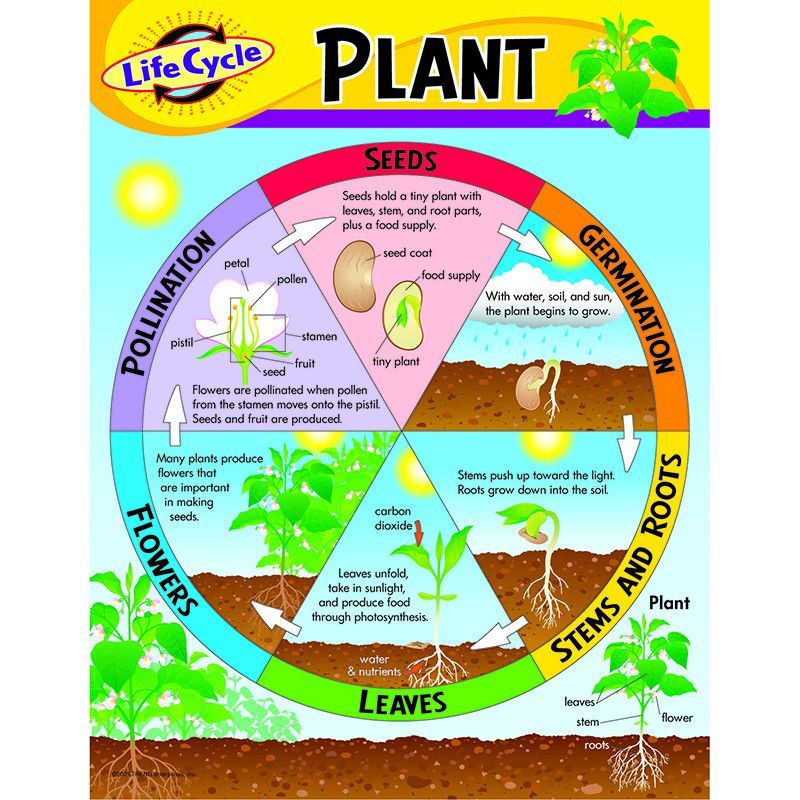
Energy Diagram Worksheet Answers for Easy Learning
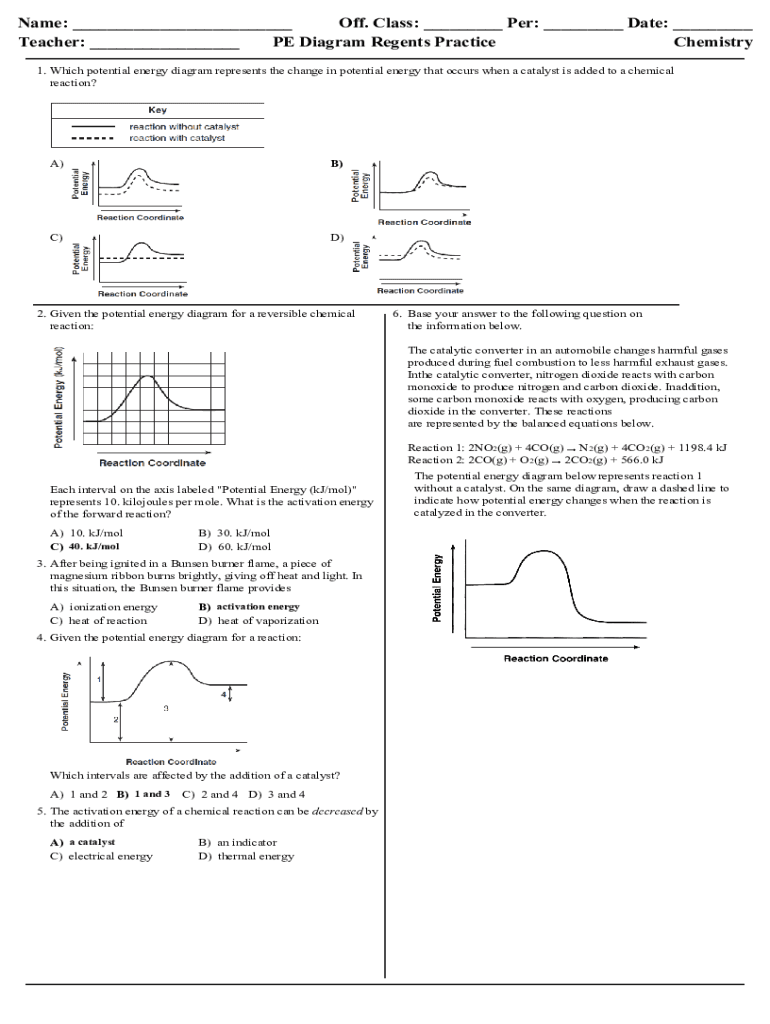
Understanding Energy Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide
Energy diagrams are graphical representations of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction or process. These diagrams are a crucial tool for chemists and students alike, as they provide a visual representation of the energy transformations that take place. In this article, we will delve into the world of energy diagrams, exploring their different types, components, and applications. We will also provide a worksheet with answers to help reinforce your understanding of energy diagrams.
Types of Energy Diagrams
There are several types of energy diagrams, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of energy diagrams include:
- Potential Energy Diagrams: These diagrams show the potential energy of a system as a function of the reaction coordinate.
- Kinetic Energy Diagrams: These diagrams show the kinetic energy of a system as a function of the reaction coordinate.
- Thermodynamic Energy Diagrams: These diagrams show the thermodynamic energy of a system, including the internal energy, enthalpy, and Gibbs free energy.
Components of Energy Diagrams
Energy diagrams typically consist of several key components, including:
- Reaction Coordinate: This is the x-axis of the diagram, which represents the progress of the reaction.
- Energy Axis: This is the y-axis of the diagram, which represents the energy of the system.
- Reactants: These are the starting materials of the reaction, represented by a horizontal line on the diagram.
- Products: These are the resulting materials of the reaction, represented by a horizontal line on the diagram.
- Transition State: This is the highest energy point on the diagram, representing the most unstable state of the system.
Interpreting Energy Diagrams
Energy diagrams provide a wealth of information about the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. By analyzing an energy diagram, you can determine:
- Energy Changes: The energy changes that occur during the reaction, including the activation energy and the overall energy change.
- Reaction Mechanism: The step-by-step process by which the reaction occurs, including the formation of intermediates and transition states.
- Reaction Rate: The rate at which the reaction occurs, including the effects of catalysts and inhibitors.
Worksheet: Energy Diagrams
The following worksheet provides a series of questions and answers to help reinforce your understanding of energy diagrams.

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the reaction coordinate on an energy diagram? | The reaction coordinate is the x-axis of the diagram, which represents the progress of the reaction. |
| What is the energy axis on an energy diagram? | The energy axis is the y-axis of the diagram, which represents the energy of the system. |
| What is the transition state on an energy diagram? | The transition state is the highest energy point on the diagram, representing the most unstable state of the system. |
| How can you determine the energy changes that occur during a reaction from an energy diagram? | You can determine the energy changes by analyzing the diagram and identifying the energy differences between the reactants, products, and transition state. |
| What is the purpose of a catalyst in a chemical reaction? | A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation energy. |
📝 Note: The answers provided in this worksheet are for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect the actual answers to specific questions.
By working through this worksheet, you should gain a better understanding of energy diagrams and how to interpret them. Remember to analyze the diagram carefully and identify the key components, including the reaction coordinate, energy axis, reactants, products, and transition state.
In conclusion, energy diagrams are a powerful tool for understanding chemical reactions and processes. By mastering the concepts and components of energy diagrams, you can gain a deeper understanding of the energy changes that occur during a reaction and make more informed decisions about the design and optimization of chemical processes.
What is the purpose of an energy diagram?
+An energy diagram is a graphical representation of the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction or process. Its purpose is to provide a visual representation of the energy transformations that take place, allowing chemists and students to analyze and understand the reaction mechanism.
What is the difference between a potential energy diagram and a kinetic energy diagram?
+A potential energy diagram shows the potential energy of a system as a function of the reaction coordinate, while a kinetic energy diagram shows the kinetic energy of a system as a function of the reaction coordinate.
How can I determine the activation energy from an energy diagram?
+The activation energy is the energy difference between the reactants and the transition state. You can determine the activation energy by analyzing the diagram and identifying the energy difference between these two points.
Related Terms:
- Energy diagrams ws
- Potential energy diagram worksheet doc
- Chemical reactions and energy worksheet
- Enzyme activation energy worksheet
- Potential energy diagram pdf