Subatomic Particle Counting Worksheet Answers Explained

Understanding Subatomic Particles and Their Counting
Atoms, the basic building blocks of matter, are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these particles has a unique role in the structure and properties of an atom. In this explanation, we will delve into the world of subatomic particles, focusing on how to count them and understand their significance in chemistry.
Subatomic Particles: A Brief Overview
Before we dive into counting subatomic particles, it’s essential to understand what each particle represents:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus (center) of an atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge (neutral) that are also found in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons can vary within atoms of the same element, leading to different isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus of an atom. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
Counting Subatomic Particles
Counting subatomic particles involves determining the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. Here are the steps to follow:
Determine the Atomic Number: The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in an atom of that element. This number can be found on the periodic table.
Determine the Mass Number: The mass number (also known as atomic mass) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. This number is also found on the periodic table and represents the average mass of an atom of that element.
Calculate the Number of Neutrons: Subtract the atomic number from the mass number to find the number of neutrons.
- Formula: Number of Neutrons = Mass Number - Atomic Number
Determine the Number of Electrons: In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons (atomic number).
Example: Counting Subatomic Particles in Carbon
Let’s apply the steps above to a carbon atom:
- Atomic Number: 6 (found on the periodic table)
- Mass Number: 12 (average atomic mass of carbon)
- Number of Protons: 6 (equal to the atomic number)
- Number of Neutrons: 12 (mass number) - 6 (atomic number) = 6 neutrons
- Number of Electrons: 6 (equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom)
Table: Subatomic Particle Count for Carbon
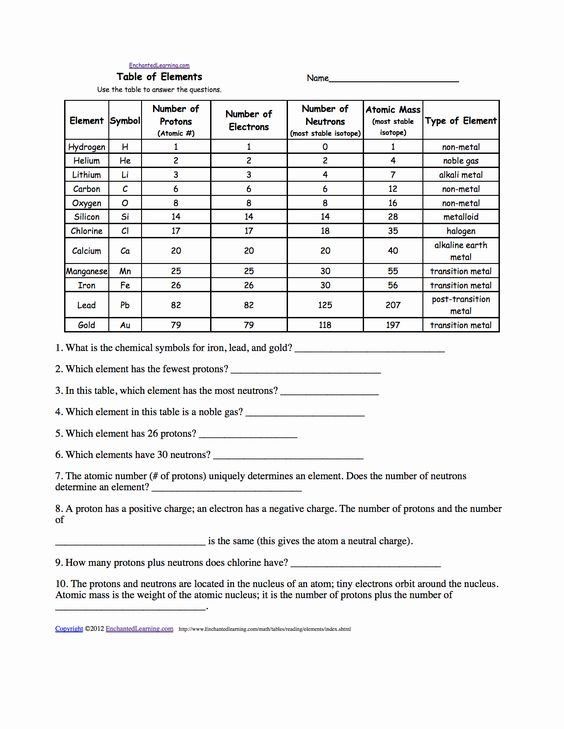
| Particle | Number in Carbon Atom |
|---|---|
| Protons | 6 |
| Neutrons | 6 |
| Electrons | 6 |
📝 Note: The actual mass of carbon can vary slightly due to the presence of isotopes (atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons), but for most purposes, the average atomic mass is used.
Importance of Counting Subatomic Particles
Understanding how to count subatomic particles is fundamental in chemistry and physics. It helps in identifying elements, understanding chemical reactions, and studying the properties of materials. The ability to calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom is a basic skill that underpins more advanced concepts in chemistry and physics.
Wrap-Up
Counting subatomic particles involves understanding the atomic number and mass number of an element and applying simple calculations to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. This skill is essential for studying chemistry and physics, as it allows for the identification of elements and the understanding of atomic structures and chemical reactions.
Why is it important to know the number of subatomic particles in an atom?
+Knowing the number of subatomic particles helps in identifying elements, understanding chemical reactions, and studying the properties of materials. It’s a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics.
How do I calculate the number of neutrons in an atom?
+The number of neutrons can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number (Number of Neutrons = Mass Number - Atomic Number).
What determines the chemical properties of an element?
+The chemical properties of an element are primarily determined by the number of electrons, especially the electrons in the outermost shell of the atom.
Related Terms:
- Isotope practice worksheet
- Periodic table practice worksheet
- Subatomic particles worksheet PDF answers