Mastering Lewis Dot Structure with Easy Worksheet Answers
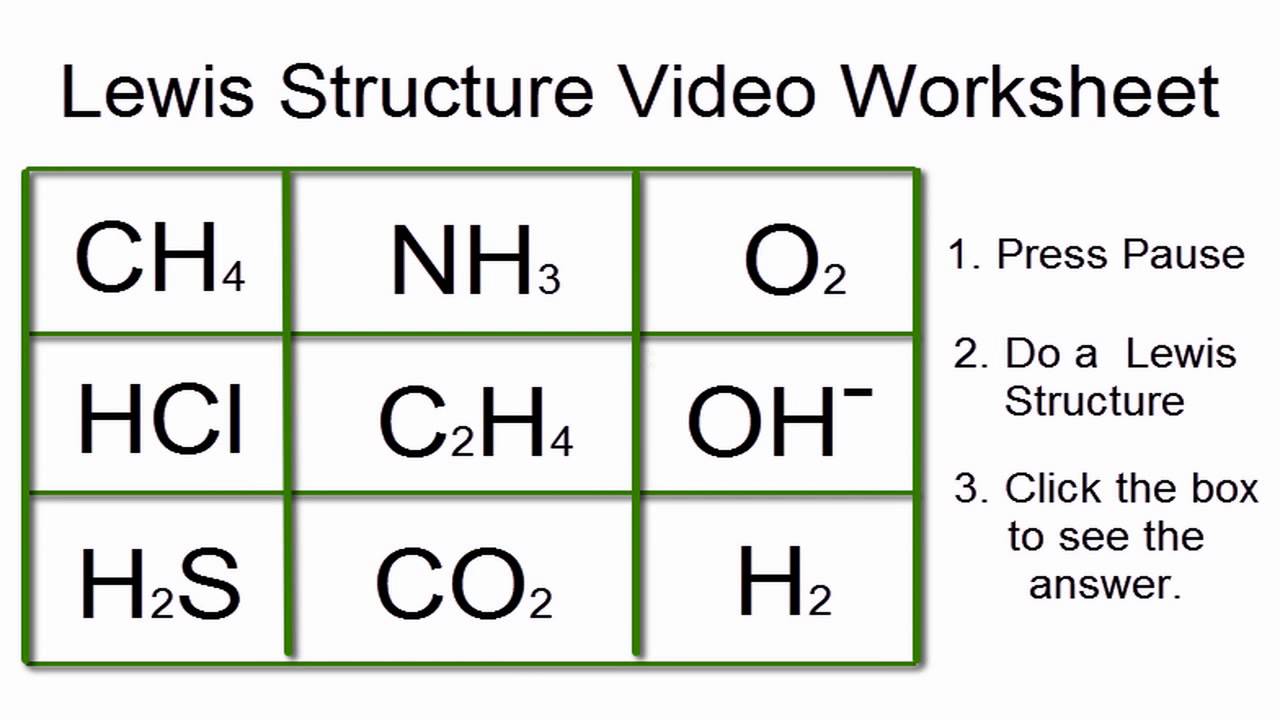
Introduction to Lewis Dot Structure
Lewis dot structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us visualize the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. It is a crucial tool for understanding chemical bonding, molecular geometry, and the properties of substances. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis dot structure, explore its basics, and provide you with easy worksheet answers to help you master this concept.
What is Lewis Dot Structure?
Lewis dot structure, also known as electron dot structure, is a method of representing the valence electrons of atoms in a molecule using dots. The structure is named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced this concept in the early 20th century. The Lewis dot structure helps us understand how atoms share electrons to form chemical bonds.
How to Draw Lewis Dot Structure
Drawing a Lewis dot structure involves several steps:
- Determine the central atom: Identify the central atom in the molecule, which is usually the least electronegative atom.
- Calculate the total number of valence electrons: Calculate the total number of valence electrons in the molecule by adding the valence electrons of each atom.
- Draw the skeleton structure: Draw the skeleton structure of the molecule, indicating the central atom and the surrounding atoms.
- Add electrons to the skeleton structure: Add electrons to the skeleton structure, starting with the central atom and working your way outwards.
- Satisfy the octet rule: Ensure that each atom satisfies the octet rule, which states that each atom should have eight electrons in its valence shell.
Easy Worksheet Answers
Here are some easy worksheet answers to help you practice drawing Lewis dot structures:
Example 1: Draw the Lewis dot structure of water (H2O)
- Central atom: Oxygen (O)
- Total number of valence electrons: 8 (6 from O and 2 from H)
- Skeleton structure: O-H-H
- Lewis dot structure:
📝 Note: Water has a bent molecular geometry due to the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom.
Example 2: Draw the Lewis dot structure of carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Central atom: Carbon ©
- Total number of valence electrons: 16 (4 from C and 12 from O)
- Skeleton structure: O-C-O
- Lewis dot structure:
📝 Note: Carbon dioxide has a linear molecular geometry due to the double bonds between carbon and oxygen.
Example 3: Draw the Lewis dot structure of ammonia (NH3)
- Central atom: Nitrogen (N)
- Total number of valence electrons: 8 (5 from N and 3 from H)
- Skeleton structure: N-H-H-H
- Lewis dot structure:
📝 Note: Ammonia has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry due to the lone pair on the nitrogen atom.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When drawing Lewis dot structures, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- Inconsistent number of electrons: Ensure that the total number of electrons in the Lewis dot structure matches the total number of valence electrons in the molecule.
- Incorrect placement of electrons: Place electrons in the correct positions, following the octet rule and satisfying the central atom’s valence electrons first.
- Inadequate representation of lone pairs: Ensure that lone pairs are represented correctly, as they play a crucial role in determining molecular geometry.
Conclusion
Mastering Lewis dot structure is an essential skill for any chemistry student. By understanding the basics of Lewis dot structure and practicing with easy worksheet answers, you can improve your ability to visualize molecular structures and predict chemical properties. Remember to avoid common mistakes and always satisfy the octet rule to ensure accurate representations of molecular structures.
What is the purpose of Lewis dot structure?
+The purpose of Lewis dot structure is to visualize the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules, helping us understand chemical bonding, molecular geometry, and the properties of substances.
How do I determine the central atom in a molecule?
+The central atom is usually the least electronegative atom in the molecule. You can determine the electronegativity of an atom by consulting an electronegativity table.
What is the octet rule?
+The octet rule states that each atom should have eight electrons in its valence shell. This rule helps us determine the stability of a molecule and predict its chemical properties.