Food Chains and Webs: Understanding Energy Transfer
What are Food Chains and Webs?
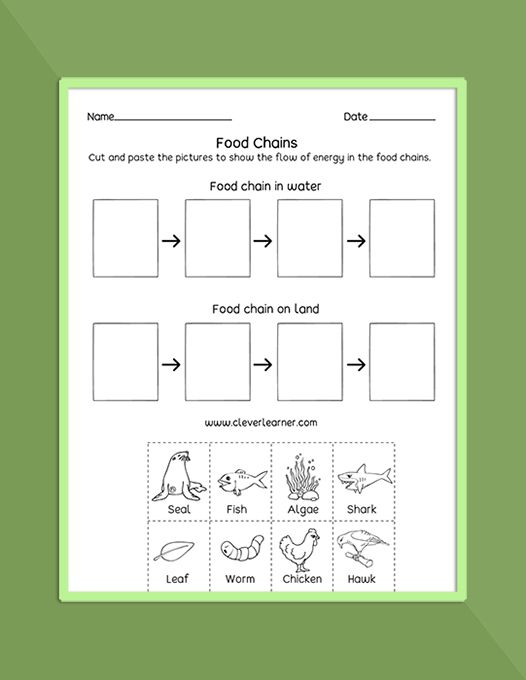
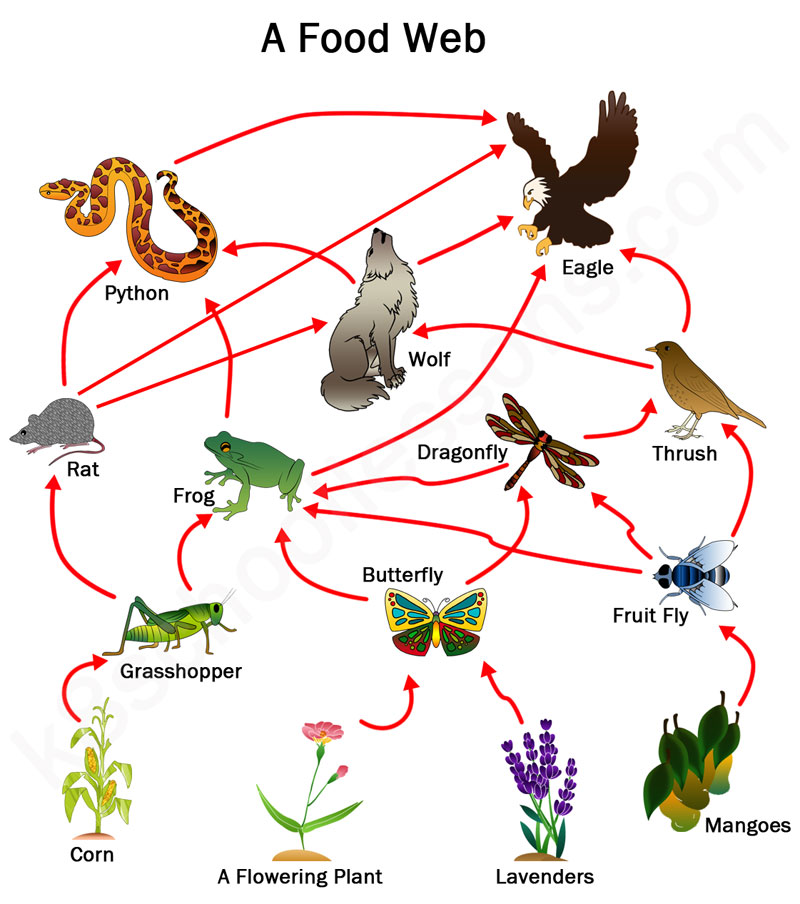
Food chains and webs are fundamental concepts in ecology that describe the feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy. A food web, on the other hand, is a complex network of interconnected food chains that show the multiple feeding relationships between different species.
Components of a Food Chain
A food chain consists of several components, including:
- Producers: These are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants and algae.
- Primary consumers: These are organisms that eat producers, such as herbivores.
- Secondary consumers: These are organisms that eat primary consumers, such as carnivores.
- Tertiary consumers: These are organisms that eat secondary consumers, such as apex predators.
- Decomposers: These are organisms that break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients.
Energy Transfer in Food Chains
Energy is transferred from one organism to another through the food chain. Producers convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which is then transferred to primary consumers when they eat the producers. This energy is then transferred to secondary consumers when they eat the primary consumers, and so on.
However, energy is lost at each trophic level due to factors such as heat, waste, and metabolism. This means that the amount of energy available to each trophic level decreases as you move up the food chain.
💡 Note: This is why there are generally fewer organisms at higher trophic levels, as there is less energy available to support them.
Types of Food Webs
There are several types of food webs, including:
- Grassland food web: This type of food web is found in grasslands and features herbivores such as deer and rabbits, which are preyed upon by carnivores such as coyotes and hawks.
- Desert food web: This type of food web is found in deserts and features organisms such as cacti, which are eaten by herbivores such as desert tortoises.
- Marine food web: This type of food web is found in oceans and features organisms such as phytoplankton, which are eaten by zooplankton, which are in turn eaten by fish.
Importance of Food Webs
Food webs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They:
- Regulate populations: Food webs help regulate the populations of different species, preventing any one species from becoming too dominant.
- Maintain biodiversity: Food webs help maintain biodiversity by providing a variety of habitats and resources for different species.
- Support ecosystem services: Food webs support ecosystem services such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling.
🌿 Note: Food webs are an important part of maintaining ecosystem health, and changes to food webs can have significant impacts on ecosystem function.
Threats to Food Webs
Food webs are threatened by several factors, including:
- Climate change: Climate change can alter the distribution and abundance of species, disrupting food webs.
- Habitat destruction: Habitat destruction can reduce the availability of resources and habitats for different species.
- Invasive species: Invasive species can outcompete native species for resources and alter food webs.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts can help protect food webs by:
- Protecting habitats: Protecting habitats can help maintain the diversity of species and the complexity of food webs.
- Controlling invasive species: Controlling invasive species can help prevent them from outcompeting native species.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture: Promoting sustainable agriculture can help reduce the impact of agriculture on ecosystems and food webs.
As we summarize the key points, it’s clear that food chains and webs play a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Understanding the components of food chains, energy transfer, and the importance of food webs can help us appreciate the complexity of ecosystems and the need to protect them.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
+A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms that eat other organisms as a source of food and energy, while a food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that show the multiple feeding relationships between different species.
Why is energy transfer important in food chains?
+Energy transfer is important in food chains because it shows how energy is passed from one organism to another, and how it is lost at each trophic level.
What are some threats to food webs?
+Food webs are threatened by several factors, including climate change, habitat destruction, and invasive species.