Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding Ecological Energy Pyramids
The concept of ecological energy pyramids is crucial in understanding the flow of energy within an ecosystem. It illustrates how energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, highlighting the inefficiencies in this process. This concept is vital for students of ecology, environmental science, and biology.
What is an Energy Pyramid?
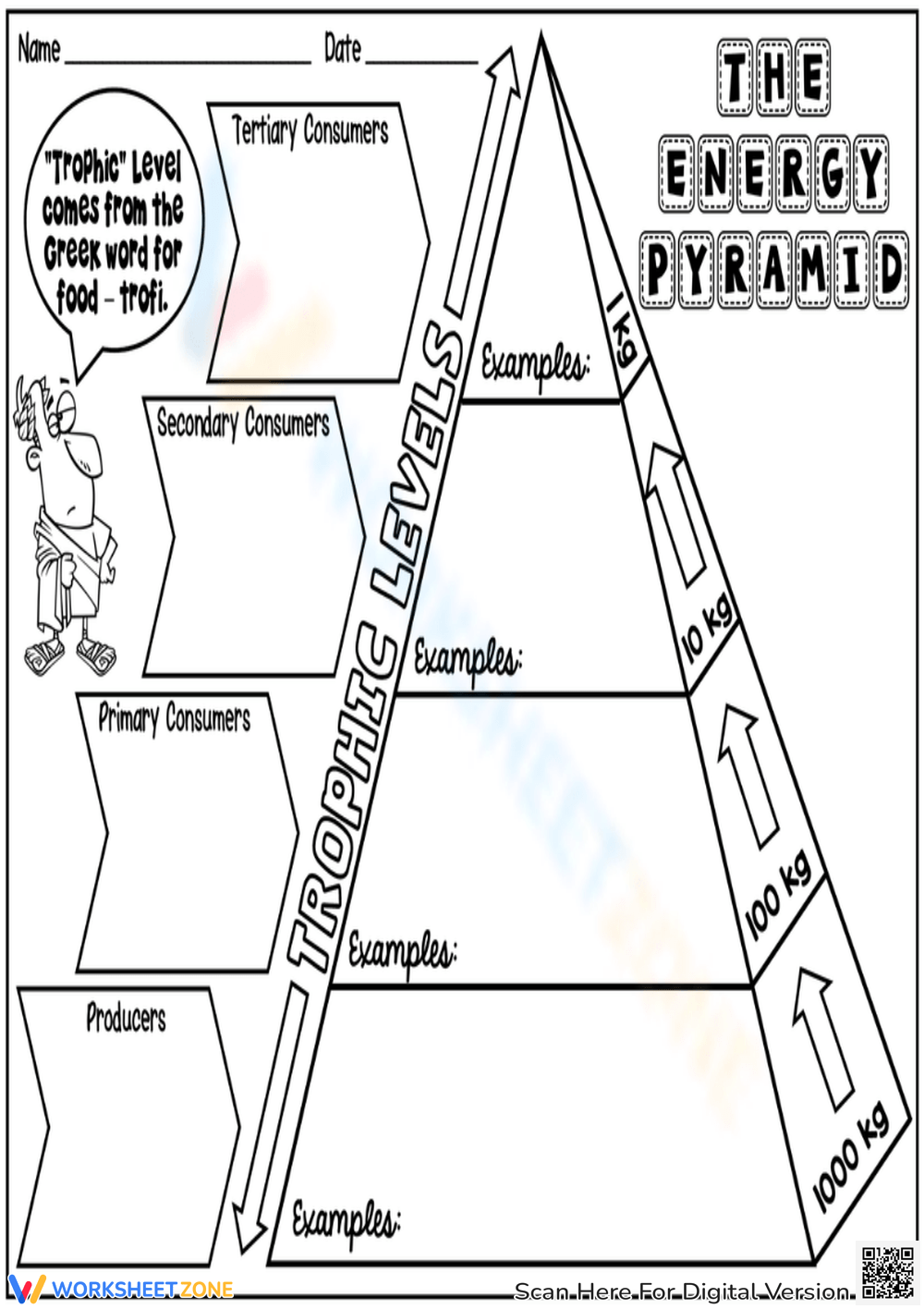
An energy pyramid, also known as a trophic pyramid or energy tower, is a graphical representation of the energy flow through the different trophic levels of an ecosystem. The pyramid is widest at the base, representing the primary producers (plants and other photosynthetic organisms), and narrowest at the top, representing the apex predators.
Key Components of an Energy Pyramid
An energy pyramid consists of the following components:
- Primary Producers (Autotrophs): These are the organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria.
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These are the organisms that consume the primary producers, such as insects, zooplankton, and herbivorous fish.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores): These are the organisms that consume the primary consumers, such as small fish, frogs, and other carnivorous animals.
- Tertiary Consumers (Apex Predators): These are the organisms that consume the secondary consumers, such as large fish, birds of prey, and other apex predators.
Energy Flow through the Pyramid
Energy flows through the pyramid as follows:
- Primary Producers: Absorb sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers: Feed on primary producers, transferring energy from one trophic level to the next.
- Secondary Consumers: Feed on primary consumers, further transferring energy up the pyramid.
- Tertiary Consumers: Feed on secondary consumers, representing the final transfer of energy in the pyramid.
Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key
Here is a sample worksheet with answers:
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the primary source of energy for an ecosystem? a) Sunlight b) Decomposers c) Primary consumers d) Secondary consumers
Answer: a) Sunlight
- Which trophic level represents the apex predators? a) Primary producers b) Primary consumers c) Secondary consumers d) Tertiary consumers
Answer: d) Tertiary consumers
- What is the main function of primary producers in an ecosystem? a) To consume primary consumers b) To produce chemical energy through photosynthesis c) To decompose organic matter d) To regulate the water cycle
Answer: b) To produce chemical energy through photosynthesis
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the main difference between a primary consumer and a secondary consumer.
Answer: A primary consumer is an organism that directly feeds on primary producers, whereas a secondary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary consumers.
- What is the energy conversion efficiency from one trophic level to the next?
Answer: The energy conversion efficiency is typically around 10%, meaning that only 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, while the remaining 90% is lost as heat or waste.
Section 3: Essay Questions
- Explain the concept of an ecological energy pyramid and its significance in understanding ecosystem dynamics.
Answer: An ecological energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the energy flow through the different trophic levels of an ecosystem. It illustrates how energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, highlighting the inefficiencies in this process. This concept is significant in understanding ecosystem dynamics, as it helps us understand how energy is allocated and how it affects the structure and function of an ecosystem.
- Describe the main components of an energy pyramid and their roles in the ecosystem.
Answer: The main components of an energy pyramid are primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. Primary producers produce their own food through photosynthesis, primary consumers feed on primary producers, secondary consumers feed on primary consumers, and tertiary consumers feed on secondary consumers. Each component plays a crucial role in the ecosystem, and their interactions shape the structure and function of the ecosystem.
📝 Note: The energy pyramid is a simplified representation of the complex energy flow through an ecosystem. In reality, there are many more trophic levels and interactions between organisms.
What is the main advantage of using an energy pyramid in ecology?
+The main advantage of using an energy pyramid in ecology is that it provides a simple and visual representation of the energy flow through an ecosystem, helping to understand the relationships between different trophic levels.
What is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems?
+The primary source of energy for most ecosystems is sunlight, which is absorbed by primary producers through photosynthesis.
What is the energy conversion efficiency from one trophic level to the next?
+The energy conversion efficiency from one trophic level to the next is typically around 10%, meaning that only 10% of the energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, while the remaining 90% is lost as heat or waste.
In conclusion, the ecological energy pyramid is a fundamental concept in understanding ecosystem dynamics. By visualizing the energy flow through the different trophic levels, we can better comprehend the relationships between organisms and how energy is allocated within an ecosystem.
Related Terms:
- Ecological pyramid Worksheet answer key
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet pdf
- Ecological pyramids POGIL
- Ecological pyramids PDF