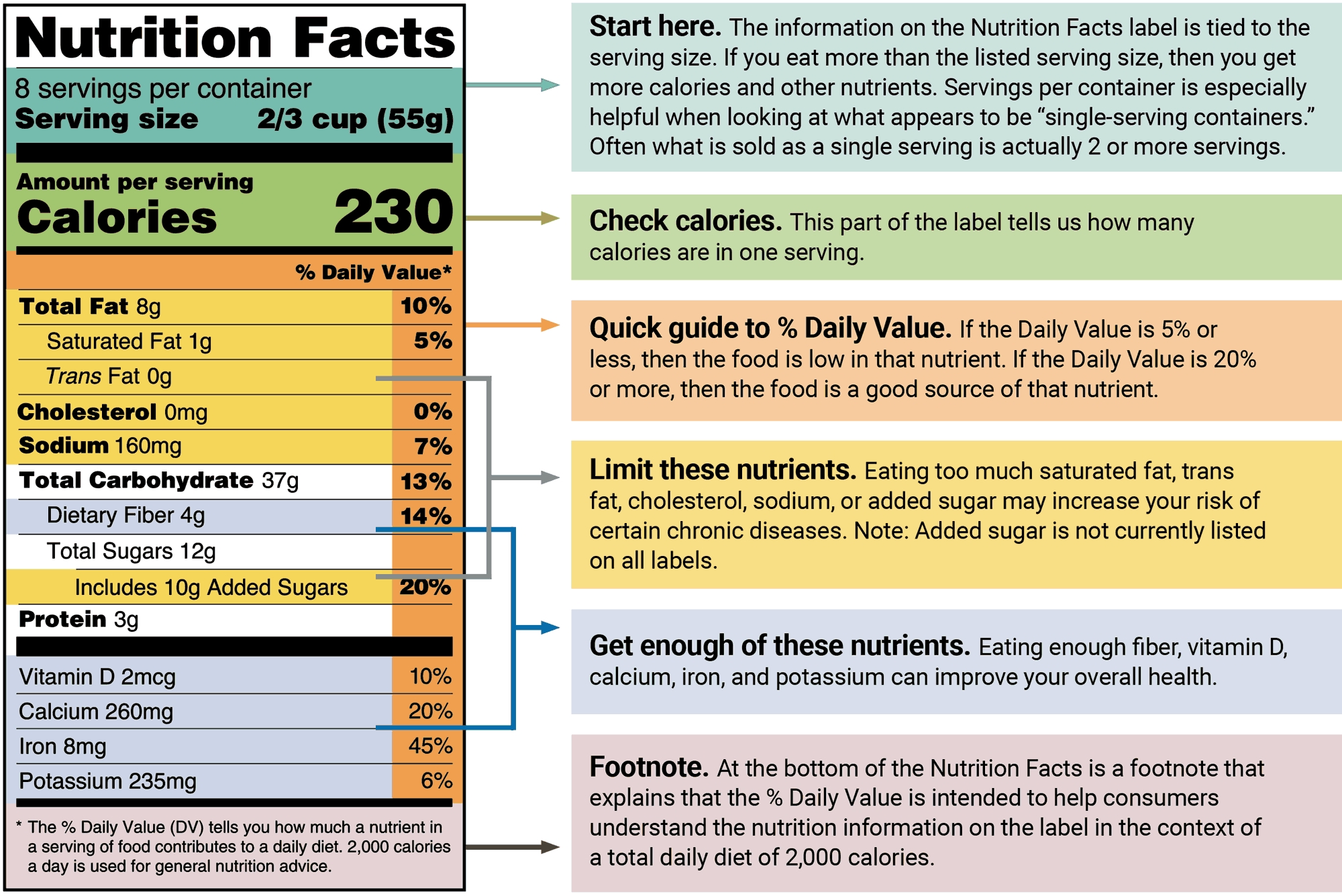
Heat Transfer Worksheet with Solutions and Examples

Heat Transfer: Understanding the Basics
Heat transfer is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that involves the transfer of thermal energy from one body to another. It is a crucial aspect of various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. In this article, we will explore the basics of heat transfer, including its definition, types, and examples.
What is Heat Transfer?
Heat transfer is the transfer of thermal energy from a system to its surroundings or vice versa. It occurs due to a temperature difference between two systems. The direction of heat transfer is always from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Types of Heat Transfer
There are three main types of heat transfer:
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact between particles or molecules.
- Convection: Heat transfer through the movement of fluids.
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves.
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles or molecules. It occurs in solids, liquids, and gases. The rate of heat transfer through conduction depends on the following factors:
- Temperature difference: The greater the temperature difference, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
- Thermal conductivity: The ability of a material to conduct heat. Metals are good conductors, while gases are poor conductors.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids. It occurs in liquids and gases. The rate of heat transfer through convection depends on the following factors:
- Temperature difference: The greater the temperature difference, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
- Fluid velocity: The faster the fluid moves, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
- Fluid density: The denser the fluid, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. It occurs in all forms of matter. The rate of heat transfer through radiation depends on the following factors:
- Temperature: The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
- Surface area: The larger the surface area, the higher the rate of heat transfer.
Examples of Heat Transfer
- Cooking: Heat transfer occurs when food is cooked on a stove or in an oven. Conduction and convection are involved in this process.
- Refrigeration: Heat transfer occurs when a refrigerator transfers heat from the interior to the exterior. Convection and radiation are involved in this process.
- Solar Heating: Heat transfer occurs when the sun’s radiation warms a building or a pool. Radiation is involved in this process.
Heat Transfer Worksheet with Solutions
Problem 1: A metal rod is heated at one end. If the temperature difference between the two ends is 100°C, and the length of the rod is 1 meter, what is the rate of heat transfer through conduction?
Solution: Assuming a thermal conductivity of 100 W/m°C, the rate of heat transfer through conduction is:
Q = k * A * (T1 - T2) / L = 100 W/m°C * 0.01 m² * 100°C / 1 m = 100 W
Problem 2: A liquid is heated in a container. If the temperature difference between the liquid and the surroundings is 50°C, and the fluid velocity is 0.1 m/s, what is the rate of heat transfer through convection?
Solution: Assuming a fluid density of 1000 kg/m³, the rate of heat transfer through convection is:
Q = h * A * (T1 - T2) = 10 W/m²°C * 0.01 m² * 50°C = 50 W
Problem 3: A building is heated by solar radiation. If the surface area of the building is 100 m², and the temperature is 20°C, what is the rate of heat transfer through radiation?
Solution: Assuming an emissivity of 0.9, the rate of heat transfer through radiation is:
Q = ε * σ * A * T^4 = 0.9 * 5.67 x 10^-8 W/m²K^4 * 100 m² * (20 + 273)^4 = 1000 W
💡 Note: These problems are simplified examples and are not meant to be used in real-world applications.
Heat Transfer Table

| Type of Heat Transfer | Description | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Heat transfer through direct contact | Q = k * A * (T1 - T2) / L |
| Convection | Heat transfer through fluid movement | Q = h * A * (T1 - T2) |
| Radiation | Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves | Q = ε * σ * A * T^4 |
The basics of heat transfer are essential in understanding various natural and industrial processes. By understanding the types of heat transfer and the factors that affect them, we can design more efficient systems and technologies.
Heat transfer is an essential concept in physics and engineering, and it has numerous applications in our daily lives. By understanding the basics of heat transfer, we can develop more efficient systems and technologies.
What is heat transfer?
+Heat transfer is the transfer of thermal energy from one body to another.
What are the types of heat transfer?
+There are three main types of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.
What is the equation for conduction?
+The equation for conduction is Q = k * A * (T1 - T2) / L.