6 Ways to Master Gerrymandering Worksheet Answers
Understanding Gerrymandering and Its Impact on Democracy
Gerrymandering is a pervasive issue in modern politics, affecting the democratic process and influencing election outcomes. It involves manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor one party or class, often leading to unequal representation. Mastering the concept of gerrymandering requires a comprehensive understanding of its history, types, and implications. This article provides a detailed analysis of gerrymandering, along with a worksheet to help readers assess their knowledge.
A Brief History of Gerrymandering
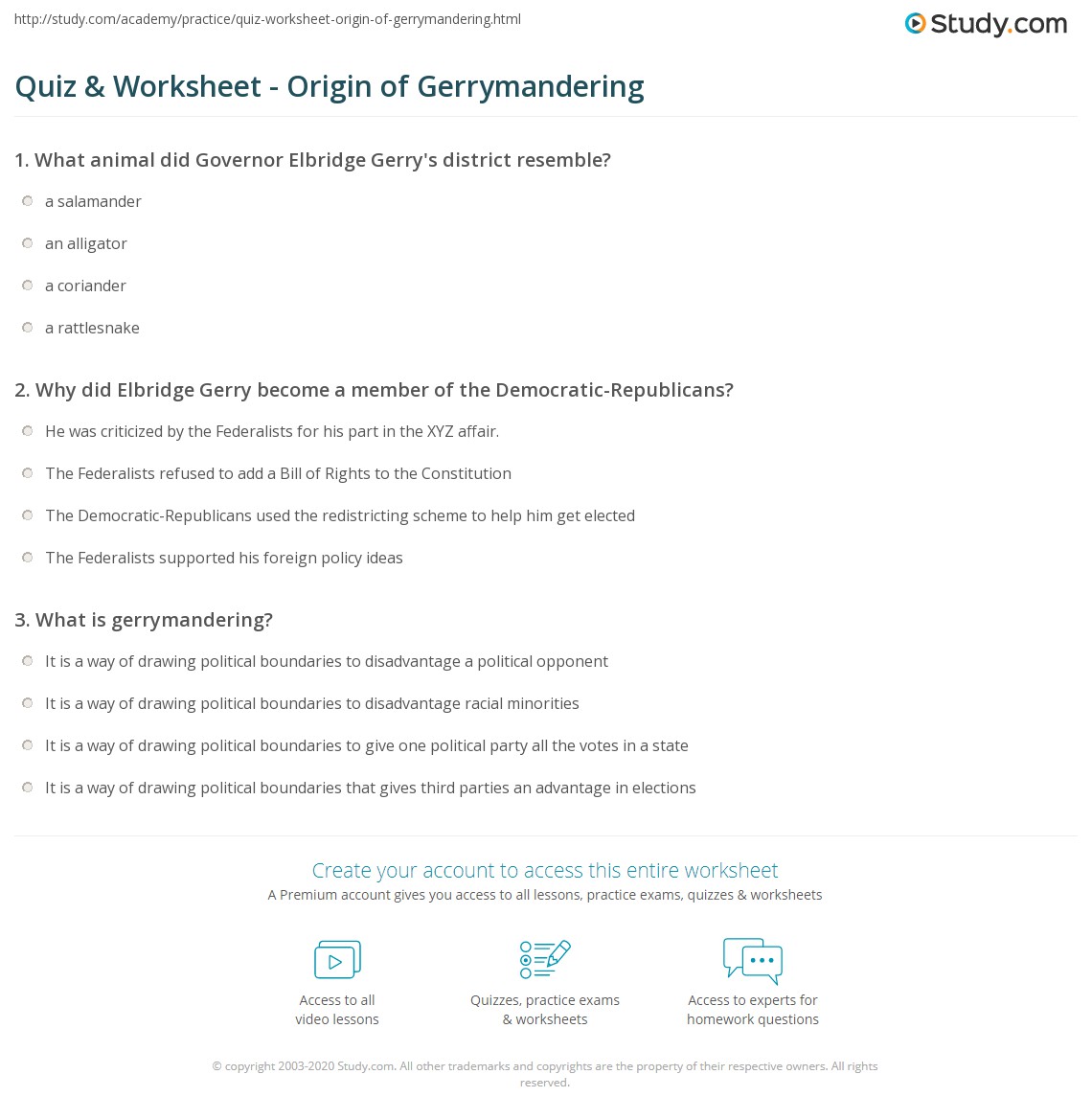
Gerrymandering has its roots in the early 19th century, when Elbridge Gerry, the Governor of Massachusetts, signed a bill that created an electoral district resembling a salamander. The term “gerrymander” was coined by combining Gerry’s name with the animal. Since then, gerrymandering has become a widespread practice in many countries, often resulting in uncompetitive elections and disenfranchisement of certain groups.
Types of Gerrymandering
There are several types of gerrymandering, including:
- Partisan gerrymandering: This involves manipulating district boundaries to favor one party over another. It can be achieved through various techniques, such as packing, cracking, and gerrymandering by omission.
- Racial gerrymandering: This type of gerrymandering involves creating districts that reduce the voting power of racial or ethnic minority groups.
- Prison gerrymandering: This practice involves counting prisoners as residents of the district where they are incarcerated, rather than their actual place of residence.
The Impact of Gerrymandering on Democracy
Gerrymandering has far-reaching consequences for democratic systems. Some of the most significant effects include:
- Uncompetitive elections: Gerrymandering often leads to uncompetitive elections, where the outcome is predetermined. This can result in low voter turnout and a lack of representation for marginalized groups.
- Disenfranchisement: Gerrymandering can disenfranchise certain groups, such as racial or ethnic minorities, by reducing their voting power.
- Polarization: Gerrymandering can contribute to polarization by creating districts that are heavily skewed towards one party or ideology.
Maching Gerrymandering Worksheet Answers
To master gerrymandering, it’s essential to assess your knowledge of the subject. Here’s a worksheet with answers to help you evaluate your understanding:
Question 1: What is the origin of the term “gerrymandering”?
A) Elbridge Gerry, the Governor of Massachusetts B) The practice of creating electoral districts C) The manipulation of district boundaries D) The disenfranchisement of marginalized groups
Answer: A) Elbridge Gerry, the Governor of Massachusetts
Question 2: What is partisan gerrymandering?
A) The creation of districts that reduce the voting power of racial or ethnic minority groups B) The manipulation of district boundaries to favor one party over another C) The practice of counting prisoners as residents of the district where they are incarcerated D) The creation of uncompetitive elections
Answer: B) The manipulation of district boundaries to favor one party over another
Question 3: What is the impact of gerrymandering on democracy?
A) Increased voter turnout and representation for marginalized groups B) Uncompetitive elections and disenfranchisement of certain groups C) Polarization and the creation of districts that are heavily skewed towards one party or ideology D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
Question 4: What is prison gerrymandering?
A) The practice of creating electoral districts that resemble a salamander B) The manipulation of district boundaries to favor one party over another C) The counting of prisoners as residents of the district where they are incarcerated D) The disenfranchisement of marginalized groups
Answer: C) The counting of prisoners as residents of the district where they are incarcerated
Question 5: What is the primary goal of gerrymandering?
A) To create competitive elections and increase voter turnout B) To disenfranchise marginalized groups and reduce their voting power C) To manipulate district boundaries to favor one party or class D) To create uncompetitive elections and polarize the electorate
Answer: C) To manipulate district boundaries to favor one party or class
Question 6: What is the most effective way to combat gerrymandering?
A) Redistricting commissions B) Judicial intervention C) Legislative reform D) Public awareness and advocacy
Answer: D) Public awareness and advocacy
📝 Note: While all the options listed above can be effective ways to combat gerrymandering, public awareness and advocacy are crucial in bringing attention to the issue and pushing for reform.
To master gerrymandering, it’s essential to understand its history, types, and implications. By assessing your knowledge through this worksheet, you can identify areas where you need to improve your understanding. Remember, combating gerrymandering requires a comprehensive approach, including public awareness and advocacy, redistricting commissions, judicial intervention, and legislative reform.
What is the difference between partisan and racial gerrymandering?
+Partisan gerrymandering involves manipulating district boundaries to favor one party over another, while racial gerrymandering involves creating districts that reduce the voting power of racial or ethnic minority groups.
How does gerrymandering affect voter turnout?
+Gerrymandering can lead to uncompetitive elections, which can result in low voter turnout. When voters feel that their vote won’t make a difference, they are less likely to participate in the electoral process.
What is the role of the judiciary in combating gerrymandering?
+The judiciary plays a crucial role in combating gerrymandering by declaring unconstitutional electoral district boundaries that have been manipulated for partisan or racial gain.