5 Ways to Master Ionic and Covalent Compounds

Understanding Ionic and Covalent Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide
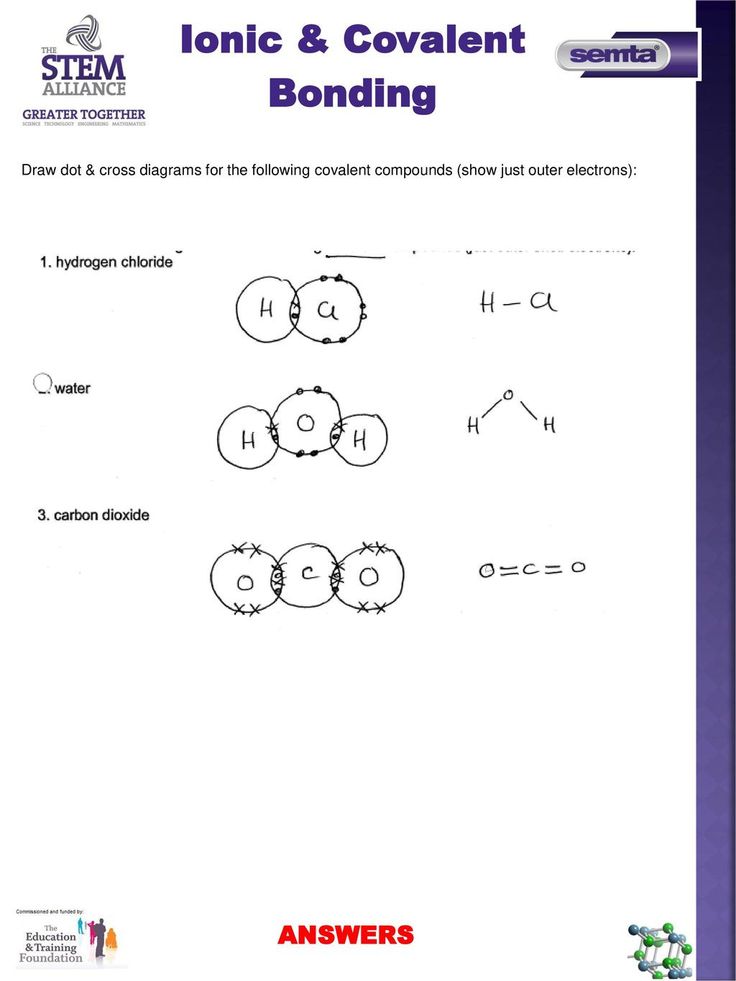
Ionic and covalent compounds are two fundamental types of chemical compounds that form the basis of chemistry. Ionic compounds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. Covalent compounds, on the other hand, are formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a molecule. Mastering the concepts of ionic and covalent compounds is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions and processes.
1. Learn the Basics of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a cation, while a non-metal atom gains one or more electrons to form an anion. The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions holds them together, forming a strong ionic bond. To master ionic compounds, you need to understand the following key concepts:
- Electron transfer: Understand how electrons are transferred between atoms to form ions.
- Ion formation: Learn how to identify the ions formed by different elements.
- Ionic bonding: Understand how the electrostatic attraction between ions holds them together.
💡 Note: Ionic compounds are typically formed between metals and non-metals.
2. Understand Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to form a molecule. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, holding them together. To master covalent compounds, you need to understand the following key concepts:
- Electron sharing: Understand how atoms share electrons to form a covalent bond.
- Molecular structure: Learn how to determine the molecular structure of covalent compounds.
- Polarity: Understand how the polarity of a molecule affects its properties.
🔍 Note: Covalent compounds can be polar or non-polar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms.
3. Practice Writing Formulas and Names
Writing formulas and names of ionic and covalent compounds is an essential skill in chemistry. To master this skill, you need to practice writing formulas and names of different compounds. Here are some tips:
- Ionic compounds: Write the formula by combining the symbols of the cation and anion.
- Covalent compounds: Write the formula by combining the symbols of the atoms and indicating the number of atoms of each element.
- Names: Learn the rules for naming ionic and covalent compounds, including the use of prefixes and suffixes.
| Compound | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| Water | H2O | Water |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
4. Understand the Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic and covalent compounds have different properties due to the nature of their bonds. To master the properties of these compounds, you need to understand the following key concepts:
- Melting and boiling points: Ionic compounds typically have higher melting and boiling points than covalent compounds.
- Solubility: Ionic compounds are typically soluble in water, while covalent compounds are not.
- Conductivity: Ionic compounds are typically good conductors of electricity, while covalent compounds are not.
💡 Note: The properties of ionic and covalent compounds are influenced by the strength of their bonds.
5. Apply Your Knowledge to Real-World Scenarios
To truly master ionic and covalent compounds, you need to apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios. Here are some examples:
- Medicine: Understanding the properties of ionic and covalent compounds is essential in medicine, where compounds are used to treat diseases.
- Environmental science: Understanding the properties of ionic and covalent compounds is essential in environmental science, where compounds are used to clean up pollutants.
- Materials science: Understanding the properties of ionic and covalent compounds is essential in materials science, where compounds are used to develop new materials.
By following these five steps, you can master ionic and covalent compounds and develop a deeper understanding of chemistry.
Mastering the concepts of ionic and covalent compounds is crucial for understanding various chemical reactions and processes. By learning the basics of ionic compounds, understanding covalent compounds, practicing writing formulas and names, understanding the properties of ionic and covalent compounds, and applying your knowledge to real-world scenarios, you can develop a deeper understanding of chemistry and its applications.
What is the main difference between ionic and covalent compounds?
+The main difference between ionic and covalent compounds is the nature of their bonds. Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. Covalent compounds, on the other hand, are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms.
What are some examples of ionic compounds?
+Some examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and potassium nitrate (KNO3).
What are some examples of covalent compounds?
+Some examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4).