Mastering Ionic Compounds: Names and Formulas Made Easy
Understanding Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are a type of chemical compound that is formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in a chemical bond. This bond is typically between a metal and a nonmetal atom, with the metal atom losing one or more electrons to form a positive ion (cation), while the nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons to form a negative ion (anion). The resulting compound is held together by the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions.
Why Learn About Ionic Compounds?
Ionic compounds are an essential part of chemistry and are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Medicine: Ionic compounds are used in many medical treatments, such as antacids and antihistamines.
- Electronics: Ionic compounds are used in the production of semiconductors and other electronic components.
- Environmental Science: Ionic compounds are used to clean up contaminated soil and water.
Mastering Ionic Compounds: Names and Formulas Made Easy
In this article, we will explore the rules for naming and writing formulas for ionic compounds.
Naming Ionic Compounds
The rules for naming ionic compounds are as follows:
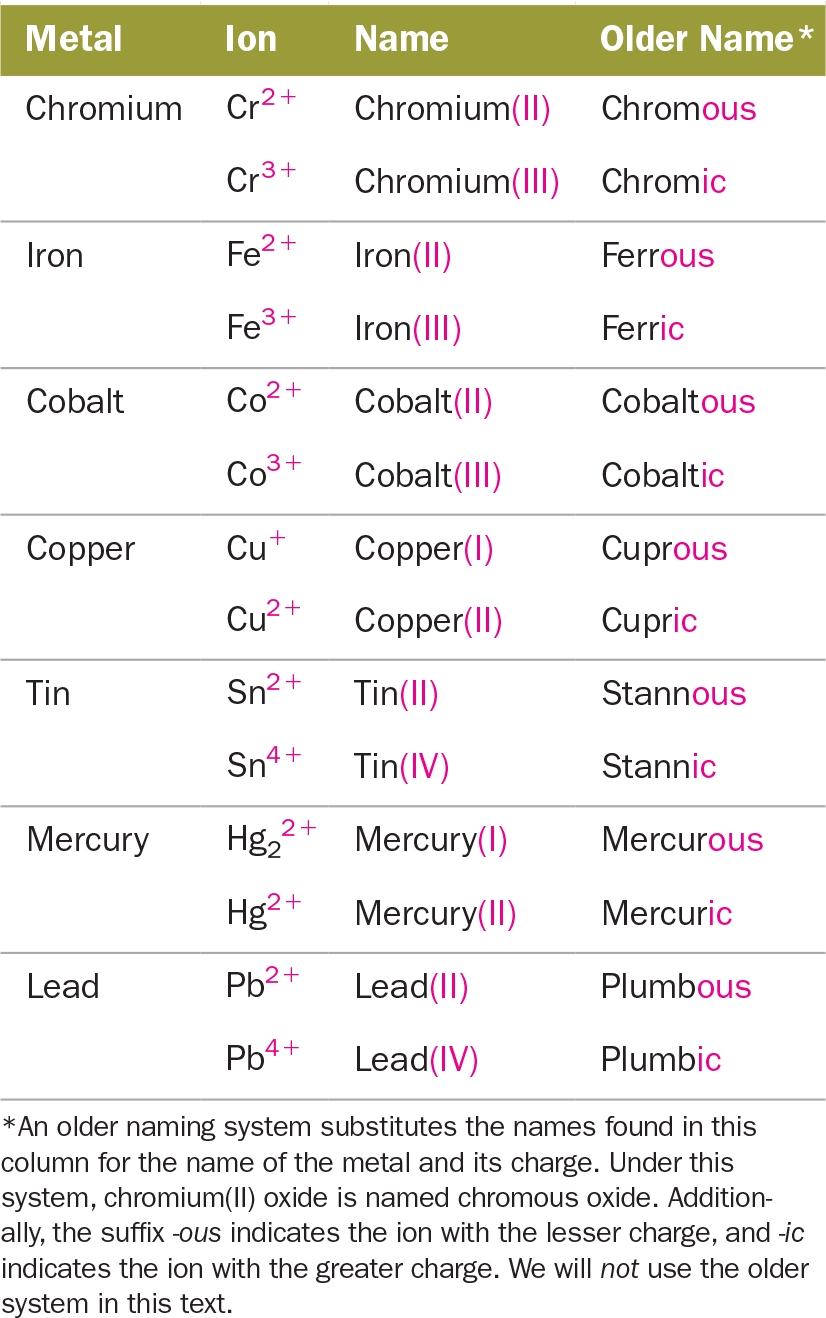
- Monoatomic Cations: When a metal forms a cation with a single charge, its name is the same as the element. For example, Na+ is named sodium.
- Polyatomic Cations: When a metal forms a cation with multiple charges, its name is modified to indicate the charge. For example, Cu2+ is named copper(II).
- Anions: When a nonmetal forms an anion, its name is modified to end in -ide. For example, Cl- is named chloride.
- Compounds: When naming an ionic compound, the cation is named first, followed by the anion. For example, NaCl is named sodium chloride.
Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds
The rules for writing formulas for ionic compounds are as follows:
- Monoatomic Cations: The symbol of the cation is written first, followed by the symbol of the anion. For example, NaCl.
- Polyatomic Cations: The symbol of the cation is written first, followed by the symbol of the anion. The charge on the cation is indicated in parentheses. For example, Cu(NO3)2.
- Compounds with Multiple Cations: When a compound has multiple cations, the symbols of the cations are written in alphabetical order, followed by the symbol of the anion. For example, Ca(OH)2.

| Cation | Anion | Compound Name | Compound Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Cl- | Sodium Chloride | NaCl |
| Mg2+ | O2- | Magnesium Oxide | MgO |
| Al3+ | P3- | Aluminum Phosphide | AlP |
📝 Note: When writing formulas for ionic compounds, it is essential to balance the charges between the cations and anions.
Practice Problems
Try the following practice problems to test your understanding of naming and writing formulas for ionic compounds:
- Problem 1: What is the name and formula of the compound formed between calcium (Ca2+) and sulfate (SO42-)?
- Problem 2: What is the name and formula of the compound formed between copper (Cu2+) and nitrate (NO3-)?
- Problem 3: What is the name and formula of the compound formed between magnesium (Mg2+) and hydroxide (OH-)?
Solutions to Practice Problems
- Solution 1: The name of the compound is calcium sulfate, and the formula is CaSO4.
- Solution 2: The name of the compound is copper(II) nitrate, and the formula is Cu(NO3)2.
- Solution 3: The name of the compound is magnesium hydroxide, and the formula is Mg(OH)2.
In summary, mastering the rules for naming and writing formulas for ionic compounds is essential for success in chemistry. By understanding the rules for naming cations, anions, and compounds, and by practicing writing formulas, you will be well on your way to becoming a chemistry expert.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion, typically formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons. An anion is a negatively charged ion, typically formed when a nonmetal atom gains one or more electrons.
How do I determine the charge on a cation or anion?
+The charge on a cation or anion can be determined by looking at the number of electrons gained or lost by the atom. For example, a sodium atom that loses one electron will have a charge of +1, while a chlorine atom that gains one electron will have a charge of -1.
What is the difference between a monoatomic cation and a polyatomic cation?
+A monoatomic cation is a cation that consists of a single atom, while a polyatomic cation is a cation that consists of multiple atoms.