5 Simple Ways to Master Interest Calculations

Understanding the Concept of Interest
Interest is a fundamental concept in finance that refers to the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment. It is a crucial aspect of personal finance, business, and economics. Mastering interest calculations can help you make informed decisions about your financial resources, investments, and debts. In this article, we will explore five simple ways to master interest calculations and take control of your finances.
1. Understand the Types of Interest
Before diving into interest calculations, it is essential to understand the different types of interest. There are two primary types of interest:
- Simple Interest: Simple interest is calculated as a percentage of the principal amount borrowed or invested. It is typically used for short-term loans, credit cards, and savings accounts.
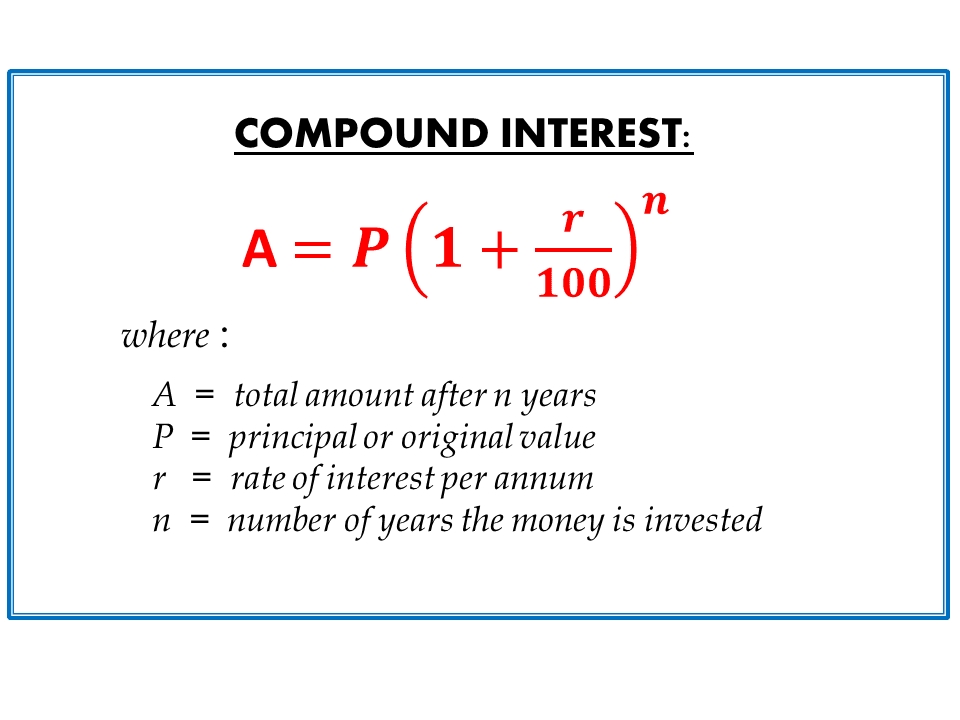
- Compound Interest: Compound interest, on the other hand, is calculated on both the principal amount and any accrued interest. It is commonly used for long-term investments, such as certificates of deposit (CDs), bonds, and retirement accounts.
Key Differences Between Simple and Compound Interest
| Simple Interest | Compound Interest | |
|---|---|---|
| Calculation | Principal x Rate x Time | Principal x (1 + Rate)^Time |
| Accrual | Interest accrues only on the principal | Interest accrues on the principal and accrued interest |
📝 Note: Understanding the difference between simple and compound interest is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
2. Calculate Simple Interest
Calculating simple interest is straightforward. You can use the following formula:
Simple Interest = Principal x Rate x Time
Where:
- Principal is the initial amount borrowed or invested
- Rate is the interest rate as a decimal
- Time is the time period in years
For example, if you borrow $1,000 at an interest rate of 5% per annum for 2 years, the simple interest would be:
Simple Interest = 1,000 x 0.05 x 2 = 100
Simple Interest Calculation Example
| Principal | Rate | Time | Simple Interest |
|---|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | 5% | 2 years | $100 |
3. Calculate Compound Interest
Calculating compound interest is slightly more complex. You can use the following formula:
Compound Interest = Principal x (1 + Rate)^Time - Principal
Where:
- Principal is the initial amount borrowed or invested
- Rate is the interest rate as a decimal
- Time is the time period in years
For example, if you invest $1,000 at an interest rate of 5% per annum for 2 years, the compound interest would be:
Compound Interest = 1,000 x (1 + 0.05)^2 - 1,000 = $110.25
Compound Interest Calculation Example
| Principal | Rate | Time | Compound Interest |
|---|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | 5% | 2 years | $110.25 |
4. Use a Financial Calculator or Spreadsheet
While manual calculations can be helpful, using a financial calculator or spreadsheet can simplify the process. Most financial calculators and spreadsheets have built-in functions for calculating simple and compound interest.
For example, in Microsoft Excel, you can use the following formulas:
- Simple Interest: =IPMT(principal, rate, time)
- Compound Interest: =FV(principal, rate, time)
5. Practice with Real-World Scenarios
To master interest calculations, it is essential to practice with real-world scenarios. Try calculating the interest on your savings account, credit card, or loan. You can also use online calculators or worksheets to practice.
By following these five simple steps, you can master interest calculations and take control of your finances. Remember to understand the types of interest, calculate simple and compound interest, use a financial calculator or spreadsheet, and practice with real-world scenarios.
The knowledge of interest calculations can help you make informed decisions about your financial resources, investments, and debts. By mastering interest calculations, you can:
- Save money: By understanding how interest works, you can save money on loans and credit cards.
- Invest wisely: By calculating compound interest, you can make informed decisions about your investments.
- Manage debt: By understanding how interest accrues on debt, you can manage your debt more effectively.
By applying these concepts to your financial life, you can achieve financial stability and security.