Isotopes and Ions Worksheet Answer Key Explained
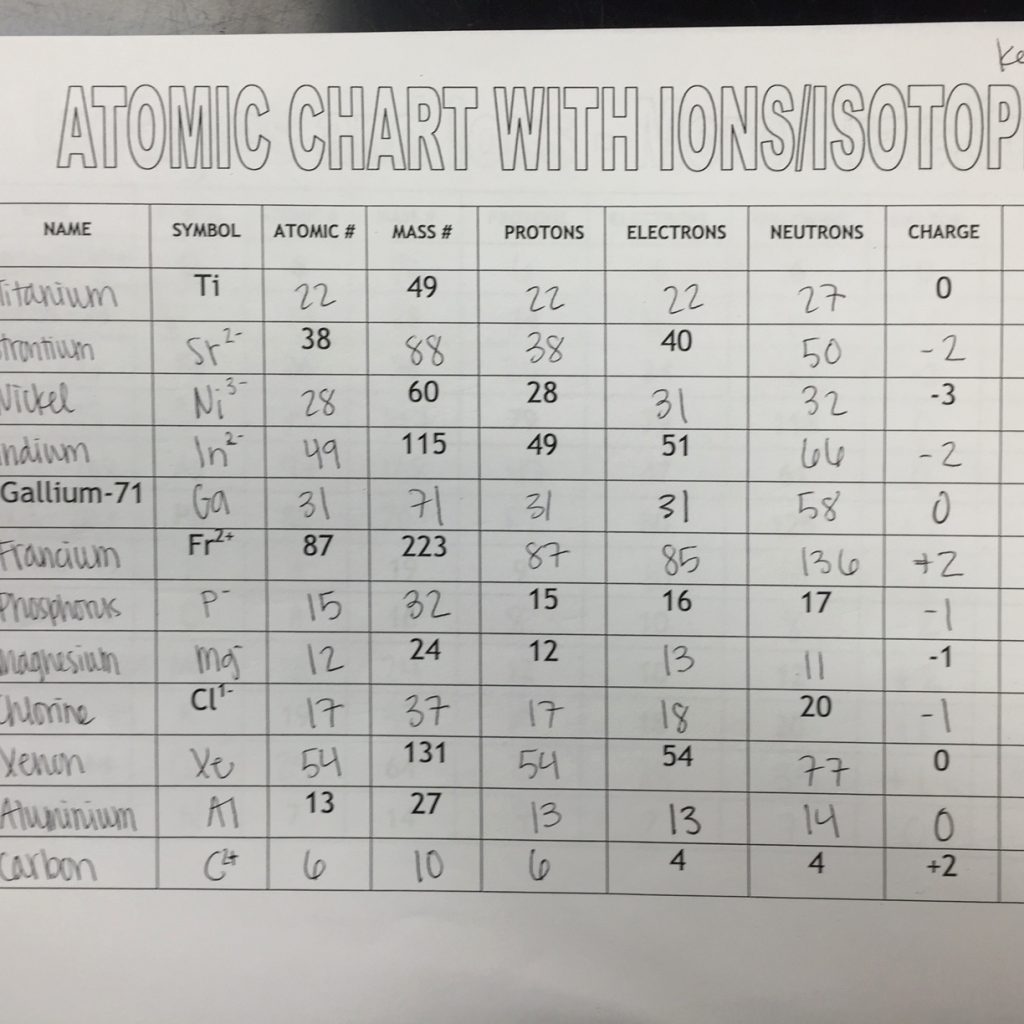
Understanding Isotopes and Ions
Isotopes and ions are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are often confused with each other. However, they are distinct and play crucial roles in understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules. In this explanation, we will delve into the world of isotopes and ions, exploring their definitions, differences, and significance in chemistry.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes: Atoms with the Same Atomic Number but Different Mass Numbers
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) but different mass numbers (total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus). This means that isotopes have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons, leading to variations in their atomic mass.
Examples of Isotopes:
- Hydrogen-1 (Protium), Hydrogen-2 (Deuterium), and Hydrogen-3 (Tritium): These are isotopes of hydrogen with different numbers of neutrons (0, 1, and 2, respectively).
- Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14: These are isotopes of carbon with different numbers of neutrons (6, 7, and 8, respectively).
What are Ions?
Ions: Atoms or Molecules with an Electric Charge
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. Ions can be formed through various means, including chemical reactions, ionization, and radiation.
Examples of Ions:
- Sodium Ion (Na+): A sodium atom that has lost one electron, resulting in a positive charge.
- Chloride Ion (Cl-): A chlorine atom that has gained one electron, resulting in a negative charge.
Key Differences between Isotopes and Ions:
- Atomic Number: Isotopes have the same atomic number, while ions have a different number of electrons, which affects their charge.
- Mass Number: Isotopes have different mass numbers due to varying numbers of neutrons, while ions have the same mass number as their parent atom.
- Electric Charge: Isotopes have no net electric charge, while ions have a positive or negative charge.
Importance of Isotopes and Ions in Chemistry:
- Isotopes: Isotopes play a crucial role in understanding the properties of elements, such as their atomic mass, chemical behavior, and radioactive decay.
- Ions: Ions are essential in understanding chemical reactions, acid-base chemistry, and the behavior of electrolytes.
Common Applications of Isotopes and Ions:
- Medical Imaging: Isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) scans.
- Food Irradiation: Ions are used to sterilize food and extend its shelf life.
- Environmental Monitoring: Isotopes are used to track the movement of pollutants and study environmental processes.
📝 Note: Isotopes and ions are often used interchangeably, but it's essential to understand the distinction between these two concepts to avoid confusion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, isotopes and ions are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are essential to understanding the behavior of atoms and molecules. While isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers, ions have a different number of electrons, resulting in a net electric charge. Understanding the differences between isotopes and ions is crucial in various fields, including medicine, environmental science, and food technology.
What is the difference between isotopes and ions?
+Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers, while ions have a different number of electrons, resulting in a net electric charge.
What are some examples of isotopes?
+Hydrogen-1 (Protium), Hydrogen-2 (Deuterium), and Hydrogen-3 (Tritium) are examples of isotopes of hydrogen.
What are some common applications of isotopes and ions?
+Isotopes are used in medical imaging, while ions are used in food irradiation and environmental monitoring.
Related Terms:
- Atoms, ions and isotopes Worksheet
- Isotope Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Isotope Practice Worksheet answers PDF
- Isotope ion worksheet



