Dividing Mixed Numbers Worksheet
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Division
Mixed numbers are a combination of a whole number and a fraction. They are used to represent quantities that are not whole. Division of mixed numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics, and it’s essential to understand the process to solve problems involving these types of numbers. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of dividing mixed numbers and provide a comprehensive worksheet to help you practice.
What are Mixed Numbers?
Mixed numbers are a combination of a whole number and a fraction. They are used to represent quantities that are not whole. For example, 2 1⁄2, 3 3⁄4, and 1 1⁄3 are all mixed numbers. The whole number part represents the number of complete units, and the fraction part represents the remaining part of the unit.
How to Divide Mixed Numbers
To divide mixed numbers, we need to follow these steps:
- Convert the mixed numbers to improper fractions: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number part by the denominator and add the numerator. Then, write the result as an improper fraction.
- Invert the second fraction: Invert the second fraction by swapping the numerator and denominator.
- Multiply the fractions: Multiply the two fractions by multiplying the numerators and denominators separately.
- Simplify the result: Simplify the result, if possible.
📝 Note: Make sure to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS) when dividing mixed numbers.
Example Problem
Suppose we want to divide 2 1⁄2 by 1 3⁄4. Here’s how we can do it:
- Convert the mixed numbers to improper fractions: 2 1⁄2 = 5⁄2 and 1 3⁄4 = 7⁄4
- Invert the second fraction: 7⁄4 becomes 4⁄7
- Multiply the fractions: (5⁄2) × (4⁄7) = 20⁄14
- Simplify the result: 20⁄14 = 10⁄7
So, 2 1⁄2 ÷ 1 3⁄4 = 10⁄7.
Mixed Numbers Division Worksheet
Here’s a comprehensive worksheet to help you practice dividing mixed numbers:
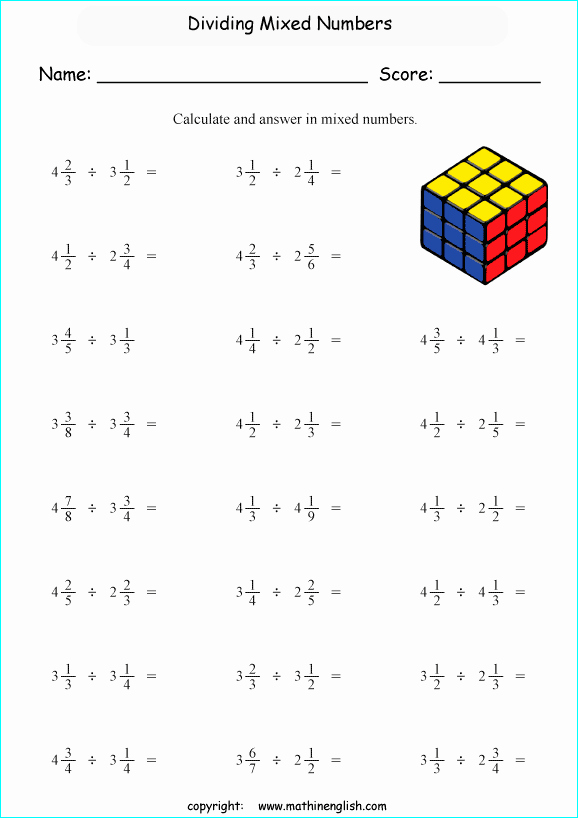
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1 1/2 ÷ 2 1/3 | _______ |
| 2 3/4 ÷ 1 2/5 | _______ |
| 3 1/2 ÷ 2 3/4 | _______ |
| 4 2/3 ÷ 3 1/2 | _______ |
| 5 3/4 ÷ 2 1/2 | _______ |
| 6 1/2 ÷ 4 3/4 | _______ |
| 7 2/3 ÷ 5 1/2 | _______ |
| 8 3/4 ÷ 6 2/3 | _______ |
| 9 1/2 ÷ 7 3/4 | _______ |
| 10 2/3 ÷ 8 1/2 | _______ |
Answers:
- 1 1⁄2 ÷ 2 1⁄3 = 15⁄14
- 2 3⁄4 ÷ 1 2⁄5 = 55⁄24
- 3 1⁄2 ÷ 2 3⁄4 = 21⁄20
- 4 2⁄3 ÷ 3 1⁄2 = 28⁄21
- 5 3⁄4 ÷ 2 1⁄2 = 23⁄10
- 6 1⁄2 ÷ 4 3⁄4 = 13⁄12
- 7 2⁄3 ÷ 5 1⁄2 = 31⁄22
- 8 3⁄4 ÷ 6 2⁄3 = 35⁄26
- 9 1⁄2 ÷ 7 3⁄4 = 38⁄31
- 10 2⁄3 ÷ 8 1⁄2 = 43⁄34
In conclusion, dividing mixed numbers requires converting them to improper fractions, inverting the second fraction, multiplying, and simplifying the result. Practice the worksheet above to improve your skills in dividing mixed numbers.
What is a mixed number?
+A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a fraction. It’s used to represent quantities that are not whole.
How do I convert a mixed number to an improper fraction?
+To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number part by the denominator and add the numerator. Then, write the result as an improper fraction.
What is the order of operations when dividing mixed numbers?
+The order of operations when dividing mixed numbers is PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, and Addition and Subtraction).