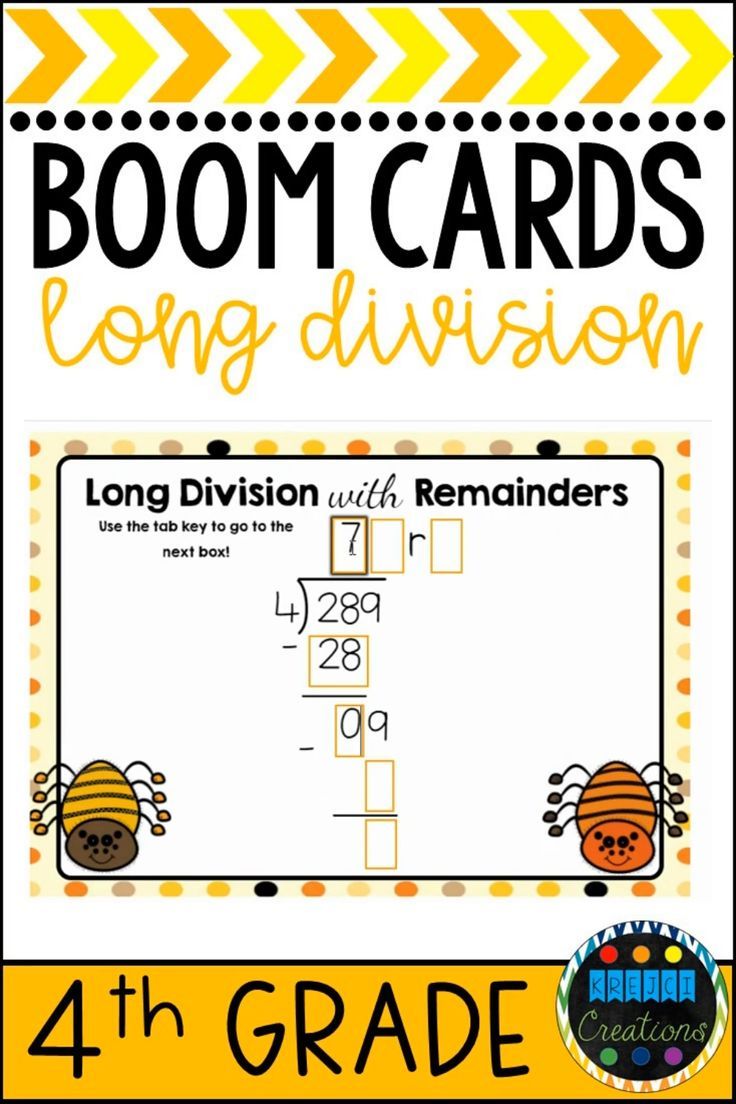
Mastering Long Division with Remainders: A Comprehensive Guide
Long division is a fundamental math operation that can be daunting for many students, especially when dealing with remainders. However, with the right approach and practice, anyone can master long division with remainders. In this article, we will explore five effective ways to improve your long division skills and become proficient in handling remainders.
Understanding the Basics of Long Division
Before diving into the methods, it’s essential to understand the basics of long division. Long division is a step-by-step process of dividing a large number (dividend) by a smaller number (divisor) to find the quotient and remainder. The dividend is written on top of a line, and the divisor is written below it. The quotient is the result of the division, and the remainder is the amount left over.
Method 1: The Standard Long Division Method
The standard long division method is the most common approach to long division. This method involves the following steps:
- Write the dividend on top of a line and the divisor below it.
- Divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor and write the result below the line.
- Multiply the result by the divisor and subtract the product from the dividend.
- Bring down the next digit of the dividend and repeat the process.
- Continue this process until the dividend is reduced to zero or a remainder is obtained.
💡 Note: It's essential to check your work by multiplying the quotient by the divisor and adding the remainder to ensure the result equals the original dividend.
Method 2: The Partial Quotients Method
The partial quotients method is a variation of the standard long division method. This method involves finding partial quotients by dividing the dividend into smaller parts.
- Divide the first part of the dividend by the divisor to find the first partial quotient.
- Multiply the first partial quotient by the divisor and subtract the product from the first part of the dividend.
- Bring down the next part of the dividend and repeat the process.
- Continue this process until the entire dividend is reduced to zero or a remainder is obtained.
Method 3: The Chunking Method
The chunking method is a visual approach to long division. This method involves breaking down the dividend into smaller chunks or groups of digits.
- Divide the first chunk of the dividend by the divisor to find the first partial quotient.
- Multiply the first partial quotient by the divisor and subtract the product from the first chunk of the dividend.
- Bring down the next chunk of the dividend and repeat the process.
- Continue this process until the entire dividend is reduced to zero or a remainder is obtained.
Method 4: The Area Model Method
The area model method is a visual approach to long division that uses rectangles to represent the dividend and divisor.
- Draw a rectangle to represent the dividend and divide it into smaller rectangles to represent the divisor.
- Fill in the rectangles to represent the product of the divisor and quotient.
- Find the remainder by counting the number of rectangles that are not filled.
Method 5: Using Technology to Practice Long Division
In today’s digital age, there are many online tools and apps that can help you practice long division with remainders. These tools can provide you with interactive exercises and quizzes to help you improve your skills.
- Search for online resources, such as Khan Academy or Mathway, that offer interactive long division exercises.
- Use apps, such as Photomath or Math Tricks, that provide step-by-step solutions to long division problems.
- Practice regularly to improve your skills and build confidence.
Conclusion
Mastering long division with remainders takes time and practice, but with the right approach, anyone can become proficient. By using the methods outlined in this article, you can improve your long division skills and become more confident in your ability to handle remainders. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources to supplement your learning.
What is the difference between the standard long division method and the partial quotients method?
+
The standard long division method involves dividing the dividend by the divisor in a single step, while the partial quotients method involves finding partial quotients by dividing the dividend into smaller parts.
How can I check my work when using the standard long division method?
+
You can check your work by multiplying the quotient by the divisor and adding the remainder to ensure the result equals the original dividend.
What is the chunking method, and how does it work?
+
The chunking method involves breaking down the dividend into smaller chunks or groups of digits, and then dividing each chunk by the divisor to find the partial quotients.