5 Tips to Master Lipids Worksheet Answer Key
Mastering Lipids: Understanding the Basics
Lipids are a fundamental component of living organisms, playing a crucial role in energy storage, cell membrane structure, and signaling pathways. Despite their importance, lipids can be a challenging topic to grasp, especially for students. In this article, we will provide 5 tips to help you master lipids and ace your lipids worksheet.
TIP 1: Understand the Classification of Lipids
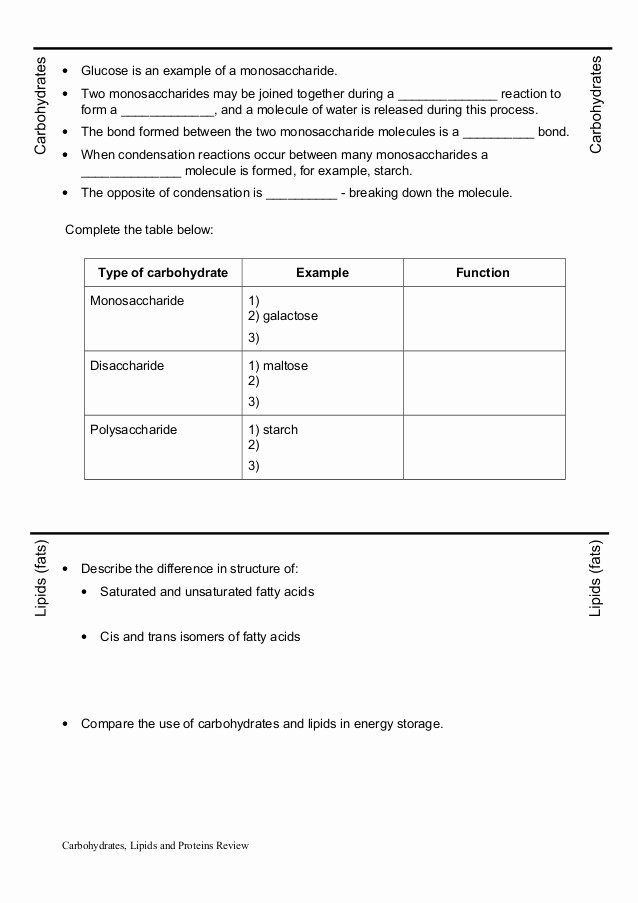
Lipids are a diverse group of biomolecules that can be classified into several categories based on their chemical structure and function. The main classes of lipids are:
- Triglycerides (triacylglycerols): composed of glycerol and three fatty acid chains, serving as energy storage molecules.
- Phospholipids: consisting of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group, forming the structural basis of cell membranes.
- Sterols: a subgroup of lipids with a four-ring system, including cholesterol and ergosterol, which play a crucial role in membrane structure and function.
- Waxes: a type of lipid that serves as a protective coating on plant leaves and fruits.
💡 Note: Understanding the different classes of lipids is essential to mastering the topic.
TIP 2: Learn the Structure of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are the building blocks of lipids, consisting of a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head. The structure of fatty acids is crucial in determining the physical and chemical properties of lipids.
- Saturated fatty acids: have a single bond between carbon atoms, resulting in a straight chain.
- Unsaturated fatty acids: have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms, resulting in a kinked chain.
- Trans fatty acids: have a double bond with a trans configuration, resulting in a straight chain.
Fatty Acid Structure Table

| Type of Fatty Acid | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated | Single bond between carbon atoms | Palmitic acid |
| Unsaturated | One or more double bonds between carbon atoms | Oleic acid |
| Trans | Double bond with a trans configuration | Elaidic acid |
TIP 3: Understand the Role of Lipids in Cell Membranes
Lipids play a crucial role in the structure and function of cell membranes. The lipid bilayer, composed of phospholipids, provides a hydrophobic barrier that regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
- Fluid mosaic model: describes the dynamic nature of the lipid bilayer, with lipids and proteins interacting to form a fluid, semi-permeable membrane.
TIP 4: Learn the Key Lipid Metabolism Pathways
Lipid metabolism involves the breakdown and synthesis of lipids, which is essential for energy production and membrane maintenance.
- Beta-oxidation: the breakdown of fatty acids to produce energy.
- Fatty acid synthesis: the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA.
TIP 5: Practice, Practice, Practice
Mastering lipids requires practice and application of knowledge. Make sure to:
- Work on lipids worksheet problems: to reinforce your understanding of lipid classification, structure, and function.
- Use online resources: such as interactive diagrams and quizzes to supplement your learning.
- Join a study group: to discuss challenging topics and learn from others.
By following these 5 tips, you will be well on your way to mastering lipids and acing your lipids worksheet.
In summary, mastering lipids requires a deep understanding of their classification, structure, and function, as well as their role in cell membranes and metabolism. By practicing and applying your knowledge, you will become proficient in lipids and be able to tackle challenging worksheet problems with confidence.
What are the main classes of lipids?
+The main classes of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols, and waxes.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
+Saturated fatty acids have a single bond between carbon atoms, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
What is the role of lipids in cell membranes?
+Lipids play a crucial role in the structure and function of cell membranes, providing a hydrophobic barrier that regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
Related Terms:
- Lipids Worksheet PDF
- Lipids Review Worksheet
- Lipids Questions and Answers PDF
- 3 major groups of lipids