Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Made Easy
Understanding Dihybrid Cross: A Step-by-Step Guide
Dihybrid cross is a fundamental concept in genetics that helps us understand the inheritance of two genes. It’s a crucial topic for students of biology, genetics, and related fields. However, many students find it challenging to grasp, especially when it comes to solving dihybrid cross problems. In this post, we’ll break down the dihybrid cross concept and provide a step-by-step guide to make it easier to understand.
What is Dihybrid Cross?
Dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves two genes, each with two alleles. Alleles are different forms of a gene, and they can be either dominant or recessive. In a dihybrid cross, we study the inheritance of two genes, typically represented by the letters “R” and “r” for one gene, and “B” and “b” for the other gene.
Key Concepts to Understand
Before diving into the dihybrid cross worksheet, let’s review some essential concepts:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an individual, represented by letters (e.g., RR, Rr, rr).
- Phenotype: The physical appearance of an individual, resulting from the genotype (e.g., red, white).
- Dominant: An allele that will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of it.
- Recessive: An allele that will only be expressed if an individual has two copies of it.
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Steps
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move on to the step-by-step guide for solving dihybrid cross problems.
Step 1: Write the genotypes of the parents
Identify the genotypes of the two parents involved in the cross. Use the letters “R” and “r” for one gene, and “B” and “b” for the other gene.
Step 2: Determine the possible gametes
For each parent, determine the possible gametes (sperm or egg cells) they can produce. Remember, each gamete will have one allele for each gene.
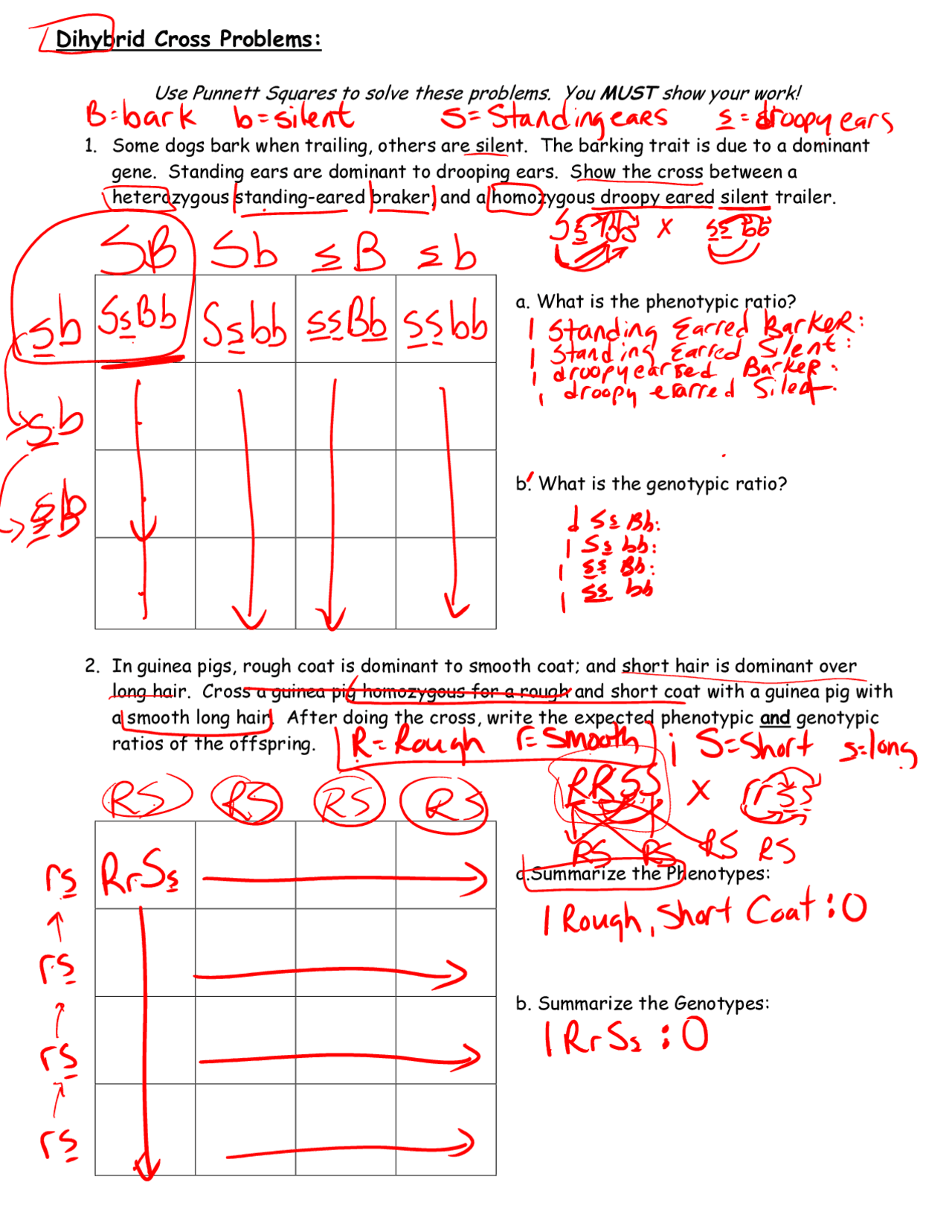
Step 3: Create a Punnett square
Draw a Punnett square, which is a table that shows all possible combinations of gametes from the two parents. The rows and columns represent the gametes from each parent.
Step 4: Fill in the Punnett square
Fill in the Punnett square with the possible genotypes of the offspring. Each box in the table represents a unique combination of alleles.
Step 5: Determine the phenotypes
Determine the phenotypes of the offspring by looking at the genotypes in the Punnett square. Remember, dominant alleles will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies.
Step 6: Calculate the probabilities
Calculate the probabilities of each phenotype by counting the number of boxes with each genotype and dividing by the total number of boxes.
📝 Note: Make sure to label each step clearly and use the correct notation (e.g., "Rr" for a heterozygous genotype).
Example Problem: Solving a Dihybrid Cross Worksheet
Let’s work through an example problem to illustrate the steps.
Suppose we want to study the inheritance of two genes: one that controls flower color (R = red, r = white) and one that controls plant height (B = tall, b = short). We have two parents: one with the genotype “RRBb” and the other with the genotype “rrBb”.
Step 1: Write the genotypes of the parents
Parent 1: RRBb Parent 2: rrBb
Step 2: Determine the possible gametes
Parent 1: RB, Rb, rB, rb Parent 2: rB, rb
Step 3: Create a Punnett square

| rB | rb | |
|---|---|---|
| RB | RrBb | Rrb |
| Rb | RrBb | Rrb |
| rB | rrBb | rrB |
| rb | rrBb | rrb |
Step 4: Fill in the Punnett square
| rB | rb | |
|---|---|---|
| RB | RrBb | Rrb |
| Rb | RrBb | Rrb |
| rB | rrBb | rrB |
| rb | rrBb | rrb |
Step 5: Determine the phenotypes
Phenotypes: Red, tall (RrBb) Red, short (Rrb) White, tall (rrBb) White, short (rrb)
Step 6: Calculate the probabilities
| Phenotype | Probability |
|---|---|
| Red, tall | 2⁄8 = 1⁄4 |
| Red, short | 2⁄8 = 1⁄4 |
| White, tall | 2⁄8 = 1⁄4 |
| White, short | 2⁄8 = 1⁄4 |
Now that we’ve worked through an example problem, you should feel more confident in solving dihybrid cross worksheets.
Additional Tips and Tricks
- Use a diagram to visualize the Punnett square and the possible genotypes.
- Pay attention to the notation and use the correct letters to represent the alleles.
- Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
📝 Note: Practice makes perfect! Work through multiple dihybrid cross problems to reinforce your understanding.
In summary, solving dihybrid cross worksheets requires a step-by-step approach and attention to detail. By following these steps and practicing with example problems, you’ll become more confident in your ability to solve dihybrid cross problems.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
+Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype refers to the physical appearance resulting from the genotype.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a table that shows all possible combinations of gametes from two parents, helping us determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
How do I calculate the probabilities of each phenotype?
+Count the number of boxes with each genotype in the Punnett square and divide by the total number of boxes to calculate the probability of each phenotype.