3 Ways to Identify Elements Compounds or Mixtures
Understanding the Basics: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
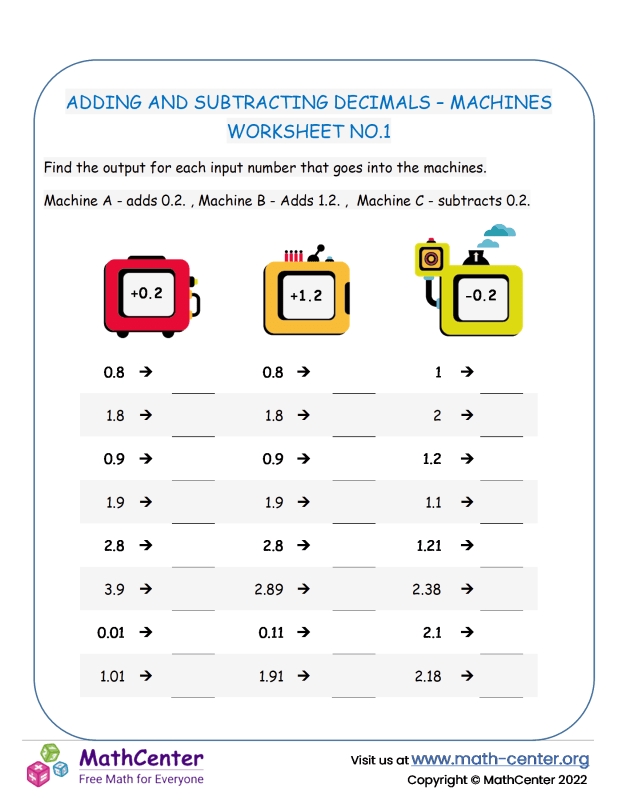
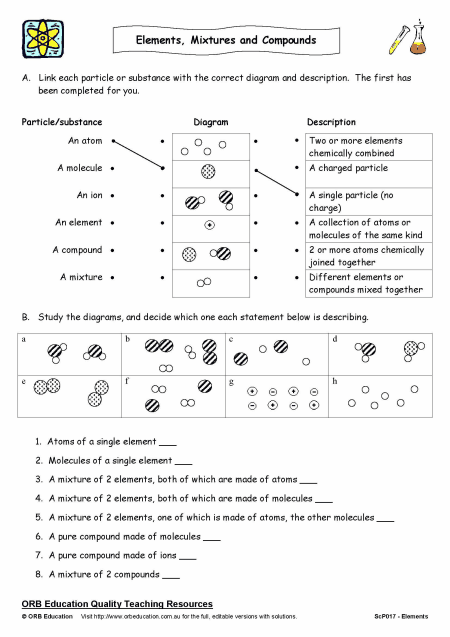
In chemistry, matter can be classified into three main categories: elements, compounds, and mixtures. Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom, while compounds are formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. Mixtures, on the other hand, are physical combinations of two or more substances, where the components are not chemically bonded. Identifying whether a substance is an element, compound, or mixture is crucial in various scientific and industrial applications.
Method 1: Analyzing Chemical Composition
One way to identify elements, compounds, or mixtures is by analyzing their chemical composition. This involves determining the types and proportions of atoms present in the substance.
- Elements: Have a fixed composition, consisting of only one type of atom. For example, oxygen (O2) is a molecule composed of two oxygen atoms.
- Compounds: Have a fixed composition, consisting of two or more different elements chemically bonded together. For example, water (H2O) is a compound composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Mixtures: Have a variable composition, consisting of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. For example, air is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2).
🔍 Note: Analyzing chemical composition can be done using various techniques, such as spectroscopy or chromatography.
Method 2: Observing Physical Properties
Another way to identify elements, compounds, or mixtures is by observing their physical properties, such as appearance, smell, and melting point.
- Elements: Typically have distinct physical properties, such as a characteristic color or smell. For example, sulfur (S) has a yellow color and a distinctive odor.
- Compounds: May exhibit different physical properties than their individual component elements. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl, or table salt) is a white crystalline solid, whereas its component elements, sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl2), are a soft, silvery metal and a yellowish-green gas, respectively.
- Mixtures: May exhibit a range of physical properties, depending on the composition of the mixture. For example, a mixture of sand and water may appear as a cloudy liquid or a wet solid, depending on the proportions of the components.
Method 3: Conducting Chemical Tests
Conducting chemical tests is another way to identify elements, compounds, or mixtures. This involves reacting the substance with other chemicals to observe the resulting reactions.
- Elements: Typically react with other elements to form compounds. For example, sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl2) to form sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Compounds: May react with other compounds or elements to form new compounds. For example, water (H2O) reacts with sodium (Na) to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Mixtures: May react with other chemicals to produce a range of reactions, depending on the composition of the mixture. For example, a mixture of copper oxide (CuO) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) may produce a range of reactions, including the formation of copper sulfate (CuSO4).
| Method | Elements | Compounds | Mixtures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzing Chemical Composition | Fixed composition, one type of atom | Fixed composition, two or more elements | Variable composition, two or more substances |
| Observing Physical Properties | Distinct physical properties | Physical properties different from component elements | Physical properties depend on composition |
| Conducting Chemical Tests | React with other elements to form compounds | React with other compounds or elements to form new compounds | React with other chemicals to produce a range of reactions |
In conclusion, identifying elements, compounds, or mixtures requires a combination of analytical techniques, including analyzing chemical composition, observing physical properties, and conducting chemical tests. By applying these methods, scientists and researchers can accurately classify substances and gain a deeper understanding of their properties and behavior.
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
+An element is a pure substance consisting of only one type of atom, whereas a compound is a substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together.
How can I determine if a substance is a mixture?
+A mixture can be identified by its variable composition and physical properties, which depend on the proportions of the component substances. Conducting chemical tests can also help determine if a substance is a mixture.
What is the importance of identifying elements, compounds, and mixtures?
+Accurately identifying elements, compounds, and mixtures is crucial in various scientific and industrial applications, such as materials science, pharmaceuticals, and environmental monitoring.