Master Decimal Division with This Free Worksheet Guide
Understanding Decimal Division: A Comprehensive Guide
Decimal division is a fundamental concept in mathematics that can be challenging for many students to grasp. However, with the right approach and practice, anyone can master decimal division. In this guide, we will provide a free worksheet and a step-by-step tutorial on how to perform decimal division with ease.
What is Decimal Division?
Decimal division is a mathematical operation that involves dividing a decimal number by another decimal number. It is similar to regular division, but it requires a deeper understanding of place value and decimal concepts.
Why is Decimal Division Important?
Decimal division is an essential concept in mathematics and real-life applications. It is used in various fields such as science, engineering, finance, and economics. Mastering decimal division can help you solve problems involving measurements, conversions, and calculations.
How to Perform Decimal Division
Performing decimal division is similar to regular division, but it requires a few extra steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform decimal division:
- Write the dividend and divisor: Write the dividend (the number being divided) and the divisor (the number by which we are dividing) in the division symbol.
- Move the decimal point: Move the decimal point in the divisor to the right until it becomes a whole number.
- Multiply the dividend: Multiply the dividend by 10 (or 100, 1000, etc.) to make it a whole number.
- Perform the division: Perform the division as you would with whole numbers.
- Move the decimal point: Move the decimal point in the quotient (result) to the left by the same number of places that you moved the decimal point in the divisor.
🤔 Note: It's essential to keep track of the decimal point and move it accordingly to get the correct answer.
Examples of Decimal Division
Let’s practice decimal division with some examples:
Example 1: 12.5 ÷ 2.5 =?
Solution:
- Write the dividend and divisor: 12.5 ÷ 2.5
- Move the decimal point: 125 ÷ 25
- Multiply the dividend: 125 × 1 = 125
- Perform the division: 125 ÷ 25 = 5
- Move the decimal point: 5.0
Answer: 5.0
Example 2: 45.6 ÷ 3.2 =?
Solution:
- Write the dividend and divisor: 45.6 ÷ 3.2
- Move the decimal point: 456 ÷ 32
- Multiply the dividend: 456 × 1 = 456
- Perform the division: 456 ÷ 32 = 14.25
- Move the decimal point: 14.25
Answer: 14.25
Common Mistakes in Decimal Division
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when performing decimal division:
- Not moving the decimal point: Failing to move the decimal point in the divisor and dividend can result in incorrect answers.
- Not keeping track of place value: Failing to keep track of place value can lead to errors in the quotient.
- Rounding errors: Rounding errors can occur when dividing decimal numbers. Make sure to keep the decimal places accurate.
🤦 Note: Practice, practice, practice! The more you practice decimal division, the more comfortable you'll become with the concept.
Free Worksheet Guide
Here is a free worksheet guide to help you practice decimal division:
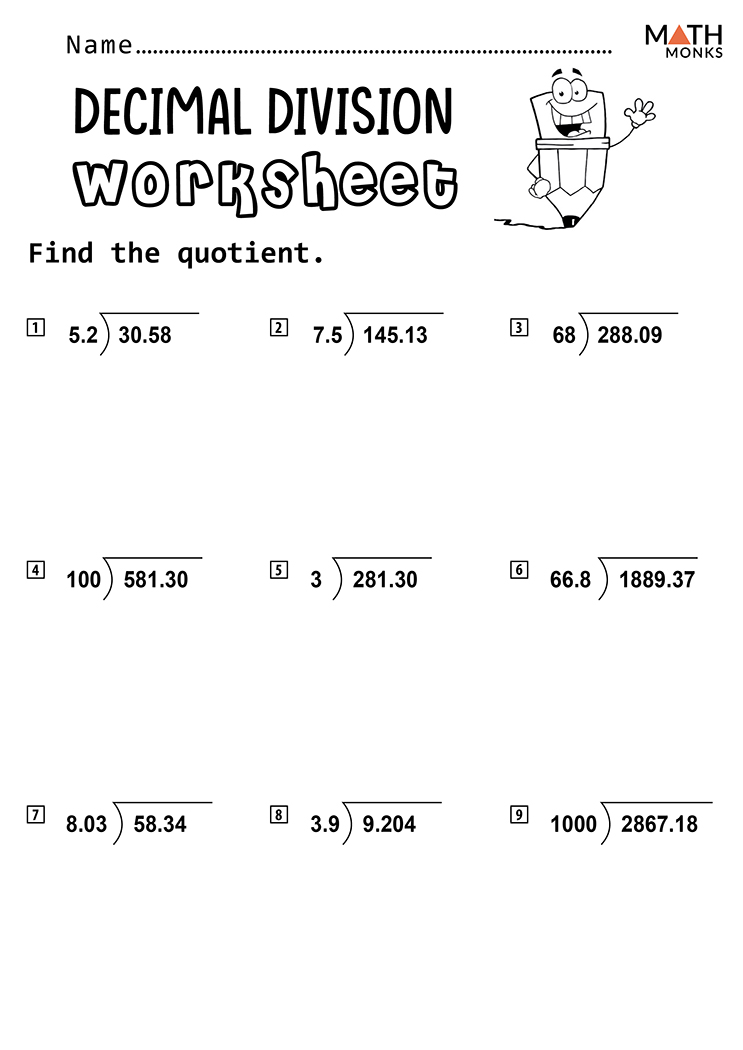
| Dividend | Divisor | Quotient |
|---|---|---|
| 12.5 | 2.5 | _____ |
| 45.6 | 3.2 | _____ |
| 23.4 | 4.5 | _____ |
| 56.7 | 2.1 | _____ |
| 98.2 | 3.5 | _____ |
Answers:
- 5.0
- 14.25
- 5.2
- 27.0
- 28.06
Conclusion
Mastering decimal division takes practice and patience. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing with the free worksheet, you’ll become more confident and proficient in your ability to perform decimal division. Remember to keep track of the decimal point and place value to avoid common mistakes.
What is decimal division?
+Decimal division is a mathematical operation that involves dividing a decimal number by another decimal number.
Why is decimal division important?
+Decimal division is essential in mathematics and real-life applications, including science, engineering, finance, and economics.
How do I perform decimal division?
+Perform decimal division by moving the decimal point in the divisor to the right, multiplying the dividend by 10, performing the division, and moving the decimal point in the quotient to the left.