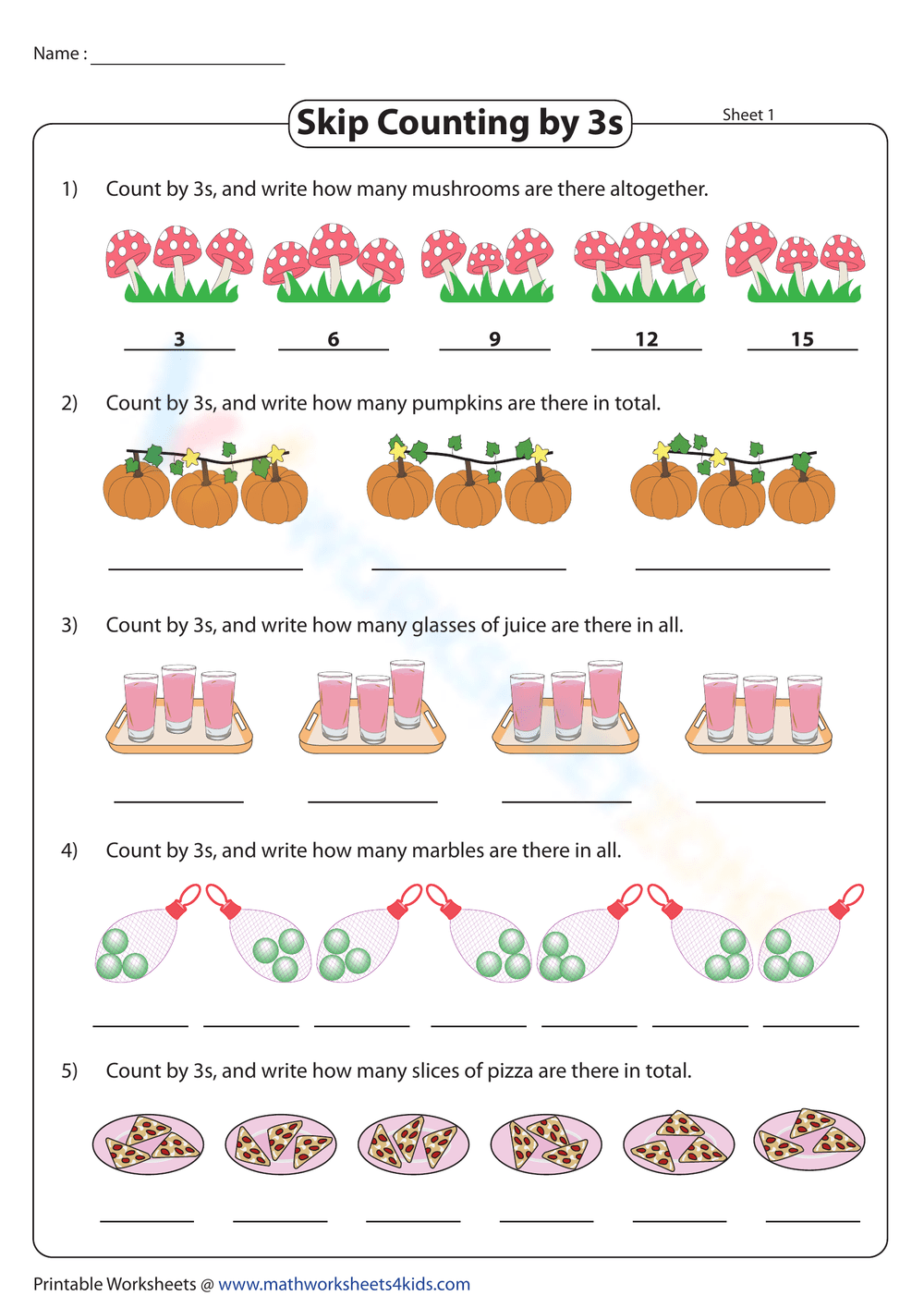
Limiting Reactant Practice Problems Worksheet Answers

Understanding Limiting Reactants in Chemical Reactions
In chemistry, a limiting reactant is a substance that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. Identifying the limiting reactant is crucial in determining the yield of a reaction and optimizing the use of reactants. In this article, we will explore the concept of limiting reactants, discuss how to identify them, and provide practice problems to help reinforce understanding.
What is a Limiting Reactant?
A limiting reactant is a reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction before the reaction is complete. This means that there is not enough of the limiting reactant to react with all of the other reactants, resulting in an incomplete reaction. The limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
How to Identify the Limiting Reactant
To identify the limiting reactant, you need to follow these steps:
- Write the balanced equation: Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Calculate the mole ratio: Calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product.
- Determine the limiting reactant: Determine which reactant is the limiting reactant by comparing the mole ratio of each reactant to the product.
💡 Note: The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
Limiting Reactant Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to help you reinforce your understanding of limiting reactants:
Problem 1
Consider the following reaction:
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
If 2.5 moles of Na and 1.5 moles of Cl2 are used, which reactant is the limiting reactant?
Answer
To determine the limiting reactant, we need to calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product.
Mole ratio of Na: 2.5 mol / 2 mol (from the balanced equation) = 1.25 Mole ratio of Cl2: 1.5 mol / 1 mol (from the balanced equation) = 1.5
Since the mole ratio of Cl2 is smaller, Cl2 is the limiting reactant.
Problem 2
Consider the following reaction:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
If 4 moles of H2 and 2 moles of O2 are used, which reactant is the limiting reactant?
Answer
To determine the limiting reactant, we need to calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product.
Mole ratio of H2: 4 mol / 2 mol (from the balanced equation) = 2 Mole ratio of O2: 2 mol / 1 mol (from the balanced equation) = 2
Since the mole ratio of both reactants is the same, neither reactant is limiting.
Problem 3
Consider the following reaction:
Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2
If 1 mole of Ca and 3 moles of HCl are used, which reactant is the limiting reactant?
Answer
To determine the limiting reactant, we need to calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product.
Mole ratio of Ca: 1 mol / 1 mol (from the balanced equation) = 1 Mole ratio of HCl: 3 mol / 2 mol (from the balanced equation) = 1.5
Since the mole ratio of Ca is smaller, Ca is the limiting reactant.
Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to the practice problems:
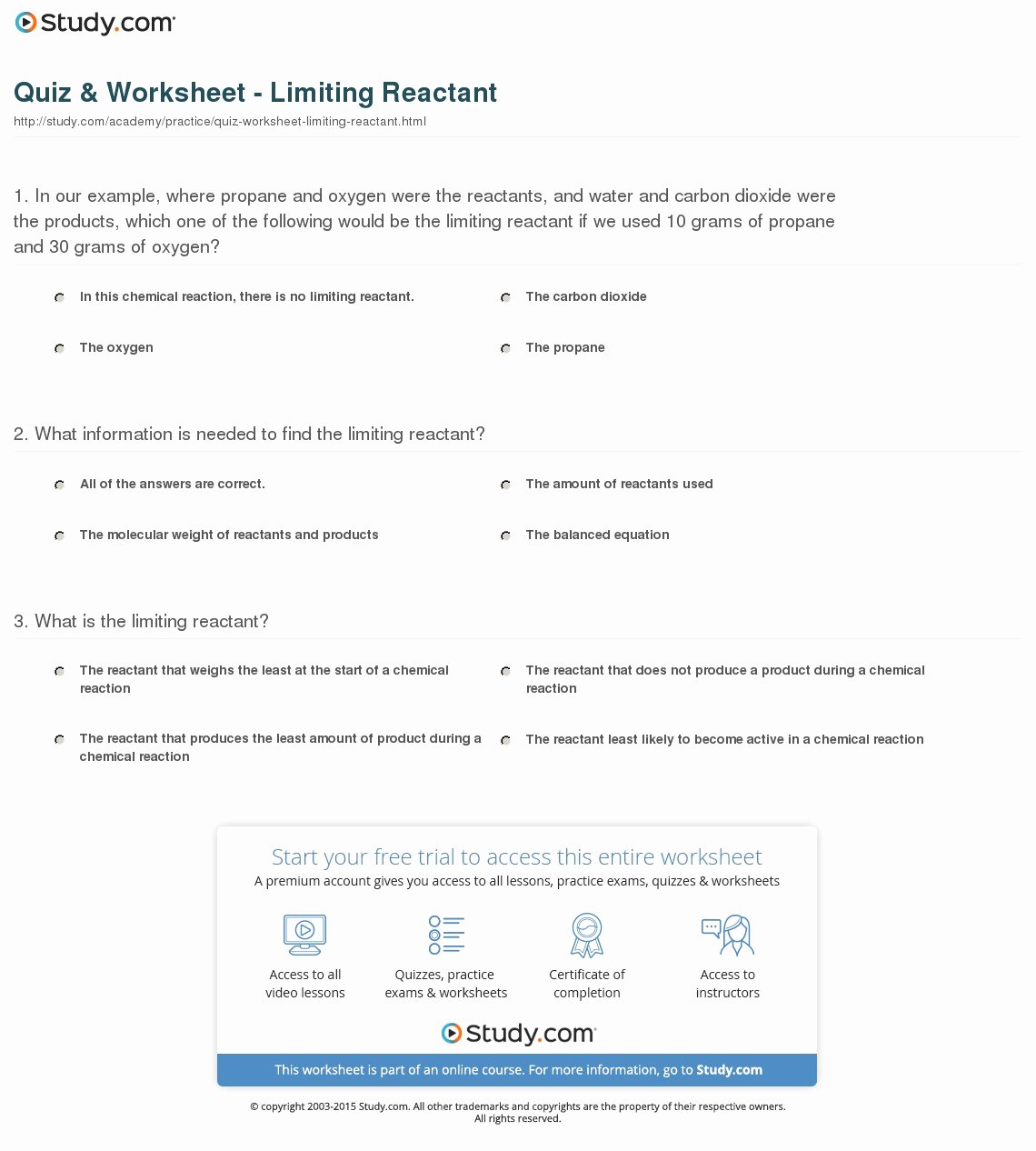
| Problem | Limiting Reactant |
|---|---|
| 1 | Cl2 |
| 2 | None |
| 3 | Ca |
Conclusion
Identifying the limiting reactant is crucial in determining the yield of a reaction and optimizing the use of reactants. By following the steps outlined in this article and practicing with sample problems, you can become proficient in identifying the limiting reactant. Remember to always calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product and determine which reactant has the smallest mole ratio.
What is the definition of a limiting reactant?
+A limiting reactant is a substance that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
How do I identify the limiting reactant?
+To identify the limiting reactant, write the balanced equation, calculate the mole ratio of each reactant to the product, and determine which reactant has the smallest mole ratio.
What happens when there is no limiting reactant?
+If there is no limiting reactant, the reaction will continue until one of the reactants is completely consumed, and the yield of the product will be determined by the amount of that reactant.
Related Terms:
- Limiting reactant quiz Answers
- Worksheet on limiting Reactants
- Stoichiometry Worksheet