Mastering Ionic and Covalent Bonds Made Easy
Understanding the Basics of Chemical Bonds
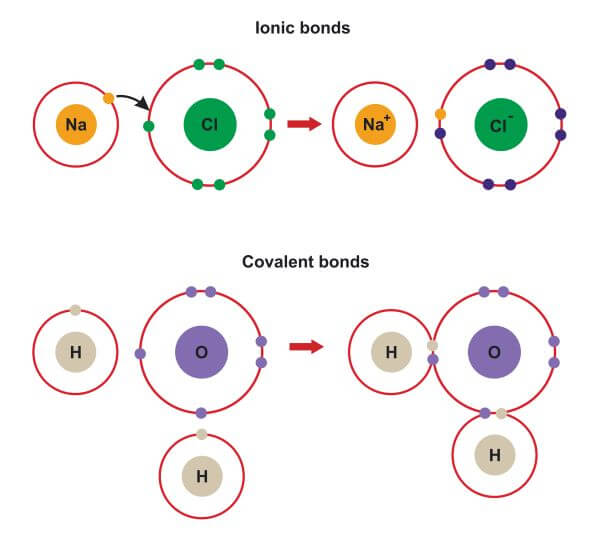
When it comes to chemistry, one of the most fundamental concepts is the chemical bond. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. There are several types of chemical bonds, but in this article, we will focus on two of the most common types: ionic and covalent bonds.
What are Ionic Bonds?
Ionic bonds are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions is what holds them together and forms an ionic bond. Ionic bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals.
Key Characteristics of Ionic Bonds:
- Electron Transfer: Ionic bonds involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another.
- Ion Formation: The transfer of electrons results in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
- Electrostatic Attraction: The attraction between the oppositely charged ions is what holds them together and forms an ionic bond.
- Metal-Nonmetal Compounds: Ionic bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals.
What are Covalent Bonds?
Covalent bonds, on the other hand, are formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a full outer energy level. This sharing of electrons results in a strong chemical bond between the atoms. Covalent bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of nonmetals.
Key Characteristics of Covalent Bonds:
- Electron Sharing: Covalent bonds involve the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between atoms.
- Nonmetal Compounds: Covalent bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of nonmetals.
- Polarity: Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, depending on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms.
- Strong Bonds: Covalent bonds are typically stronger than ionic bonds.
Factors that Influence the Formation of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Several factors influence the formation of ionic and covalent bonds, including:
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons is known as electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativity tend to form covalent bonds, while those with low electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds.
- Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is known as ionization energy. Atoms with low ionization energy tend to form ionic bonds, while those with high ionization energy tend to form covalent bonds.
- Atomic Radius: The size of an atom can also influence the formation of ionic and covalent bonds. Atoms with large atomic radii tend to form ionic bonds, while those with small atomic radii tend to form covalent bonds.
💡 Note: Understanding the factors that influence the formation of ionic and covalent bonds is crucial for predicting the type of bond that will form between two atoms.
Common Examples of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Here are some common examples of ionic and covalent compounds:
- Ionic Compounds:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
- Aluminum oxide (Al2O3)
- Covalent Compounds:
- Water (H2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
Key Differences between Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Here are the key differences between ionic and covalent bonds:
- Bond Formation: Ionic bonds are formed through the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons.
- Bond Strength: Covalent bonds are typically stronger than ionic bonds.
- Polarity: Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, while ionic bonds are always polar.

| Type of Bond | Bond Formation | Bond Strength | Polarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic | Electron transfer | Typically weaker | Always polar |
| Covalent | Electron sharing | Typically stronger | Polar or nonpolar |
In conclusion, mastering ionic and covalent bonds requires a deep understanding of the fundamental concepts of chemistry. By understanding the key characteristics, factors that influence the formation, and common examples of ionic and covalent compounds, you can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of chemistry.
Recap of Key Points
- Ionic bonds are formed through the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds are formed through the sharing of electrons.
- Ionic bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are typically found in compounds that consist of nonmetals.
- Electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius are factors that influence the formation of ionic and covalent bonds.
- Covalent bonds are typically stronger than ionic bonds.
- Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar, while ionic bonds are always polar.
What is the main difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
+The main difference between ionic and covalent bonds is the way in which the atoms share electrons. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
What are some common examples of ionic compounds?
+Some common examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and aluminum oxide (Al2O3).
What is electronegativity, and how does it influence the formation of ionic and covalent bonds?
+Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons. Atoms with high electronegativity tend to form covalent bonds, while those with low electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds.



