7 Essential Facts About Ions and Isotopes
What are Ions and Isotopes?
Ions and isotopes are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are often confused with each other. While they are related, they describe different aspects of atomic structure. In this article, we will delve into the world of ions and isotopes, exploring their definitions, types, and importance in chemistry.
1. Definition of Ions
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. When an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negatively charged ion, known as an anion. Conversely, when an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion, known as a cation. Ions are formed when an atom or molecule interacts with other atoms or molecules, resulting in the transfer of electrons.
2. Types of Ions
There are two main types of ions: cations and anions.
- Cations: Positively charged ions, formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. Examples of cations include sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), and aluminum (Al3+).
- Anions: Negatively charged ions, formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. Examples of anions include chloride (Cl-), oxide (O2-), and sulfide (S2-).
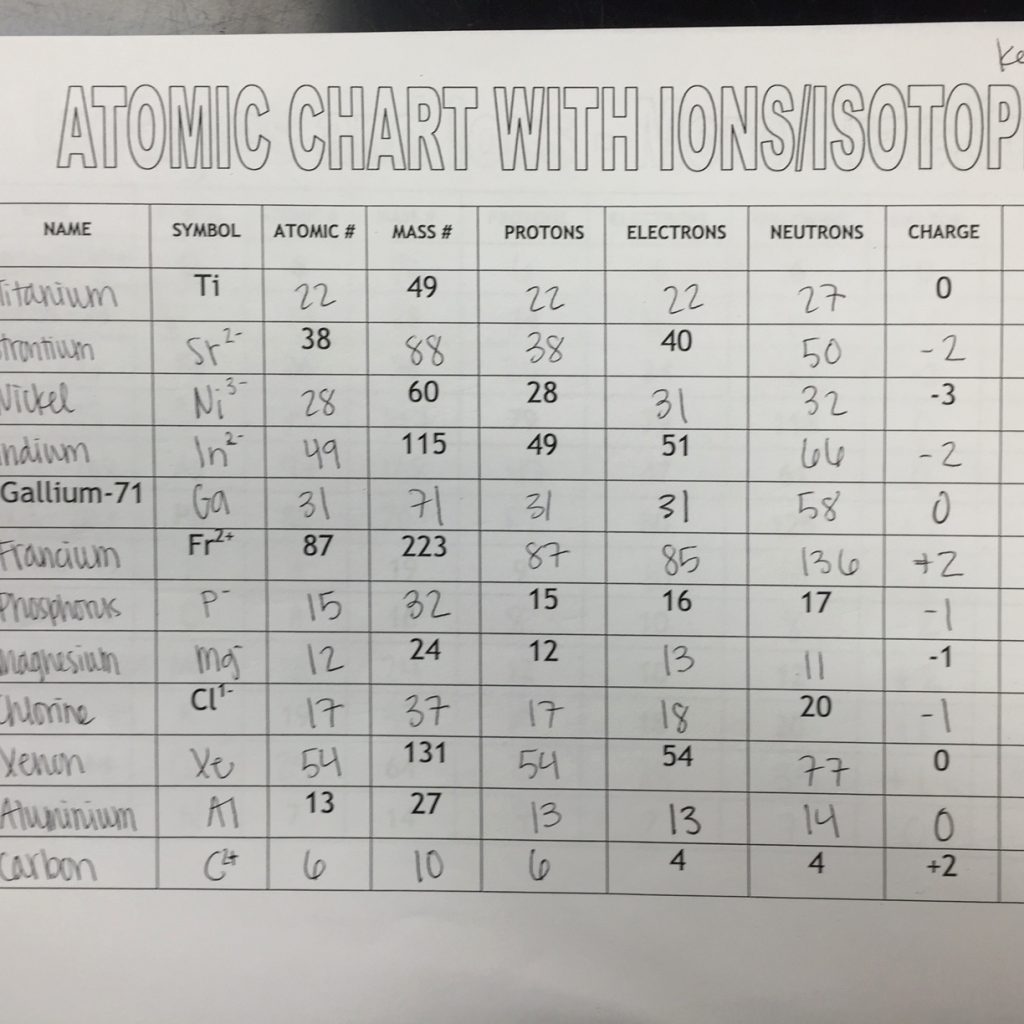
3. Definition of Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atomic mass of the isotopes, but not their chemical properties. Isotopes are denoted by their mass number, which is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
4. Types of Isotopes
There are two main types of isotopes: stable and radioactive.
- Stable Isotopes: Isotopes that do not undergo radioactive decay, meaning they remain stable over time. Examples of stable isotopes include carbon-12 (12C) and oxygen-16 (16O).
- Radioactive Isotopes: Isotopes that undergo radioactive decay, emitting radiation as they transform into more stable isotopes. Examples of radioactive isotopes include carbon-14 (14C) and radon-222 (222Rn).
5. Importance of Ions and Isotopes in Chemistry
Ions and isotopes play a crucial role in chemistry, particularly in the fields of physical chemistry, organic chemistry, and biochemistry.
- Chemical Reactions: Ions participate in chemical reactions, forming compounds and molecules. Understanding the behavior of ions is essential for predicting and controlling chemical reactions.
- Isotopic Labeling: Isotopes are used as tracers in chemical reactions, allowing researchers to track the movement of atoms and molecules. This technique is commonly used in biochemistry and medicine.
- Geochemistry: Isotopes are used to study the Earth’s geology, including the formation of rocks and minerals. By analyzing the isotopic composition of rocks and minerals, scientists can reconstruct the Earth’s history.
6. Applications of Ions and Isotopes
Ions and isotopes have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine: Ions and isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
- Environmental Science: Isotopes are used to study the movement of pollutants in the environment and to track the fate of chemicals in ecosystems.
- Agriculture: Isotopes are used to study the movement of nutrients in plants and to develop more efficient fertilizers.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, ions and isotopes are essential concepts in chemistry that describe different aspects of atomic structure. Understanding the behavior of ions and isotopes is crucial for predicting and controlling chemical reactions, and their applications are diverse and far-reaching. By exploring the world of ions and isotopes, we can gain a deeper understanding of the chemical world and develop new technologies and techniques to improve our daily lives.
What is the difference between ions and isotopes?
+Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but differ in the number of neutrons.
What are the types of ions?
+There are two main types of ions: cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions).
What are the applications of isotopes in medicine?
+Isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), to diagnose and treat diseases.
Related Terms:
- Ions and isotopes Worksheet PDF
- Atoms, ions and isotopes Worksheet
- Isotope Practice Worksheet answers PDF
- Isotope Practice Worksheet pdf
- Ions Practice Worksheet