Mitosis vs Meiosis: Key Differences Explained
Cell Division: The Foundation of Life
Cell division is a fundamental process in the life cycle of all living organisms. It is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. While both processes involve the division of a cell, they have distinct differences in terms of their purpose, stages, and outcomes.
What is Mitosis?
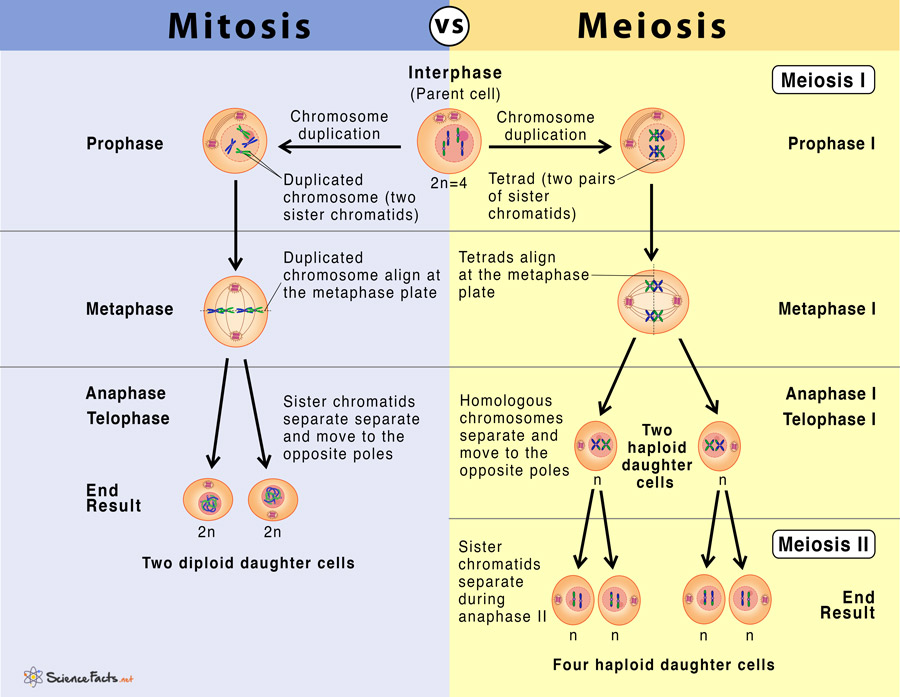
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in the production of two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in multicellular organisms. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, which are non-reproductive cells that make up the majority of an organism’s body.
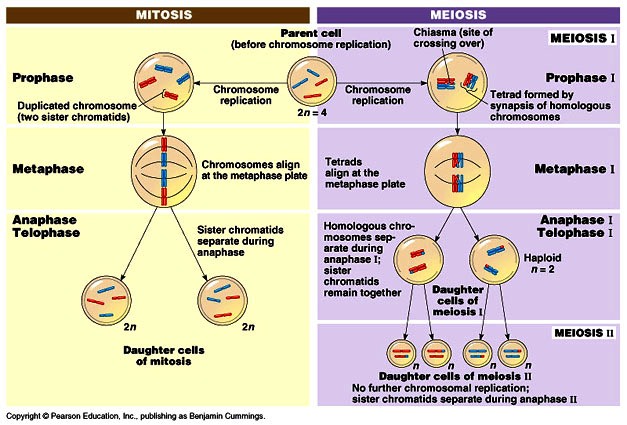
Stages of Mitosis:
- Prophase: The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells (gametes) to produce four non-identical daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is crucial for the reproduction of eukaryotic organisms, as it allows for the mixing of genetic material and increases genetic diversity.
Stages of Meiosis:
- Prophase I: Homologous chromosomes pair up, and crossing over occurs.
- Metaphase I: The paired chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase I: The homologous chromosomes separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Prophase II: A second round of cell division occurs, with the sister chromatids separating.
- Metaphase II: The sister chromatids align at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into four non-identical daughter cells.
Key Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Number of Cell Divisions: Mitosis involves one round of cell division, while meiosis involves two consecutive rounds.
- Number of Daughter Cells: Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four daughter cells.
- Number of Chromosomes: Mitosis results in daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis results in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
- Genetic Diversity: Meiosis increases genetic diversity through crossing over and independent assortment, while mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells.
| Characteristics | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Cell Divisions | 1 | 2 |
| Number of Daughter Cells | 2 | 4 |
| Number of Chromosomes | Same as parent cell | Half of parent cell |
| Genetic Diversity | No increase | Increased through crossing over and independent assortment |
🔍 Note: While mitosis and meiosis are two distinct processes, they share some similarities in terms of their stages and molecular mechanisms.
In conclusion, mitosis and meiosis are two essential processes that allow living organisms to grow, reproduce, and adapt to their environments. Understanding the key differences between these two processes is crucial for appreciating the complexity and diversity of life on Earth.
What is the main purpose of mitosis?
+The main purpose of mitosis is to produce genetically identical daughter cells for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in multicellular organisms.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of cell divisions and the number of daughter cells produced. Mitosis involves one round of cell division and produces two daughter cells, while meiosis involves two consecutive rounds and produces four daughter cells.
Why is meiosis important for genetic diversity?
+Meiosis is important for genetic diversity because it allows for the mixing of genetic material through crossing over and independent assortment, resulting in increased genetic diversity among offspring.