Master 5 Essential Lewis Structure Drawing Steps
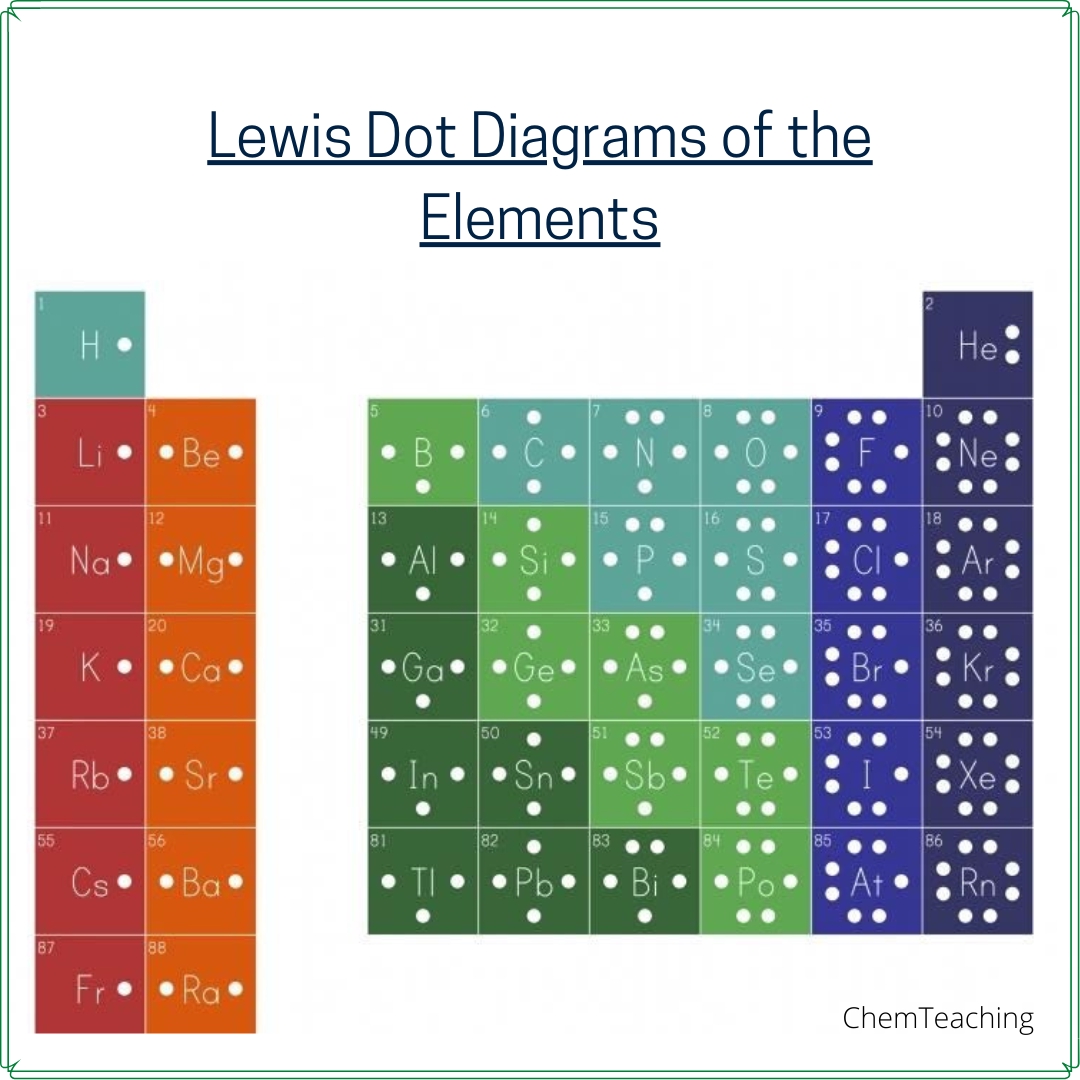
Understanding Lewis Structures: A Comprehensive Guide
Lewis structures are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule. They provide a visual representation of the electrons in a molecule, helping us understand the molecular structure, properties, and reactivity. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis structures, exploring the essential steps to draw them accurately.
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
The first step in drawing a Lewis structure is to calculate the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, which participate in chemical bonding. To determine the total number of valence electrons, you need to know the atomic number of each element in the molecule.
- For main-group elements (s- and p-block elements): The number of valence electrons is equal to the group number (number of electrons in the outermost energy level).
- For transition metals (d-block elements): The number of valence electrons is equal to the number of electrons in the outermost energy level (s- and d-electrons).
🔥 Note: Some elements, like hydrogen and helium, have a special case for valence electrons. Hydrogen has one valence electron, while helium has two.
Step 2: Draw the Skeletal Structure
The skeletal structure is a basic representation of the molecule, showing the arrangement of atoms. It’s essential to draw the skeletal structure before adding electrons to ensure that the molecule is structurally correct. When drawing the skeletal structure:
- Use the least electronegative atom as the central atom: In most cases, this is the atom with the lowest electronegativity value.
- Arrange the surrounding atoms around the central atom: The number of surrounding atoms depends on the type of bond (single, double, or triple) and the geometry of the molecule.
Step 3: Add Single Bonds and Remaining Electrons
Once the skeletal structure is drawn, add single bonds between the central atom and the surrounding atoms. Each single bond represents two shared electrons. If there are remaining electrons, add them to the surrounding atoms, ensuring that each atom has a full outer energy level (eight electrons in the outermost energy level).
- Add electrons to achieve a full outer energy level: If an atom has fewer than eight electrons in its outermost energy level, add electrons to satisfy the octet rule.
- Form double or triple bonds if necessary: If there are too many electrons around the central atom, form double or triple bonds to reduce the number of electrons.
Step 4: Minimize Formal Charges
Formal charges are a way to assign charges to atoms in a molecule, indicating the distribution of electrons. Minimizing formal charges ensures that the molecule is stable and has the lowest possible energy.
- Calculate formal charges: Use the formula: Formal Charge = (number of valence electrons) - (number of non-bonding electrons) - (1⁄2) * (number of bonding electrons).
- Adjust the structure to minimize formal charges: Rearrange the electrons or bonds to minimize formal charges, if necessary.
Step 5: Verify the Structure Using the Octet Rule and VSEPR Theory
Finally, verify the structure by applying the octet rule and VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory.
- Octet rule: Ensure that each atom has a full outer energy level (eight electrons in the outermost energy level).
- VSEPR theory: Check that the molecule’s shape is consistent with the VSEPR theory, which predicts the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom.
| Element | Valence Electrons | Group Number |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1A |
| Carbon (C) | 4 | 4A |
| Oxygen (O) | 6 | 6A |
In conclusion, drawing Lewis structures is a fundamental skill in chemistry, requiring attention to detail and a solid understanding of chemical bonding. By following the five essential steps outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to mastering Lewis structures and gaining a deeper understanding of molecular structures and properties.
What is the purpose of drawing Lewis structures?
+Drawing Lewis structures helps us understand the molecular structure, properties, and reactivity of a molecule.
What is the octet rule, and why is it important?
+The octet rule states that each atom should have a full outer energy level (eight electrons in the outermost energy level). This rule helps us predict the stability and reactivity of a molecule.
What is VSEPR theory, and how does it relate to Lewis structures?
+VSEPR theory predicts the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom, helping us determine the shape of a molecule. Lewis structures are used to visualize the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, which is essential for applying VSEPR theory.