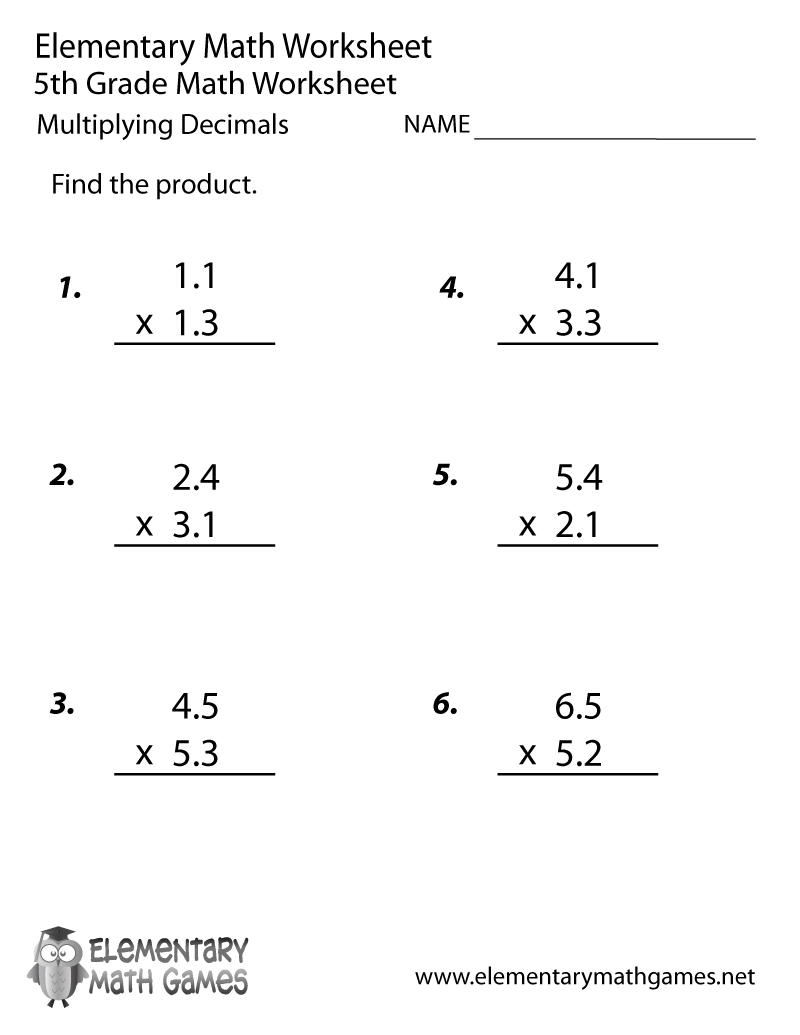
6 Essential Elements of Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet

Understanding Compounds and Mixtures: A Comprehensive Guide
Compounds and mixtures are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that are often confused with one another. While they may seem similar, they have distinct properties and characteristics that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the world of compounds and mixtures, exploring their definitions, types, and key differences.
What are Compounds?
A compound is a substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together. This bond can be ionic, covalent, or metallic, and it results in the creation of a new substance with properties distinct from those of its individual elements. Compounds can be composed of atoms of the same element, such as oxygen (O2), or atoms of different elements, such as water (H2O).
🔍 Note: Compounds have a fixed ratio of elements, and their composition cannot be altered by physical means.
Types of Compounds
There are several types of compounds, including:
- Molecular compounds: These compounds are composed of molecules, which are groups of atoms bonded together. Examples include water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Ionic compounds: These compounds are composed of ions, which are atoms or groups of atoms that have gained or lost electrons. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- Metallic compounds: These compounds are composed of metals and nonmetals, and they exhibit properties of both. Examples include brass (CuZn) and bronze (CuSn).
What are Mixtures?
A mixture is a physical blend of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together. Mixtures can be composed of elements, compounds, or a combination of both. Unlike compounds, mixtures do not have a fixed ratio of components, and their composition can be altered by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.
🔍 Note: Mixtures have a variable composition, and their properties are determined by the properties of their individual components.
Types of Mixtures
There are several types of mixtures, including:
- Homogeneous mixtures: These mixtures have a uniform composition and properties throughout. Examples include air and solutions.
- Heterogeneous mixtures: These mixtures have a non-uniform composition and properties. Examples include suspensions and colloids.
Key Differences between Compounds and Mixtures
The following table highlights the key differences between compounds and mixtures:
| Property | Compounds | Mixtures |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fixed ratio of elements | Variable composition |
| Chemical Bonding | Chemically bonded | Not chemically bonded |
| Properties | Properties distinct from individual elements | Properties determined by individual components |
Conclusion
In conclusion, compounds and mixtures are two distinct concepts in chemistry that are often confused with one another. Compounds are substances formed by the chemical bonding of two or more elements, while mixtures are physical blends of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together. Understanding the key differences between compounds and mixtures is essential for mastering chemistry and navigating the world of elements and substances.
What is the difference between a compound and a mixture?
+A compound is a substance formed by the chemical bonding of two or more elements, while a mixture is a physical blend of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded together.
Can a compound be broken down into its individual elements?
+No, a compound cannot be broken down into its individual elements by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.
What is the difference between a homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture?
+A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition and properties throughout, while a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition and properties.
Related Terms:
- Element compound and mixture
- Quiz element compound mixture