Mitosis vs Meiosis: Key Differences Explained
Understanding the Fundamentals of Cell Division
Cell division is a crucial process in biology, essential for the growth, development, and reproduction of living organisms. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. While both processes involve the division of cells, they serve distinct purposes and have distinct characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between mitosis and meiosis, exploring their mechanisms, functions, and significance in various biological contexts.
What is Mitosis?
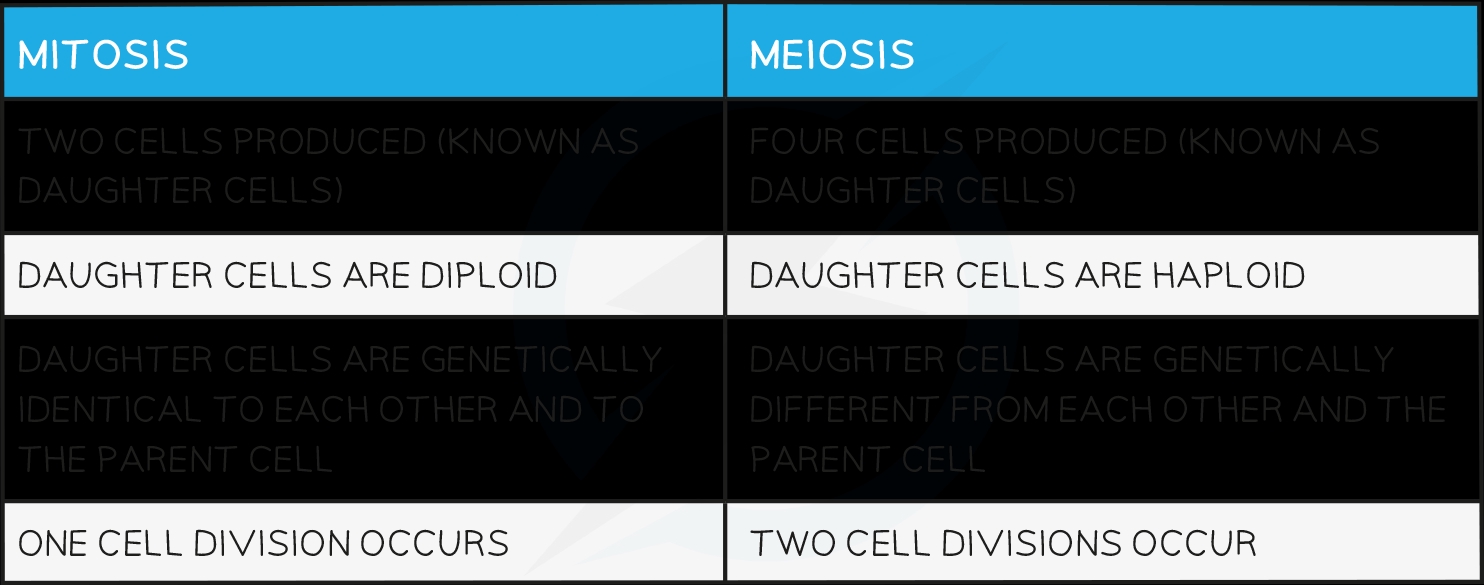
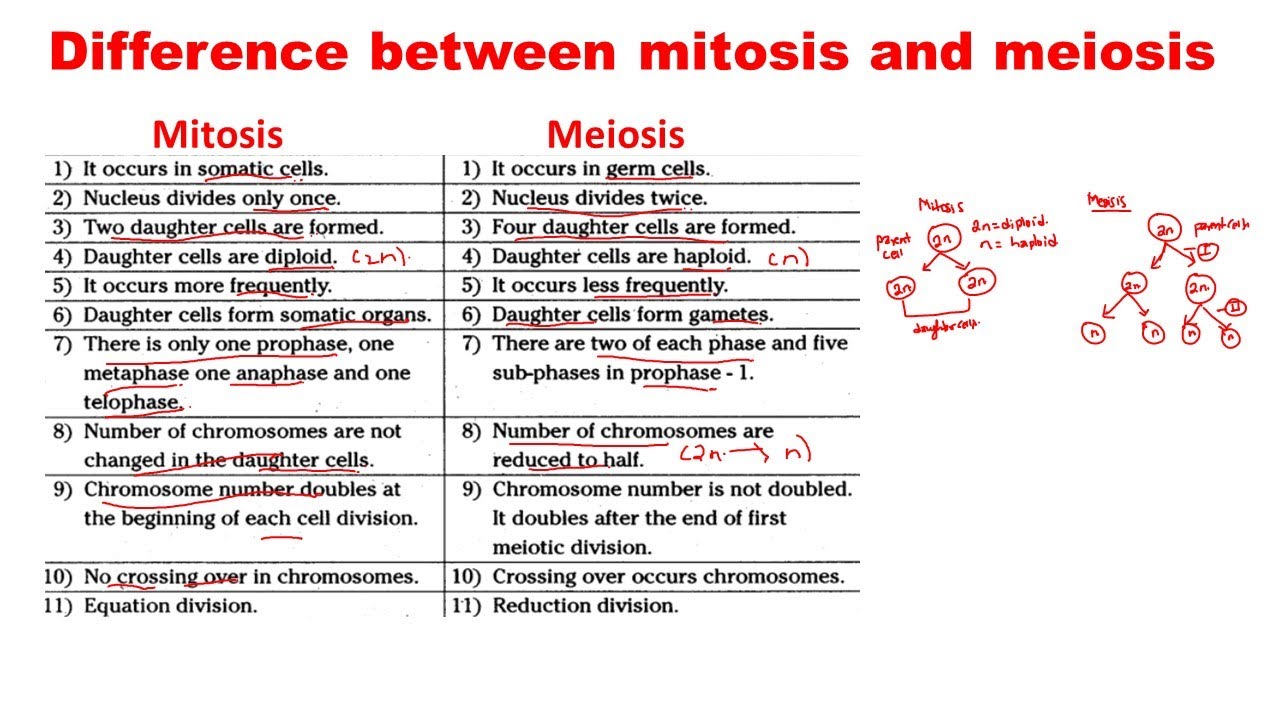
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in the production of two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process occurs in somatic cells, which are non-reproductive cells found in various tissues and organs of the body. Mitosis is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, as it allows for the replacement of old or damaged cells with new ones.
The Mitotic Process
Mitosis consists of four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes align at the center of the cell, attached to the spindle fibers. Anaphase involves the separation of sister chromatids, which move to opposite poles of the cell. Finally, during telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin.
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, or gametes, such as sperm and egg cells. Meiosis results in the production of four non-identical daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is crucial for sexual reproduction, as it allows for the mixing of genetic material from two parents to create offspring with unique combinations of traits.
The Meiotic Process
Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I is further divided into four stages: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. In metaphase I, the paired chromosomes align at the center of the cell. Anaphase I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, which move to opposite poles of the cell. Telophase I marks the end of meiosis I.
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, with the exception that it involves the separation of sister chromatids. The resulting four daughter cells are haploid, meaning they have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Key Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
| Mitosis | Meiosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues | Sexual reproduction and genetic diversity |
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Genetic identity | Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell | Daughter cells are genetically unique and non-identical |
| Number of chromosomes | Daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell | Daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell |
| Type of cells involved | Somatic cells (non-reproductive cells) | Gametes (reproductive cells) |
💡 Note: While mitosis and meiosis are two distinct processes, they share some similarities, such as the involvement of spindle fibers and the separation of chromosomes.
Significance of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are both essential for the survival and reproduction of living organisms. Mitosis allows for the growth and maintenance of tissues, while meiosis enables the creation of genetically unique offspring through sexual reproduction. Understanding the mechanisms and differences between these two processes is crucial for appreciating the complexity and diversity of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mitosis and meiosis are two fundamental processes in biology that serve distinct purposes and have distinct characteristics. Mitosis is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, while meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. By understanding the key differences between these two processes, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of life.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+
The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced and their genetic identity. Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically unique daughter cells.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
+
The purpose of mitosis is for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. It allows for the replacement of old or damaged cells with new ones.
What is the significance of meiosis?
+
Meiosis is significant because it allows for the creation of genetically unique offspring through sexual reproduction, increasing genetic diversity and allowing for adaptation to changing environments.
Related Terms:
- Meiosis Worksheet with answers
- Stages of mitosis Worksheet answers