Graduated Cylinder Worksheet Practice for Science Students

Understanding Graduated Cylinders: A Practical Guide for Science Students
As a science student, it’s essential to have a strong foundation in measurement skills, particularly when working with liquids. One of the most commonly used tools in laboratories and classrooms is the graduated cylinder. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of graduated cylinders, how to read them accurately, and provide practice exercises to help you master this crucial skill.
What is a Graduated Cylinder?
A graduated cylinder is a transparent, cylindrical container with markings to indicate different volumes of liquid. It’s used to measure the volume of liquids accurately, typically in milliliters (mL) or liters (L). Graduated cylinders come in various sizes, ranging from 10 mL to 2000 mL or more.
Parts of a Graduated Cylinder
Before we dive into reading graduated cylinders, let’s familiarize ourselves with its parts:
- Gradations: The markings on the side of the cylinder indicating different volumes.
- Meniscus: The curved surface of the liquid.
- Zero line: The line indicating the zero mark on the cylinder.
How to Read a Graduated Cylinder
Reading a graduated cylinder requires attention to detail and a clear understanding of the markings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Hold the cylinder upright: Make sure the cylinder is straight and level.
- Identify the meniscus: Locate the curved surface of the liquid.
- Find the zero line: Identify the zero mark on the cylinder.
- Read the volume: Look at the marking on the cylinder that is at eye level with the meniscus. This is the volume of the liquid.
Tips:
- Always read the volume from the bottom of the meniscus.
- Use a ruler or other straight edge to help you read the marking accurately.
- If the meniscus is below the zero line, the volume is zero.
Graduated Cylinder Worksheet Practice
Now that you understand the basics of graduated cylinders, it’s time to practice! Here are some exercises to help you become proficient in reading graduated cylinders:
Exercise 1: Reading Graduated Cylinders
Read the volume of the liquid in each graduated cylinder:
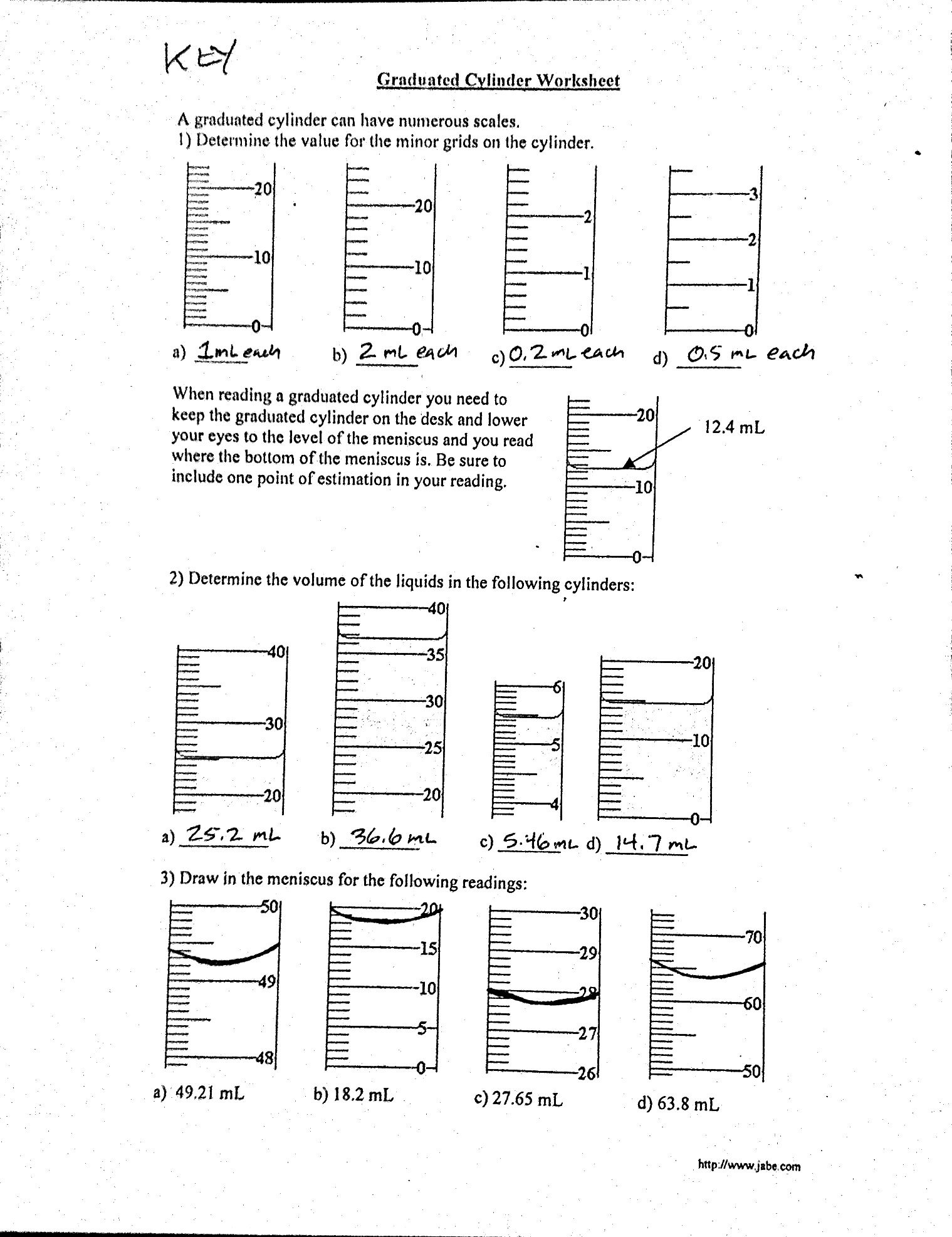
| Cylinder | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|
| A | ? |
| B | ? |
| C | ? |
| D | ? |
Answers:
- Cylinder A: 25 mL
- Cylinder B: 50 mL
- Cylinder C: 100 mL
- Cylinder D: 200 mL
Exercise 2: Filling Graduated Cylinders
You need to fill a 100 mL graduated cylinder with water. If you already have 50 mL of water in the cylinder, how much more water do you need to add?
- Answer: 50 mL
Exercise 3: Measuring Liquid Volumes
Measure the volume of the liquid in each graduated cylinder using the markings:
| Cylinder | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|
| A | 25.5 mL |
| B | 50.2 mL |
| C | 100.8 mL |
| D | 200.5 mL |
Answers:
- Cylinder A: 25.5 mL
- Cylinder B: 50.2 mL
- Cylinder C: 100.8 mL
- Cylinder D: 200.5 mL
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with graduated cylinders, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can affect accuracy:
- Not holding the cylinder upright: This can cause the liquid to spill or the meniscus to be distorted.
- Not reading the volume from the bottom of the meniscus: This can result in inaccurate readings.
- Not using a ruler or straight edge: This can make it difficult to read the markings accurately.
📝 Note: Always handle graduated cylinders with care, as they can break easily. Make sure to clean and dry the cylinder thoroughly after use.
Conclusion
Mastering the skill of reading graduated cylinders is essential for science students. With practice and attention to detail, you can become proficient in using graduated cylinders to measure liquid volumes accurately. Remember to avoid common mistakes and always handle the cylinders with care. By following the exercises and tips outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a pro at using graduated cylinders.
What is the purpose of a graduated cylinder?
+A graduated cylinder is used to measure the volume of liquids accurately.
How do I read a graduated cylinder?
+Hold the cylinder upright, identify the meniscus, find the zero line, and read the volume from the bottom of the meniscus.
What is the meniscus?
+The meniscus is the curved surface of the liquid in the graduated cylinder.
Related Terms:
- Graduated cylinder Worksheet answer key
- Graduated cylinder Worksheet PDF
- Reading graduated cylinders practice
- Reading a graduated cylinder
- Water displacement worksheet



