Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Exercises and Answers

Understanding Kinetic and Potential Energy
Energy is a fundamental concept in physics, and it comes in various forms. Two essential types of energy are kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is stored energy that has the potential to do work. In this worksheet, we will explore exercises and answers related to kinetic and potential energy.
What is Kinetic Energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses when it is in motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on its mass and velocity. The formula for kinetic energy is:
Kinetic Energy (KE) = ½ × m × v^2
where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
What is Potential Energy?
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration. There are several types of potential energy, including:
- Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE): the energy an object has due to its height or position in a gravitational field.
- Elastic Potential Energy (EPE): the energy stored in a stretched or compressed material.
- Electrical Potential Energy (EPE): the energy an object has due to its electric charge.
The formula for gravitational potential energy is:
Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) = m × g × h
where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object.
Exercises
Exercise 1: A 2 kg ball is thrown upwards with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy at the highest point of its trajectory.
📝 Note: At the highest point, the velocity is 0 m/s, but the ball still has potential energy.
Answer: KE = ½ × 2 kg × (0 m/s)^2 = 0 J (The ball has no kinetic energy at the highest point, but it has potential energy.)
Exercise 2: A 5 kg box is lifted to a height of 2 m. Calculate its gravitational potential energy.
Answer: GPE = 5 kg × 9.8 m/s^2 × 2 m = 98 J
Exercise 3: A spring with a force constant of 100 N/m is stretched by 0.5 m. Calculate its elastic potential energy.
Answer: EPE = ½ × 100 N/m × (0.5 m)^2 = 12.5 J
More Exercises
- A 10 kg object is moving with a velocity of 5 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy.
- A 2 kg ball is thrown downwards with an initial velocity of 5 m/s. Calculate its kinetic energy after 2 seconds.
- A 50 kg person climbs a staircase of 10 m. Calculate their gravitational potential energy at the top of the staircase.
📝 Note: Use the formulas provided earlier to solve these exercises.
Answers
- KE = ½ × 10 kg × (5 m/s)^2 = 125 J
- KE = ½ × 2 kg × (5 m/s + 9.8 m/s^2 × 2 s)^2 = 235 J
- GPE = 50 kg × 9.8 m/s^2 × 10 m = 4900 J
Table: Comparison of Kinetic and Potential Energy
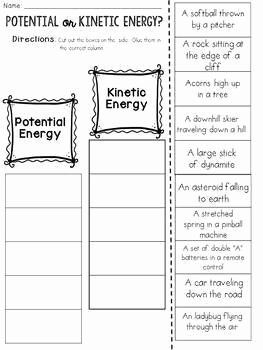
| Energy Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy (KE) | ½ × m × v^2 | A moving car |
| Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) | m × g × h | A ball at the top of a hill |
| Elastic Potential Energy (EPE) | ½ × k × x^2 | A stretched rubber band |
Kinetic energy and potential energy are essential concepts in physics, and understanding the differences between them is crucial. By solving the exercises and understanding the formulas, you can develop a deeper appreciation for the various forms of energy.
In conclusion, kinetic energy and potential energy are two fundamental types of energy that are essential to understanding the world around us. By mastering the formulas and concepts, you can apply them to various real-world situations and develop a deeper understanding of the physical world.
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
+Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is stored energy that has the potential to do work.
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
+KE = ½ × m × v^2
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
+GPE = m × g × h
Related Terms:
- Potential energy Worksheet PDF