Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet Answer Key
Lewis Dot Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide
Lewis dot diagrams are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to represent the valence electrons of atoms and molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis dot diagrams, exploring their importance, rules, and applications. We will also provide a comprehensive worksheet answer key to help students and educators alike.
What are Lewis Dot Diagrams?
Lewis dot diagrams, also known as electron dot diagrams, are a way to represent the valence electrons of an atom or molecule using dots. The diagrams show the number of valence electrons in an atom or molecule and how they are arranged around the central atom.
Why are Lewis Dot Diagrams Important?
Lewis dot diagrams are essential in chemistry because they:
- Help predict the shape of molecules
- Identify the type of bond between atoms (ionic, covalent, or metallic)
- Determine the number of valence electrons in an atom or molecule
- Facilitate the understanding of chemical reactions and bonding
Rules for Drawing Lewis Dot Diagrams
To draw a Lewis dot diagram, follow these rules:
- Determine the central atom: Identify the atom that will be the center of the diagram.
- Calculate the number of valence electrons: Determine the number of valence electrons in the atom or molecule.
- Draw the dots: Represent each valence electron as a dot around the central atom.
- Follow the octet rule: Arrange the dots to satisfy the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level.
Types of Lewis Dot Diagrams
There are several types of Lewis dot diagrams, including:
- Monoatomic ions: Diagrams that show the valence electrons of a single ion.
- Covalent molecules: Diagrams that show the shared electrons between atoms in a molecule.
- Polyatomic ions: Diagrams that show the valence electrons of a group of atoms that behave as a single ion.
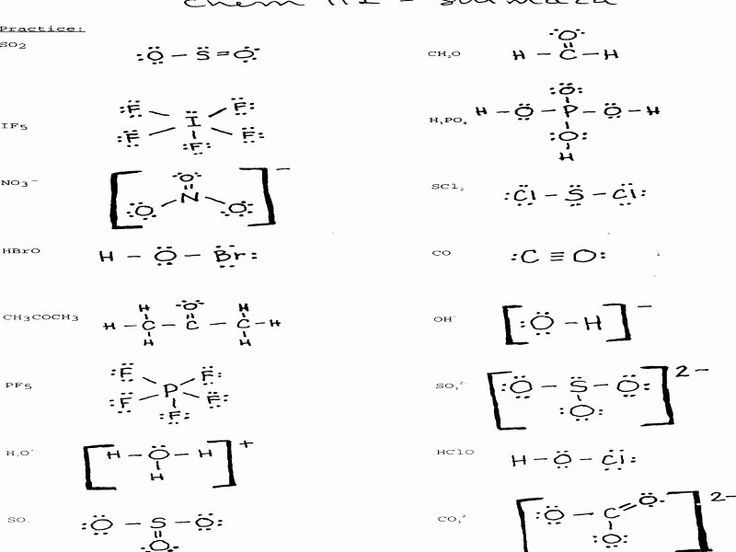
Worksheet Answer Key
Here is a comprehensive worksheet answer key for Lewis dot diagrams:

| Atom/Molecule | Lewis Dot Diagram | Number of Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | · | 1 |
| Helium (He) | · · | 2 |
| Lithium (Li) | · · · | 3 |
| Boron (B) | · · · · | 5 |
| Carbon (C) | · · · · · · | 4 |
| Nitrogen (N) | · · · · · · · | 5 |
| Oxygen (O) | · · · · · · · · | 6 |
| Fluorine (F) | · · · · · · · · · | 7 |
| Neon (Ne) | · · · · · · · · · · | 8 |
💡 Note: The Lewis dot diagrams shown above are simplified representations and may not reflect the actual arrangement of electrons in the atom or molecule.
Conclusion
Lewis dot diagrams are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to represent the valence electrons of atoms and molecules. By following the rules and guidelines outlined in this article, students and educators can create accurate Lewis dot diagrams and gain a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and reactions. The worksheet answer key provided above is a valuable resource for practicing and reinforcing this important concept.
What is the purpose of Lewis dot diagrams?
+Lewis dot diagrams are used to represent the valence electrons of atoms and molecules, helping to predict the shape of molecules, identify the type of bond between atoms, and determine the number of valence electrons.
What is the octet rule?
+The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer energy level, which typically consists of eight electrons.
How do I draw a Lewis dot diagram?
+To draw a Lewis dot diagram, determine the central atom, calculate the number of valence electrons, draw the dots, and follow the octet rule.