5 Steps to Master Electron Configuration Practice
Unlocking the Secrets of Electron Configuration: A 5-Step Guide
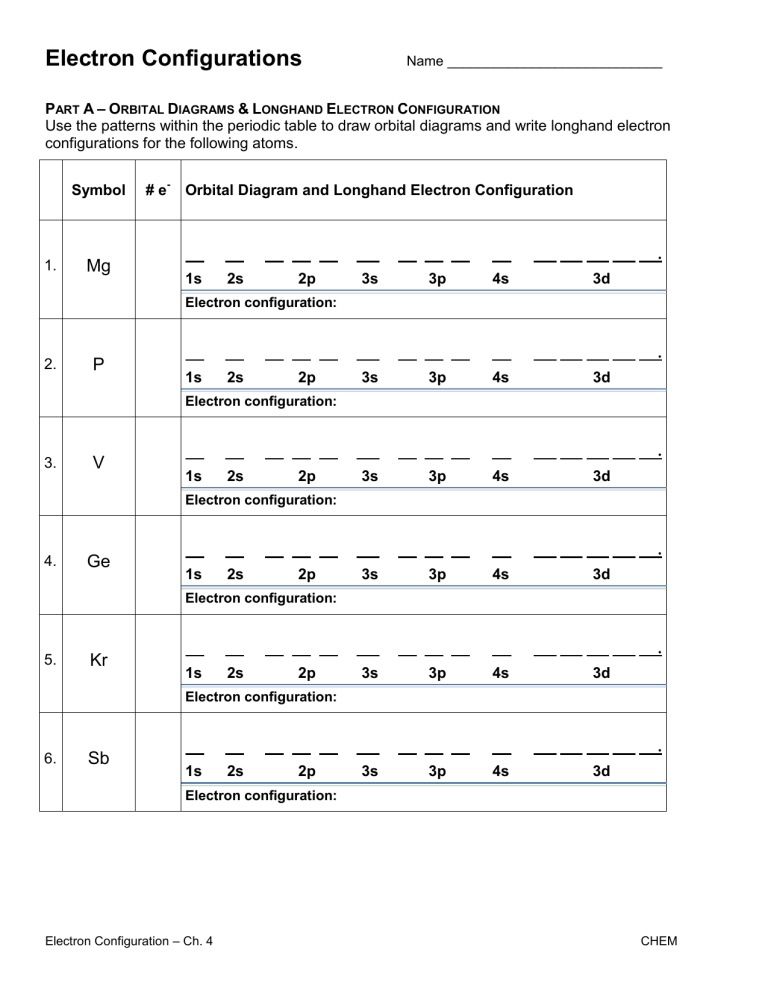
Electron configuration is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the arrangement of electrons within an atom. Mastering electron configuration is crucial for understanding various chemical properties and phenomena. However, it can be a daunting task for many students. In this article, we will break down the process into 5 manageable steps to help you practice and master electron configuration.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of electron configuration, it’s essential to grasp the basic principles. Here are a few key concepts to keep in mind:
- Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the element’s identity.
- Electron shells: Energy levels or orbitals that electrons occupy around the nucleus.
- Electron subshells: Smaller energy levels within a shell, denoted by the letters s, p, d, and f.
- Orbital: A region around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found.
🔍 Note: Familiarize yourself with the periodic table to understand the relationships between elements and their atomic numbers.
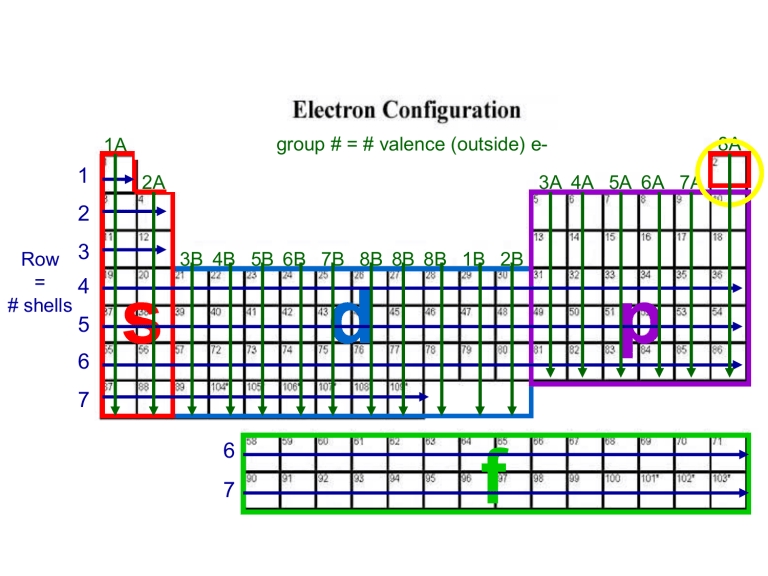
Step 2: Learning the Aufbau Principle
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first. This principle is crucial for understanding how electrons are arranged in an atom. Here’s a simplified outline of the Aufbau principle:
- First, fill the 1s orbital: The lowest energy level, which can hold up to 2 electrons.
- Next, fill the 2s and 2p orbitals: The second energy level, which can hold up to 8 electrons.
- Continue filling orbitals in order: 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, and so on.
📝 Note: Use a diagram or a periodic table to visualize the orbital filling process.
Step 3: Understanding Hund's Rule and the Pauli Exclusion Principle
Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle are essential for determining the correct electron configuration. Here’s a brief summary:
- Hund’s rule: Electrons occupy empty orbitals of the same energy level before pairing up in an already occupied orbital.
- Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers, which describe the energy, shape, and orientation of an orbital.
💡 Note: Use a diagram to illustrate the application of Hund's rule and the Pauli exclusion principle.
Step 4: Writing Electron Configurations
Now that you’ve mastered the basics and understand the key principles, it’s time to practice writing electron configurations. Here are some tips:
- Start with the atomic number: Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
- Fill the orbitals in order: Apply the Aufbau principle and fill the orbitals in the correct order.
- Use the correct notation: Write the electron configuration using the standard notation, such as 1s² 2s² 2p⁶.
📝 Note: Practice writing electron configurations for different elements to reinforce your understanding.
Step 5: Checking Your Work
Finally, it’s essential to check your work to ensure accuracy. Here are some tips:
- Verify the number of electrons: Make sure the total number of electrons matches the atomic number.
- Check the orbital order: Ensure that the orbitals are filled in the correct order.
- Use online resources: Utilize online tools or apps to check your electron configurations and provide feedback.
| Element | Atomic Number | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1s¹ |
| Helium | 2 | 1s² |
| Lithium | 3 | 1s² 2s¹ |
By following these 5 steps, you’ll be well on your way to mastering electron configuration. Remember to practice regularly and use online resources to check your work. With time and effort, you’ll become proficient in writing electron configurations and gain a deeper understanding of the atomic structure.
In summary, mastering electron configuration requires a combination of understanding the basics, learning the Aufbau principle, applying Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle, writing electron configurations, and checking your work. By following these steps and practicing regularly, you’ll become proficient in electron configuration and enhance your understanding of chemistry.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first.
What is Hund’s rule?
+Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy empty orbitals of the same energy level before pairing up in an already occupied orbital.
How do I write an electron configuration?
+Start with the atomic number, fill the orbitals in order, and use the correct notation.



