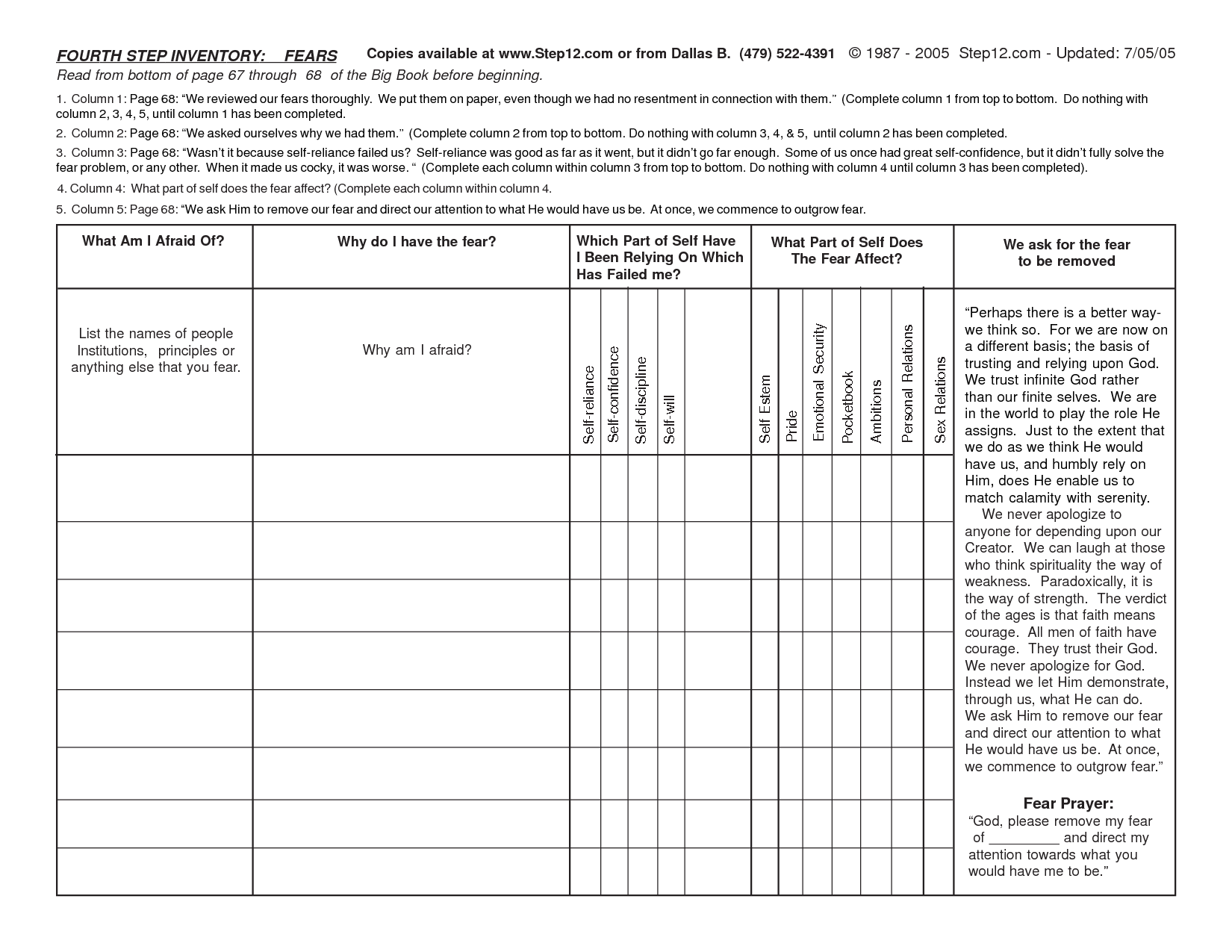
Distance and Displacement Worksheet for Physics Students

Understanding Distance and Displacement in Physics
As a physics student, you’ve probably come across the terms “distance” and “displacement” numerous times. While they may seem similar, these two concepts have distinct meanings and are crucial in understanding various physics phenomena. In this worksheet, we’ll delve into the world of distance and displacement, exploring their definitions, differences, and practical applications.
What is Distance?
Distance refers to the total length of the path traveled by an object from one point to another. It’s a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude (amount of movement) but no direction. Think of it as the total distance you’d measure with a ruler or odometer. For instance, if you travel from point A to point B and then back to point A, the total distance covered would be the sum of the distances traveled in each direction.
What is Displacement?
Displacement, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that represents the shortest distance between an object’s initial and final positions. It takes into account the direction of the movement. Displacement is measured in terms of the straight-line distance between the starting and ending points, regardless of the actual path taken. Using the same example as before, if you travel from point A to point B and then back to point A, the displacement would be zero, as you end up at the same point where you started.
Key Differences Between Distance and Displacement
Here are the main differences between distance and displacement:
- Scalar vs. Vector: Distance is a scalar quantity, while displacement is a vector quantity.
- Path Independence: Distance depends on the path taken, whereas displacement only considers the initial and final positions.
- Direction: Distance has no direction, but displacement has both magnitude and direction.
Practical Applications of Distance and Displacement
Understanding the distinction between distance and displacement is vital in various physics contexts, such as:
- Kinematics: Describing the motion of objects in terms of distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration.
- Projectile Motion: Calculating the range, maximum height, and displacement of projectiles under the influence of gravity.
- Circular Motion: Analyzing the distance and displacement of objects moving in circular paths.
Problems and Solutions
Now, let’s put your understanding of distance and displacement to the test with some practice problems!
Problem 1 A car travels from city A to city B, covering a distance of 250 km. If it returns to city A, what is the total distance traveled?
Answer: 500 km ( Distance = 250 km + 250 km )
Problem 2 An object moves from point A to point B and then to point C. If the displacement from A to B is 10 m east and from B to C is 5 m west, what is the total displacement?
Answer: 5 m east ( Displacement = 10 m east - 5 m west )
Problem 3 A runner completes a lap around a circular track with a radius of 50 m. What is the distance traveled and the displacement?
Answer: Distance = 2πr = 2 × π × 50 m ≈ 314 m; Displacement = 0 m (since the runner ends up at the starting point)
📝 Note: Pay attention to the units of measurement when solving problems. Make sure to convert between units when necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between distance and displacement is essential for physics students. By grasping these fundamental concepts, you’ll be better equipped to tackle problems in kinematics, projectile motion, circular motion, and more. Remember to always consider the path, direction, and initial and final positions when calculating distance and displacement.
What is the main difference between distance and displacement?
+The main difference is that distance is a scalar quantity, while displacement is a vector quantity. Distance measures the total length of the path, whereas displacement measures the shortest distance between the initial and final positions.
Can displacement be negative?
+No, displacement cannot be negative. Displacement is a measure of the shortest distance between two points, and it’s always positive or zero (if the object ends up at the starting point).
How do I calculate displacement in a circular motion?
+To calculate displacement in a circular motion, you need to find the straight-line distance between the initial and final positions. If the object ends up at the starting point, the displacement is zero.