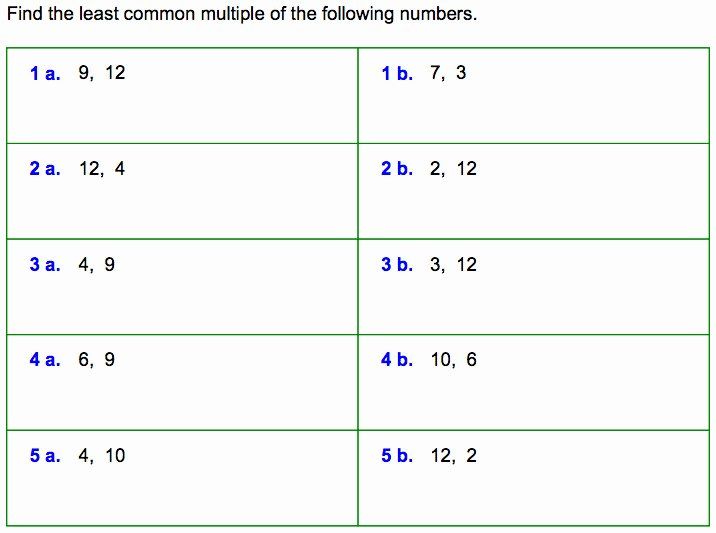
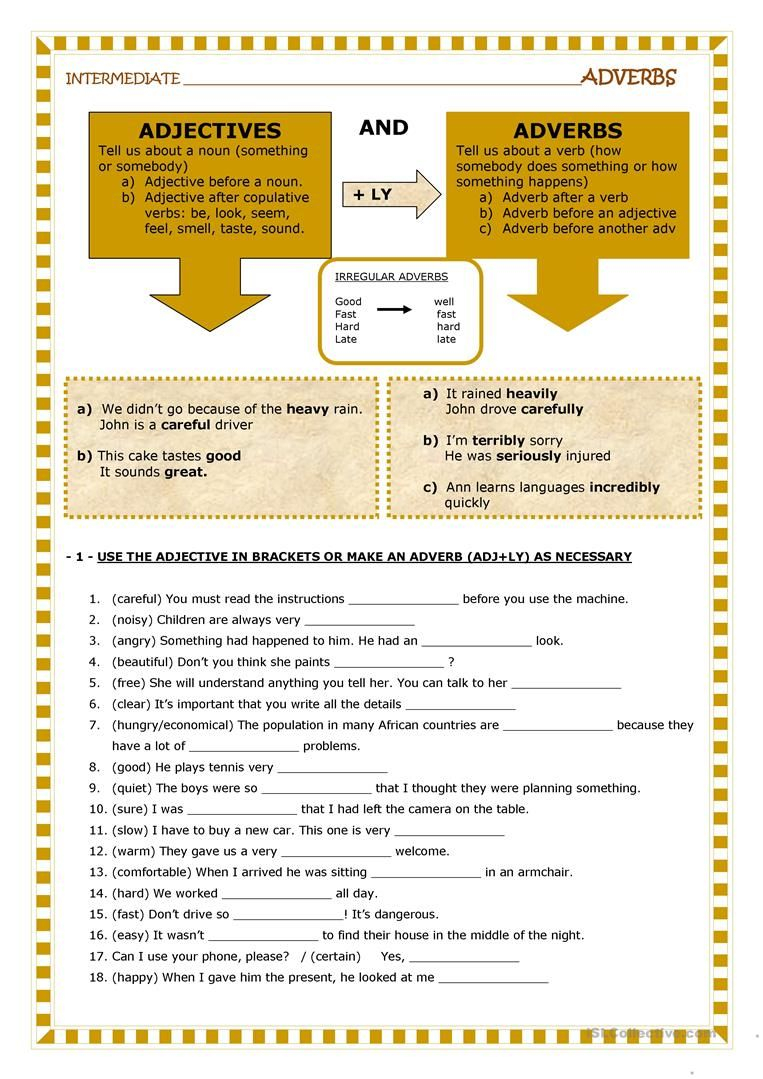
Figurative Language Worksheet 3 Answer Key

Understanding Figurative Language: A Comprehensive Guide
Figurative language is a crucial element in literature and poetry, used to convey emotions, ideas, and themes in a more vivid and engaging way. It helps readers to interpret and understand the deeper meaning of a text by using words in a non-literal sense. In this guide, we will explore the different types of figurative language, their meanings, and examples to help you better comprehend this literary device.
Types of Figurative Language
Figurative language can be categorized into several types, including:
- Simile: A comparison between two unlike things using “like” or “as.”
- Metaphor: A comparison between two unlike things without using “like” or “as.”
- Personification: Attributing human qualities or characteristics to non-human entities, such as objects or animals.
- Hyperbole: An exaggeration used for emphasis or effect.
- Idiom: A phrase or expression that has a figurative meaning that is different from the literal meaning of the individual words.
- Alliteration: The repetition of initial consonant sounds in words that are close together.
- Onomatopoeia: Words that imitate the sounds they describe.
Examples and Explanations
Let’s take a closer look at each type of figurative language with examples:
- Simile: “He ran like a cheetah” (comparing a person’s running ability to that of a cheetah).
- Metaphor: “He is a lion on the battlefield” (comparing a person to a lion without using “like” or “as”).
- Personification: “The sun smiled down on us” (giving the sun human-like qualities).
- Hyperbole: “I’m so hungry I could eat a whole elephant” (exaggerating one’s hunger).
- Idiom: “It’s raining cats and dogs” (meaning “it’s raining heavily,” not literally raining cats and dogs).
- Alliteration: “She sells seashells by the seashore” (repeating the “s” sound).
- Onomatopoeia: “The firework exploded with a loud boom” (imitating the sound of the firework).
How to Identify Figurative Language
Identifying figurative language can be challenging, but here are some tips to help you:
- Look for comparisons: Similes and metaphors are used to compare two unlike things.
- Check for exaggerations: Hyperboles are used to emphasize a point or create a strong impression.
- Watch for human-like qualities: Personification is used to give non-human entities human-like qualities.
- Pay attention to word choice: Alliteration and onomatopoeia are used to create a specific sound or effect.
Using Figurative Language in Your Writing
Using figurative language in your writing can help to:
- Create vivid imagery: Figurative language can help readers to visualize and connect with your writing.
- Convey emotions and themes: Figurative language can be used to convey complex emotions and themes in a more nuanced way.
- Add depth and complexity: Figurative language can add layers of meaning to your writing, making it more engaging and interesting.
💡 Note: Figurative language is not just limited to literature and poetry. It is also used in everyday language to add flavor and interest to our communication.
Common Figurative Language Mistakes
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using figurative language:
- Overusing figurative language: Using too much figurative language can make your writing seem forced or artificial.
- Using clichés: Avoid using overused and common figurative language expressions, such as “it’s raining cats and dogs.”
- Confusing literal and figurative language: Make sure to use figurative language correctly and avoid confusing it with literal language.
Conclusion
Figurative language is a powerful tool in literature and poetry, used to convey emotions, ideas, and themes in a more vivid and engaging way. By understanding the different types of figurative language and how to use them effectively, you can add depth, complexity, and interest to your writing.
What is the difference between a simile and a metaphor?
+A simile uses “like” or “as” to compare two unlike things, while a metaphor does not use “like” or “as” and states that one thing is another thing.
How do I identify personification in a text?
+Look for instances where human-like qualities are attributed to non-human entities, such as objects or animals.
Can I use figurative language in everyday conversation?
+Yes, figurative language is often used in everyday conversation to add flavor and interest to our communication.
Related Terms:
- Figurative language Worksheet PDF
- Figurative language worksheets
- Figurative Language Worksheet 5
- Figurative Language Worksheet 9