6 Essential Tips for Mastering Heating Curves
Understanding the Basics of Heating Curves
Heating curves are a crucial concept in physics and engineering, representing the relationship between the amount of heat energy transferred to a substance and its resulting temperature change. Mastering heating curves requires a solid grasp of thermodynamics and the ability to analyze complex data. In this article, we will explore six essential tips to help you improve your understanding of heating curves and become proficient in their application.
Tip 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Different Types of Heating Curves
There are several types of heating curves, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Specific heat capacity curves: These curves show the relationship between the amount of heat energy transferred to a substance and its resulting temperature change, taking into account the substance’s specific heat capacity.
- Latent heat curves: These curves represent the heat energy required to change the state of a substance, such as from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas.
- Sensible heat curves: These curves show the relationship between the amount of heat energy transferred to a substance and its resulting temperature change, without considering any phase changes.
🔍 Note: Understanding the different types of heating curves is crucial for accurate analysis and interpretation of thermodynamic data.
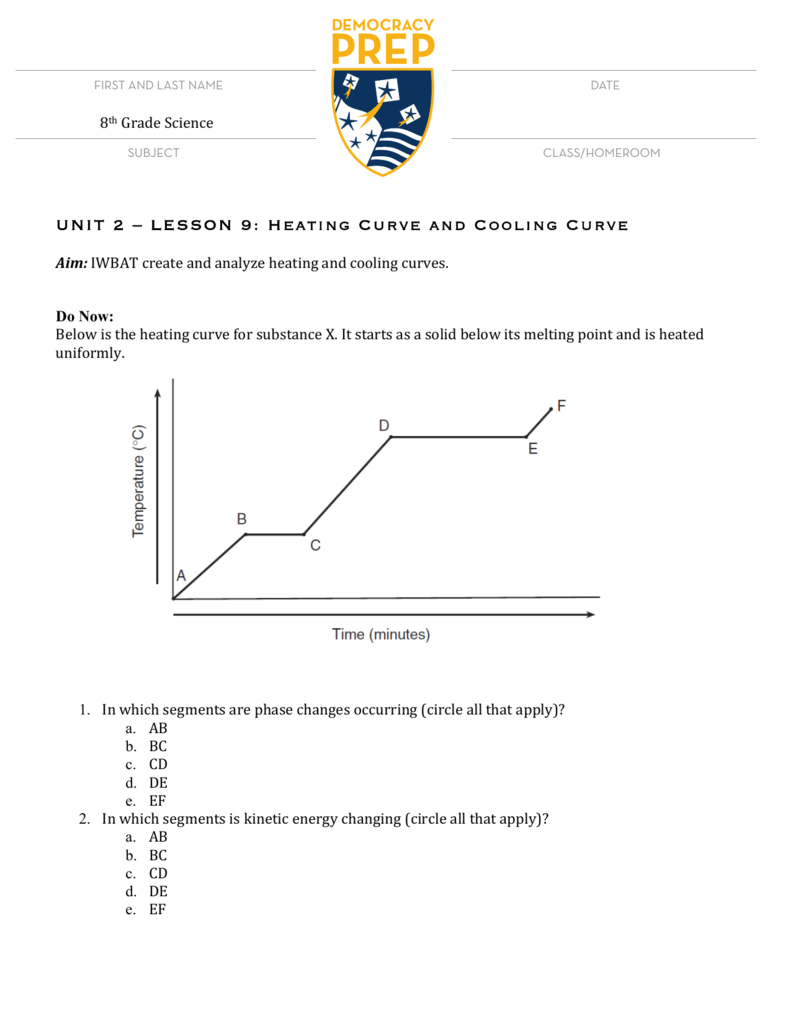
Tip 2: Analyze the Shape and Slope of the Heating Curve
The shape and slope of a heating curve can provide valuable information about the substance’s thermodynamic properties. A steeper slope indicates a higher specific heat capacity, while a flatter slope indicates a lower specific heat capacity.
- Positive slope: A positive slope indicates that the substance is absorbing heat energy, resulting in an increase in temperature.
- Negative slope: A negative slope indicates that the substance is releasing heat energy, resulting in a decrease in temperature.
- Horizontal slope: A horizontal slope indicates that the substance is undergoing a phase change, such as melting or boiling.
💡 Note: The shape and slope of the heating curve can be affected by various factors, including the substance's composition, pressure, and temperature.
Tip 3: Use Heating Curves to Determine Thermodynamic Properties
Heating curves can be used to determine various thermodynamic properties, including specific heat capacity, latent heat, and enthalpy. By analyzing the curve, you can calculate these properties and gain a deeper understanding of the substance’s thermodynamic behavior.
- Specific heat capacity: Can be calculated using the slope of the heating curve and the substance’s mass.
- Latent heat: Can be calculated using the area under the heating curve during a phase change.
- Enthalpy: Can be calculated using the area under the heating curve and the substance’s mass.
📝 Note: Accurate calculation of thermodynamic properties requires careful analysis of the heating curve and consideration of any potential errors or uncertainties.
Tip 4: Consider the Effects of Pressure and Temperature
Pressure and temperature can significantly affect the shape and slope of a heating curve. It is essential to consider these factors when analyzing and interpreting thermodynamic data.
- Pressure: Can affect the boiling and melting points of a substance, resulting in changes to the heating curve.
- Temperature: Can affect the specific heat capacity and latent heat of a substance, resulting in changes to the heating curve.
🌡️ Note: The effects of pressure and temperature on the heating curve can be complex and non-linear, requiring careful consideration and analysis.
Tip 5: Use Heating Curves to Optimize Thermal Processes
Heating curves can be used to optimize thermal processes, such as heating and cooling systems, by identifying the most efficient temperature ranges and heat transfer rates.
- Heating systems: Can be optimized by analyzing the heating curve to determine the most efficient temperature range for heat transfer.
- Cooling systems: Can be optimized by analyzing the heating curve to determine the most efficient temperature range for heat transfer.
💡 Note: Optimization of thermal processes requires careful analysis of the heating curve and consideration of any potential constraints or limitations.
Tip 6: Practice, Practice, Practice!
Mastering heating curves requires practice and experience. By working through examples and case studies, you can develop your skills and become proficient in the analysis and interpretation of thermodynamic data.
- Worked examples: Can be found in textbooks and online resources, providing a starting point for practice and analysis.
- Case studies: Can be used to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, developing problem-solving skills and expertise.
📚 Note: Practice and experience are essential for mastering heating curves and developing a deep understanding of thermodynamic principles.
In conclusion, mastering heating curves requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, analytical skills, and practical experience. By following these six essential tips, you can improve your understanding of heating curves and become proficient in their application.
What is the difference between specific heat capacity and latent heat?
+Specific heat capacity refers to the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a substance, while latent heat refers to the amount of heat energy required to change the state of a substance.
How can I use heating curves to optimize thermal processes?
+Heating curves can be used to optimize thermal processes by identifying the most efficient temperature ranges and heat transfer rates. This can be achieved by analyzing the shape and slope of the heating curve and considering the effects of pressure and temperature.
What are some common types of heating curves?
+Some common types of heating curves include specific heat capacity curves, latent heat curves, and sensible heat curves. Each type of curve has its own unique characteristics and applications.
Related Terms:
- Heating curve Worksheet pdf
- Heating curves AP Chemistry
- Heating and cooling curves worksheet