6 Ways to Master the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Unlocking the Secrets of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
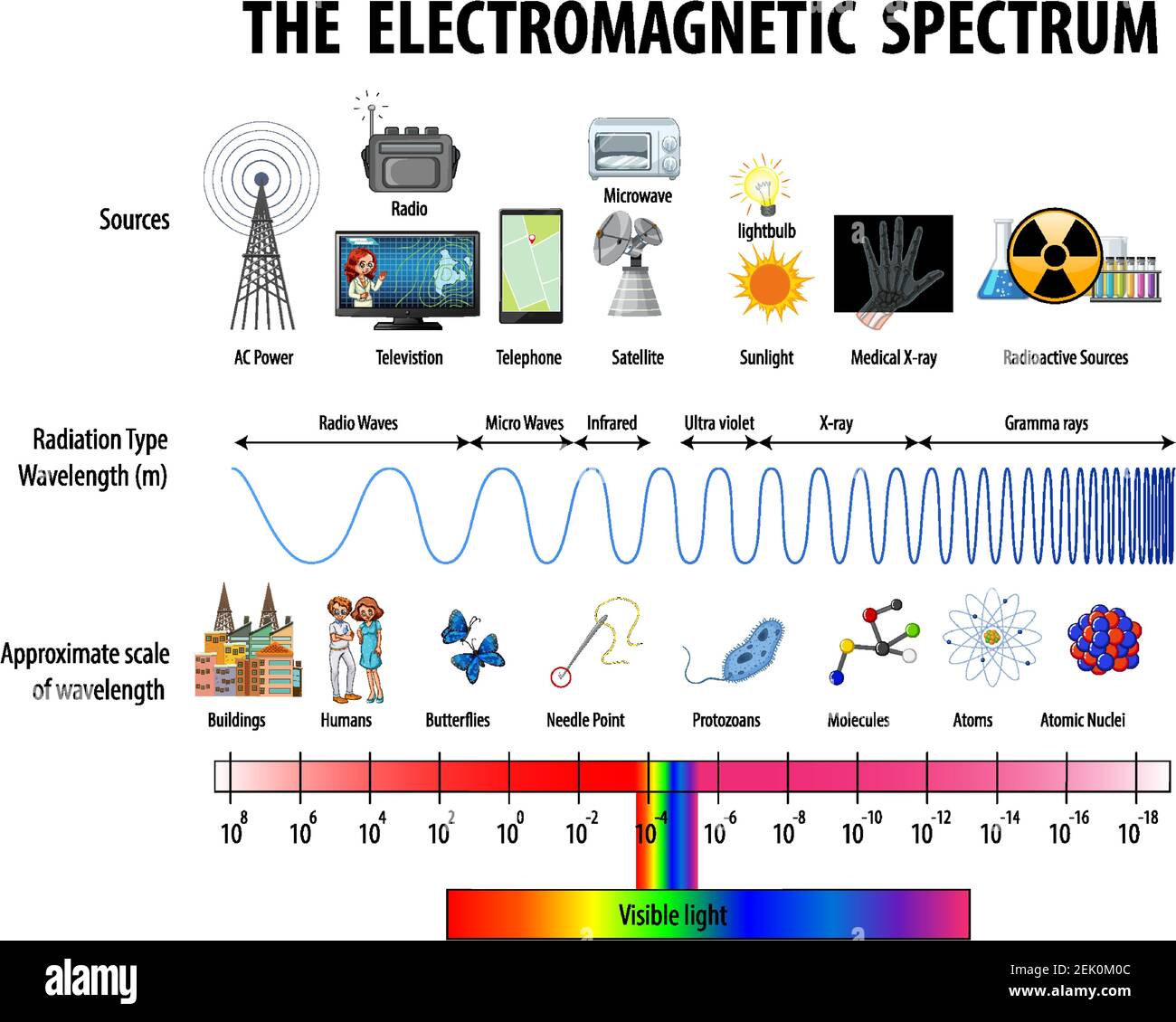
The electromagnetic spectrum is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. From the shortest wavelengths of gamma rays to the longest wavelengths of radio waves, the electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and fascinating field of study. Mastering the electromagnetic spectrum can seem daunting, but with the right approach, anyone can gain a deeper understanding of this complex topic. In this article, we will explore six ways to master the electromagnetic spectrum and unlock its secrets.
1. Understand the Basics of Electromagnetic Radiation
Before diving into the electromagnetic spectrum, it’s essential to understand the basics of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is produced by the vibration of charged particles, such as electrons. This energy can be described in terms of its frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. Frequency refers to the number of oscillations or cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz). Wavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a wave, measured in meters (m). Amplitude refers to the height of the wave, measured in meters (m).
To master the electromagnetic spectrum, it’s crucial to understand the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. This can be achieved by studying the electromagnetic wave equation, which describes how these properties are related.
2. Learn the Order of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is typically divided into several regions, each with its own unique characteristics. The order of the electromagnetic spectrum, from shortest wavelength to longest, is:
- Gamma rays
- X-rays
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation
- Visible light
- Infrared (IR) radiation
- Microwave radiation
- Radio waves
Memorizing the order of the electromagnetic spectrum is a great way to start mastering this topic. You can use mnemonic devices, such as “Gamma X-rays Ultra Violet Visible Infra Red Microwaves Radio,” to help you remember the order.
3. Study the Properties of Each Region
Each region of the electromagnetic spectrum has its own unique properties and applications. For example:
- Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies, making them useful for medical imaging and cancer treatment.
- X-rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light, making them useful for medical imaging and materials analysis.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation has shorter wavelengths than visible light, making it useful for disinfection and sterilization.
- Visible light is the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye, with wavelengths between approximately 400-700 nanometers (nm).
- Infrared (IR) radiation has longer wavelengths than visible light, making it useful for heating and thermal imaging.
- Microwave radiation has longer wavelengths than IR radiation, making it useful for cooking and wireless communication.
- Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, making them useful for broadcasting and wireless communication.
Studying the properties of each region will help you understand how the electromagnetic spectrum is used in various applications.
4. Use Visual Aids and Diagrams
Visual aids and diagrams can be incredibly helpful when trying to master the electromagnetic spectrum. Creating a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum can help you visualize the relationships between frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. You can also use graphs and charts to illustrate the properties of each region.
For example, a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum might show the following:
| Region | Frequency (Hz) | Wavelength (m) | Amplitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma rays | 10^20 - 10^22 Hz | 10^-12 - 10^-10 m | 10^-5 - 10^-3 m |
| X-rays | 10^17 - 10^20 Hz | 10^-11 - 10^-9 m | 10^-4 - 10^-2 m |
| Ultraviolet (UV) radiation | 10^15 - 10^17 Hz | 10^-8 - 10^-6 m | 10^-3 - 10^-1 m |
| Visible light | 4 x 10^14 - 8 x 10^14 Hz | 4 x 10^-7 - 8 x 10^-7 m | 10^-2 - 10^0 m |
| Infrared (IR) radiation | 10^12 - 4 x 10^14 Hz | 10^-4 - 10^-3 m | 10^-1 - 10^1 m |
| Microwave radiation | 3 x 10^9 - 10^12 Hz | 10^-2 - 10^-1 m | 10^0 - 10^1 m |
| Radio waves | 3 x 10^6 - 3 x 10^9 Hz | 10^1 - 10^4 m | 10^1 - 10^4 m |
5. Practice with Examples and Applications
Practicing with examples and applications is a great way to reinforce your understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum. Try solving problems that involve calculating frequency, wavelength, or amplitude. You can also research real-world applications of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as medical imaging, wireless communication, or solar energy.
For example, you might calculate the wavelength of a gamma ray with a frequency of 10^20 Hz:
λ = c / f λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (10^20 Hz) λ = 3 x 10^-12 m
Or, you might research the use of X-rays in medical imaging and how they are used to produce images of the body’s internal structures.
6. Review and Refine Your Understanding
Finally, review and refine your understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum regularly. Try to summarize key concepts in your own words, and ask yourself questions to test your understanding. You can also seek out additional resources, such as online tutorials or textbooks, to supplement your learning.
By following these six steps, you can master the electromagnetic spectrum and unlock its secrets. Remember to review and refine your understanding regularly, and don’t be afraid to ask for help or seek out additional resources when needed.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
+The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, from the shortest wavelengths of gamma rays to the longest wavelengths of radio waves.
What is the order of the electromagnetic spectrum?
+The order of the electromagnetic spectrum, from shortest wavelength to longest, is: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, visible light, infrared (IR) radiation, microwave radiation, and radio waves.
What are some applications of the electromagnetic spectrum?
+Some applications of the electromagnetic spectrum include medical imaging, wireless communication, solar energy, and thermal imaging.
Related Terms:
- Introduction to electromagnetic spectrum Worksheet
- Electromagnetic spectrum PDF