Electron Configuration Worksheet Answers
Understanding Electron Configuration
Electron configuration is a way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, and is used to understand the behavior of atoms and molecules. In this worksheet, we will explore the basics of electron configuration and provide answers to common problems.
Electron Configuration Basics
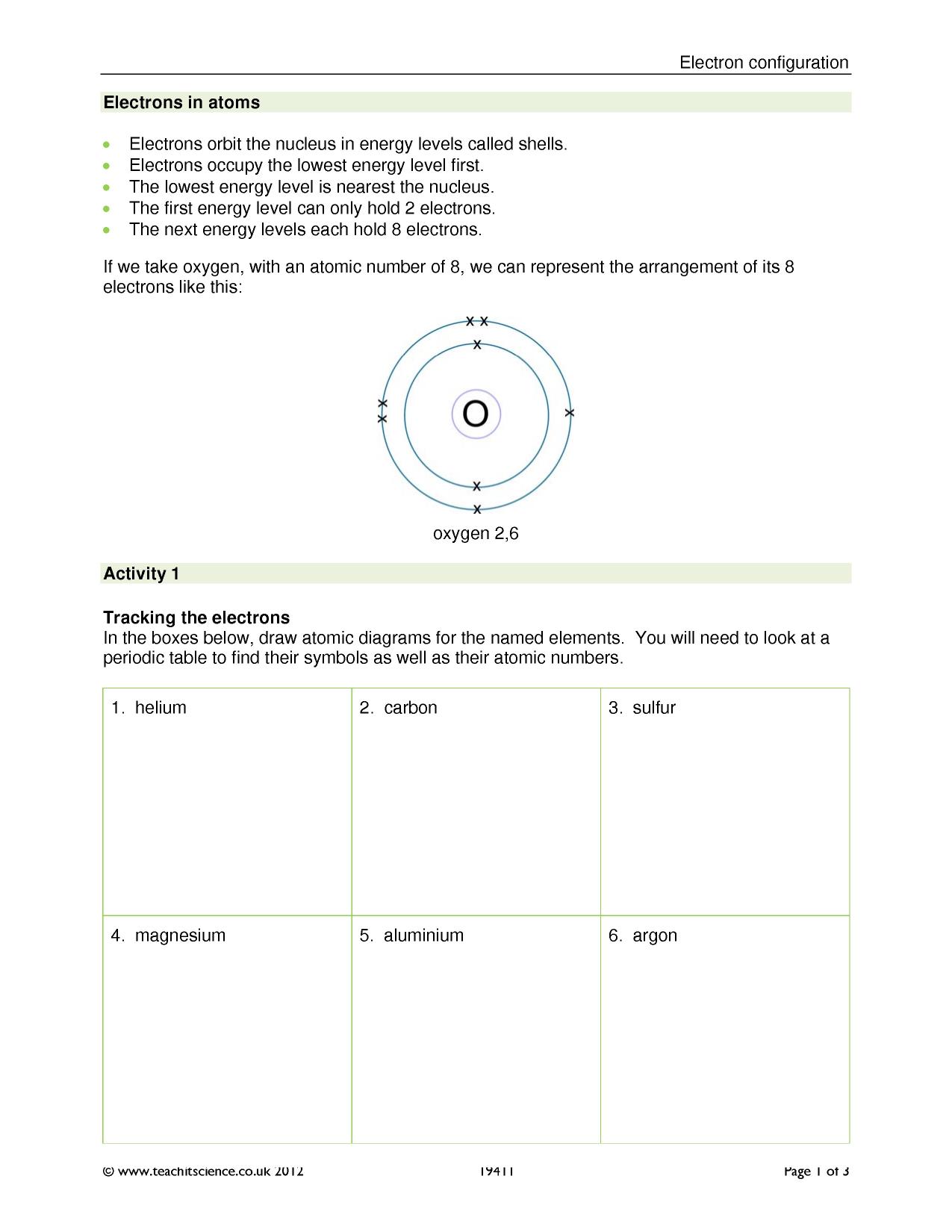
Electron configuration is based on the idea that electrons occupy specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus of an atom. Each shell has a limited capacity, and electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first. The most common way to write electron configuration is using the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle.
Aufbau Principle: Electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.
Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposite spins.
Electron Configuration Notation
Electron configuration notation is a shorthand way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It consists of a series of numbers and letters that indicate the energy level and orbital type.
Example: The electron configuration of sodium (Na) is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹.
- 1s² indicates that the first energy level has two electrons in the s-orbital.
- 2s² indicates that the second energy level has two electrons in the s-orbital.
- 2p⁶ indicates that the second energy level has six electrons in the p-orbitals.
- 3s¹ indicates that the third energy level has one electron in the s-orbital.
Electron Configuration Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to common electron configuration problems:
Problem 1: Write the electron configuration of carbon ©.
Answer: 1s² 2s² 2p²
Problem 2: Write the electron configuration of oxygen (O).
Answer: 1s² 2s² 2p⁴
Problem 3: Write the electron configuration of neon (Ne).
Answer: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶
Problem 4: Write the electron configuration of sodium (Na).
Answer: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹
Problem 5: Write the electron configuration of magnesium (Mg).
Answer: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s²
🔍 Note: Electron configuration notation can be written in different ways, but the above answers are the most common and accepted notation.
Electron Configuration Exceptions
There are some exceptions to the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. These exceptions occur when the energy levels are close together, and the electrons can jump to a higher energy level to fill a particular orbital.
Example: The electron configuration of chromium (Cr) is [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹, not [Ar] 3d⁴ 4s². This is because the 3d and 4s energy levels are close together, and the electrons jump to the 3d orbital to fill it.
🔍 Note: Electron configuration exceptions are rare, but it's essential to understand them to write the correct electron configuration.
Conclusion
Electron configuration is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. Understanding the basics of electron configuration, including the Aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion principle, and electron configuration notation, is crucial for writing the correct electron configuration of atoms. By practicing and solving electron configuration problems, you can master this concept and apply it to more complex chemistry topics.
What is electron configuration?
+Electron configuration is a way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
+The Pauli exclusion principle states that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposite spins.