Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers Key
Understanding Diffusion and Osmosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental biological processes that occur in living organisms. They play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating the movement of molecules, and facilitating the exchange of substances across cell membranes. In this article, we will delve into the world of diffusion and osmosis, exploring their definitions, mechanisms, and importance in biological systems.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process occurs in a spontaneous and random manner, resulting in the uniform distribution of particles throughout a given space. Diffusion is a vital mechanism that enables cells to obtain essential nutrients, eliminate waste products, and maintain proper ion balances.
Types of Diffusion
There are several types of diffusion, including:
- Simple diffusion: The movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a cell membrane.
- Facilitated diffusion: The movement of particles through a cell membrane with the assistance of transport proteins.
- Oxygen diffusion: The movement of oxygen molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, essential for cellular respiration.
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. This process helps regulate the balance of fluids within cells and maintain proper cellular functions. Osmosis is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing dehydration or overhydration.
Types of Osmotic Environments
Cells can exist in various osmotic environments, including:
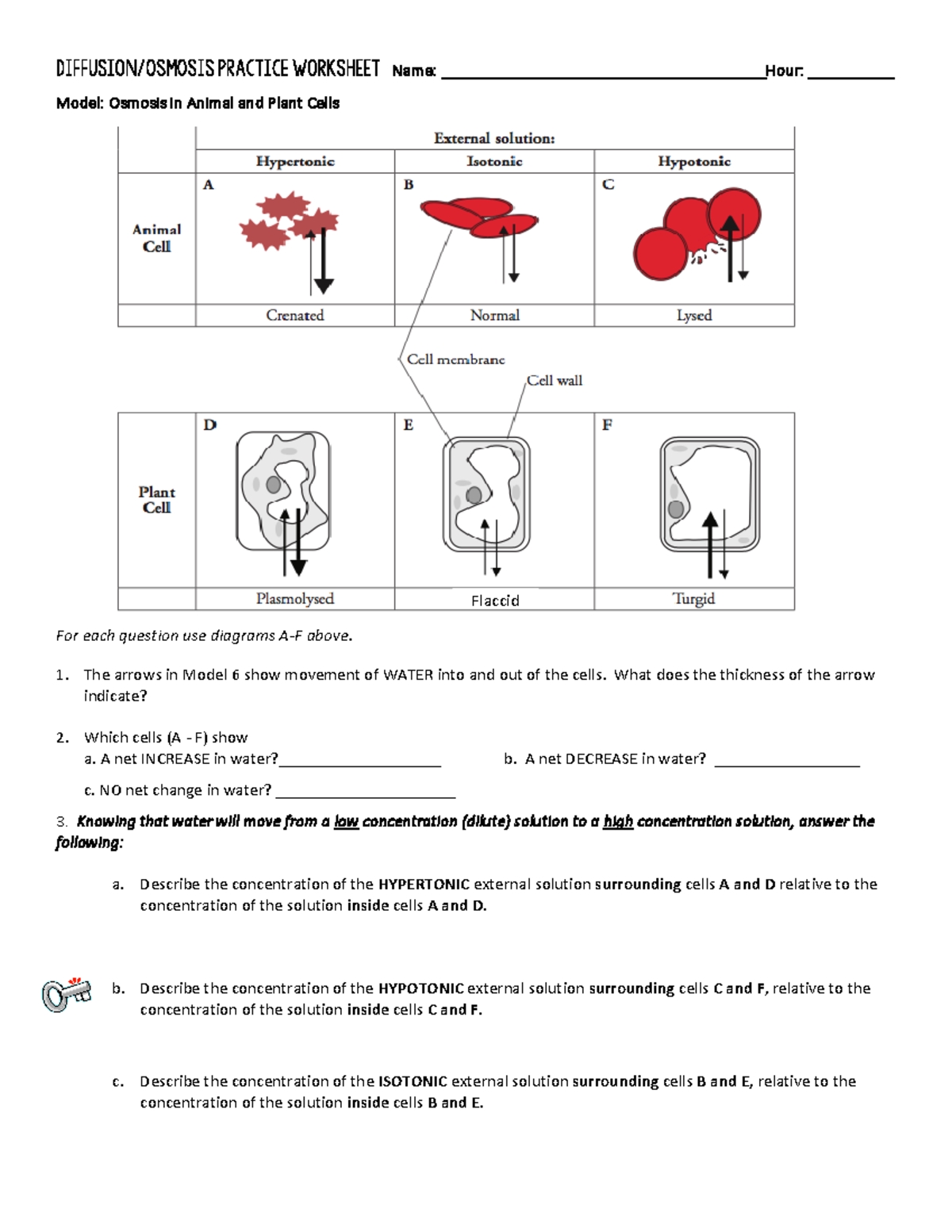
- Isotonic solutions: Solutions with the same concentration of solutes as the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
- Hypotonic solutions: Solutions with a lower concentration of solutes than the cell, resulting in water entering the cell.
- Hypertonic solutions: Solutions with a higher concentration of solutes than the cell, resulting in water leaving the cell.
📝 Note: Understanding the differences between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions is crucial for maintaining proper cellular functions.
Key Differences between Diffusion and Osmosis
While both diffusion and osmosis are essential biological processes, there are key differences between them:
- Direction of movement: Diffusion involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, whereas osmosis involves the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- Cell membrane involvement: Diffusion can occur through cell membranes, whereas osmosis requires a selectively permeable membrane to regulate the movement of water molecules.
- Importance in cellular functions: Diffusion is essential for the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and ions, whereas osmosis is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating fluid balance.
Importance of Diffusion and Osmosis in Biological Systems
Diffusion and osmosis play critical roles in maintaining proper cellular functions, including:
- Nutrient uptake: Diffusion enables cells to obtain essential nutrients, such as glucose and amino acids.
- Waste removal: Diffusion facilitates the elimination of waste products, such as urea and carbon dioxide.
- Ion balance: Diffusion helps maintain proper ion balances, essential for cellular functions and signaling pathways.
- Fluid balance: Osmosis regulates the balance of fluids within cells, preventing dehydration or overhydration.
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers Key
To test your understanding of diffusion and osmosis, try the following worksheet:

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. What is the primary function of diffusion in cells? | To facilitate the exchange of nutrients, waste products, and ions. |
| 2. What type of diffusion involves the movement of particles through a cell membrane with the assistance of transport proteins? | Facilitated diffusion |
| 3. What is the term for the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane? | Osmosis |
| 4. What type of osmotic environment results in water entering the cell? | Hypotonic solution |
| 5. What is the primary difference between diffusion and osmosis? | Direction of movement and cell membrane involvement |
📝 Note: This worksheet is designed to assess your understanding of diffusion and osmosis. Please review the material before attempting to answer the questions.
In conclusion, diffusion and osmosis are fundamental biological processes that play critical roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the movement of molecules. Understanding the mechanisms and importance of these processes is essential for appreciating the complexities of cellular biology.
What is the main difference between diffusion and osmosis?
+The main difference between diffusion and osmosis is the direction of movement and cell membrane involvement. Diffusion involves the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, whereas osmosis involves the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
What is the primary function of facilitated diffusion?
+The primary function of facilitated diffusion is to assist the movement of particles through a cell membrane, allowing cells to obtain essential nutrients and eliminate waste products.
What type of osmotic environment results in water leaving the cell?
+A hypertonic solution results in water leaving the cell, as the concentration of solutes is higher outside the cell than inside.