5 Essential Steps to Master Free Body Diagrams
Understanding the Fundamentals of Free Body Diagrams
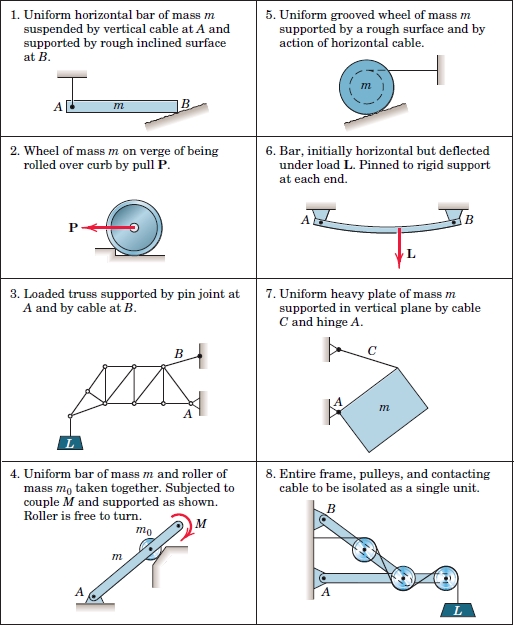
Free body diagrams are a powerful tool in physics and engineering, used to visualize and analyze the forces acting on an object. Mastering free body diagrams is essential for solving complex problems in mechanics, and it requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles. In this article, we will break down the process of creating and analyzing free body diagrams into five essential steps.
Step 1: Identify the Object and the Forces Acting on It
The first step in creating a free body diagram is to identify the object of interest and the forces acting on it. This involves carefully examining the problem and determining which forces are relevant. Forces can be classified into two main categories: internal forces and external forces. Internal forces are the forces that act within the object itself, such as tension or compression, while external forces are the forces that act on the object from outside, such as friction or gravity.
When identifying the forces, consider the following:
- What is the object’s mass and size?
- What are the external forces acting on the object, such as gravity, friction, or normal forces?
- Are there any internal forces, such as tension or compression, acting within the object?
Step 2: Choose a Coordinate System
Once you have identified the object and the forces acting on it, the next step is to choose a coordinate system. A coordinate system is a reference frame that allows you to describe the position and motion of the object. The most common coordinate system is the Cartesian coordinate system, which consists of three perpendicular axes: x, y, and z.
When choosing a coordinate system, consider the following:
- What is the orientation of the object and the forces acting on it?
- Which coordinate system will simplify the problem and make it easier to analyze?
- Are there any symmetries or constraints that can help you choose a coordinate system?
Step 3: Draw the Free Body Diagram
With the object and forces identified, and the coordinate system chosen, the next step is to draw the free body diagram. A free body diagram is a graphical representation of the object and the forces acting on it. The diagram should include the object, the forces, and the coordinate system.
When drawing the free body diagram, consider the following:
- Use arrows to represent the forces, with the direction of the arrow indicating the direction of the force.
- Use labels to identify the forces and the coordinate system.
- Keep the diagram simple and clear, avoiding clutter and unnecessary details.
Step 4: Analyze the Forces and Resolve Them into Components
Once you have drawn the free body diagram, the next step is to analyze the forces and resolve them into components. This involves breaking down each force into its x, y, and z components, using the coordinate system as a reference.
When analyzing the forces, consider the following:
- Use trigonometry to resolve the forces into components.
- Consider the magnitude and direction of each force component.
- Use the force components to calculate the net force acting on the object.
Step 5: Apply Newton's Laws of Motion
The final step is to apply Newton’s laws of motion to the free body diagram. Newton’s laws relate the forces acting on an object to its motion, and they provide a powerful tool for analyzing and predicting the behavior of objects.
When applying Newton’s laws, consider the following:
- Use the net force calculated in Step 4 to determine the acceleration of the object.
- Use Newton’s second law to relate the force and acceleration.
- Use Newton’s third law to analyze the interaction between objects.
📝 Note: Free body diagrams are a powerful tool for analyzing complex problems in mechanics. By following these five essential steps, you can master free body diagrams and become proficient in solving problems in physics and engineering.
By following these five essential steps, you can create and analyze free body diagrams with confidence. Remember to identify the object and forces, choose a coordinate system, draw the free body diagram, analyze the forces, and apply Newton’s laws of motion. With practice and patience, you will become proficient in using free body diagrams to solve complex problems in mechanics.
What is a free body diagram?
+A free body diagram is a graphical representation of an object and the forces acting on it. It is a powerful tool for analyzing and predicting the behavior of objects in physics and engineering.
What are the different types of forces that can act on an object?
+Forces can be classified into two main categories: internal forces and external forces. Internal forces are the forces that act within the object itself, such as tension or compression, while external forces are the forces that act on the object from outside, such as friction or gravity.
How do I choose a coordinate system for a free body diagram?
+When choosing a coordinate system, consider the orientation of the object and the forces acting on it. Choose a coordinate system that will simplify the problem and make it easier to analyze. Consider any symmetries or constraints that can help you choose a coordinate system.