Lewis Structure Worksheet 3
Lewis Structure Worksheet 3: Understanding the Basics of Drawing Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to represent the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. They are essential for understanding the chemical properties and behavior of molecules. In this worksheet, we will practice drawing Lewis structures for various molecules, focusing on the rules and steps involved in creating accurate representations.
Understanding the Rules for Drawing Lewis Structures
Before we begin, it’s essential to review the rules for drawing Lewis structures:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: Calculate the total number of valence electrons available in the molecule by summing the valence electrons of each atom.
- Draw the skeleton structure: Sketch the basic structure of the molecule, using single bonds to connect the atoms.
- Add electrons to the atoms: Distribute the valence electrons among the atoms, starting with the atoms that have the lowest number of valence electrons.
- Satisfy the octet rule: Ensure that each atom has a full outer energy level (an octet) by forming double or triple bonds if necessary.
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange the electrons to minimize formal charges on the atoms.
Step-by-Step Example: Drawing the Lewis Structure for CO2
Let’s practice drawing the Lewis structure for CO2, using the rules outlined above.
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: CO2 has 1 carbon atom (4 valence electrons) and 2 oxygen atoms (6 valence electrons each), totaling 16 valence electrons.
- Draw the skeleton structure: Sketch the basic structure of CO2, connecting the carbon atom to the two oxygen atoms with single bonds.
O=C=O
- Add electrons to the atoms: Distribute the valence electrons among the atoms, starting with the oxygen atoms.
:O::C::O:
- Satisfy the octet rule: Form double bonds between the carbon and oxygen atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
O=C=O
|||
:O::C::O:
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange the electrons to minimize formal charges on the atoms.
O=C=O
|||
:O::-C:-:O:
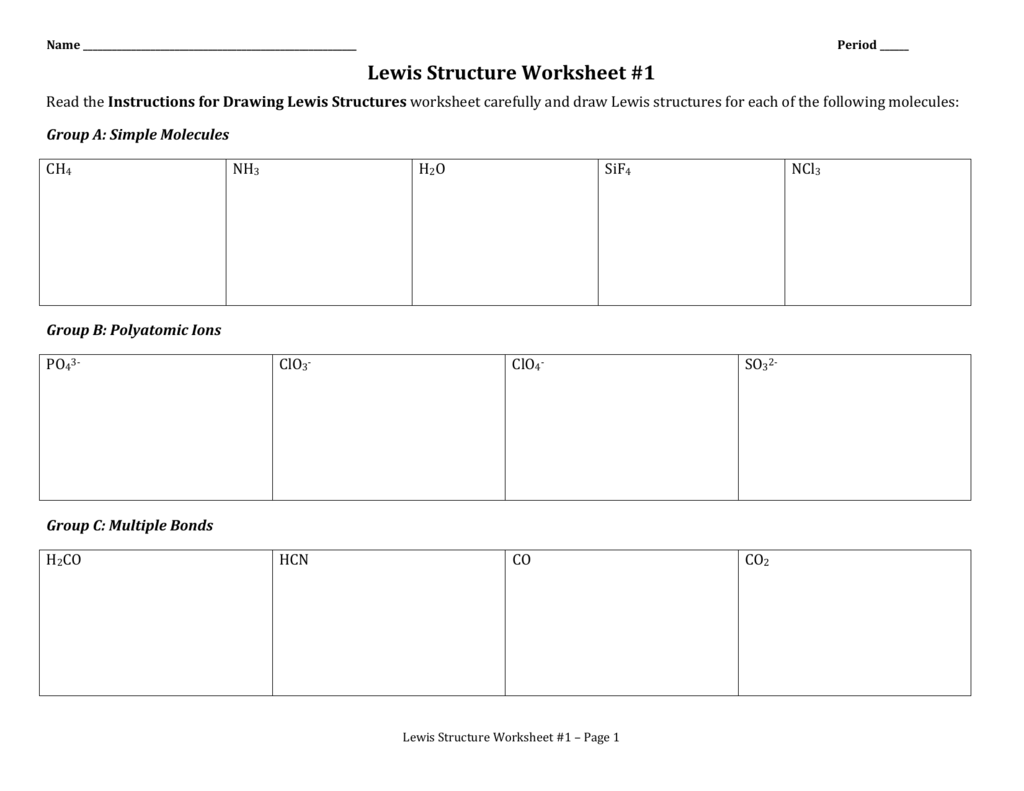
Practice Time! Drawing Lewis Structures for Various Molecules
Use the rules and steps outlined above to draw the Lewis structures for the following molecules:
CH4 (methane)
- Total valence electrons: 8
- Skeleton structure: H-C-H-H-H
- Add electrons to the atoms: :H::C::H::H::H:
- Satisfy the octet rule: Form single bonds between the carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange the electrons to minimize formal charges on the atoms.
NH3 (ammonia)
- Total valence electrons: 8
- Skeleton structure: H-N-H-H
- Add electrons to the atoms: :H::N::H::H:
- Satisfy the octet rule: Form single bonds between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange the electrons to minimize formal charges on the atoms.
H2O (water)
- Total valence electrons: 8
- Skeleton structure: H-O-H
- Add electrons to the atoms: :H::O::H:
- Satisfy the octet rule: Form single bonds between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
- Minimize formal charges: Arrange the electrons to minimize formal charges on the atoms.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Drawing Lewis Structures
When drawing Lewis structures, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Forgetting to add electrons: Make sure to account for all valence electrons when drawing the Lewis structure.
- Incorrectly assigning formal charges: Double-check the formal charges on each atom to ensure they are minimized.
- Ignoring the octet rule: Ensure that each atom has a full outer energy level (an octet) by forming double or triple bonds if necessary.
🚨 Note: When drawing Lewis structures, it's essential to use the correct number of valence electrons and to satisfy the octet rule. This ensures that the molecule is accurately represented and its chemical properties are understood.
Conclusion
Drawing Lewis structures is an essential skill in chemistry, allowing us to represent the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. By following the rules and steps outlined in this worksheet, you’ll become proficient in drawing accurate Lewis structures for various molecules. Remember to avoid common mistakes, such as forgetting to add electrons or incorrectly assigning formal charges. With practice and patience, you’ll master the art of drawing Lewis structures and gain a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and molecular structure.
What is the purpose of drawing Lewis structures?
+Drawing Lewis structures helps us understand the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules, which is essential for predicting chemical properties and behavior.
What are the key rules for drawing Lewis structures?
+The key rules for drawing Lewis structures are: determine the total number of valence electrons, draw the skeleton structure, add electrons to the atoms, satisfy the octet rule, and minimize formal charges.
What is the significance of the octet rule in Lewis structures?
+The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level (an octet). This rule is essential for understanding the stability and reactivity of molecules.