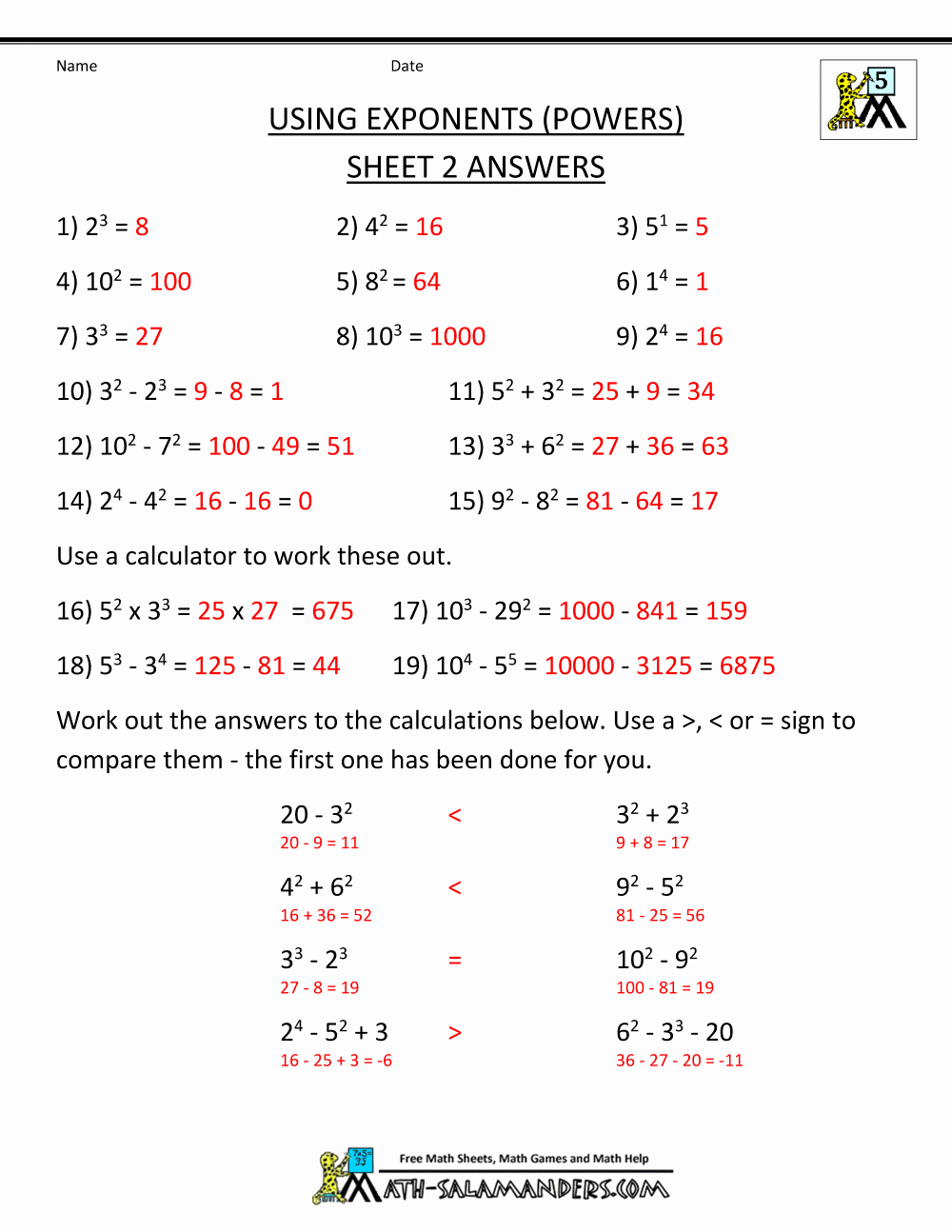
Comparing Horizontal and Vertical Integration Made Simple
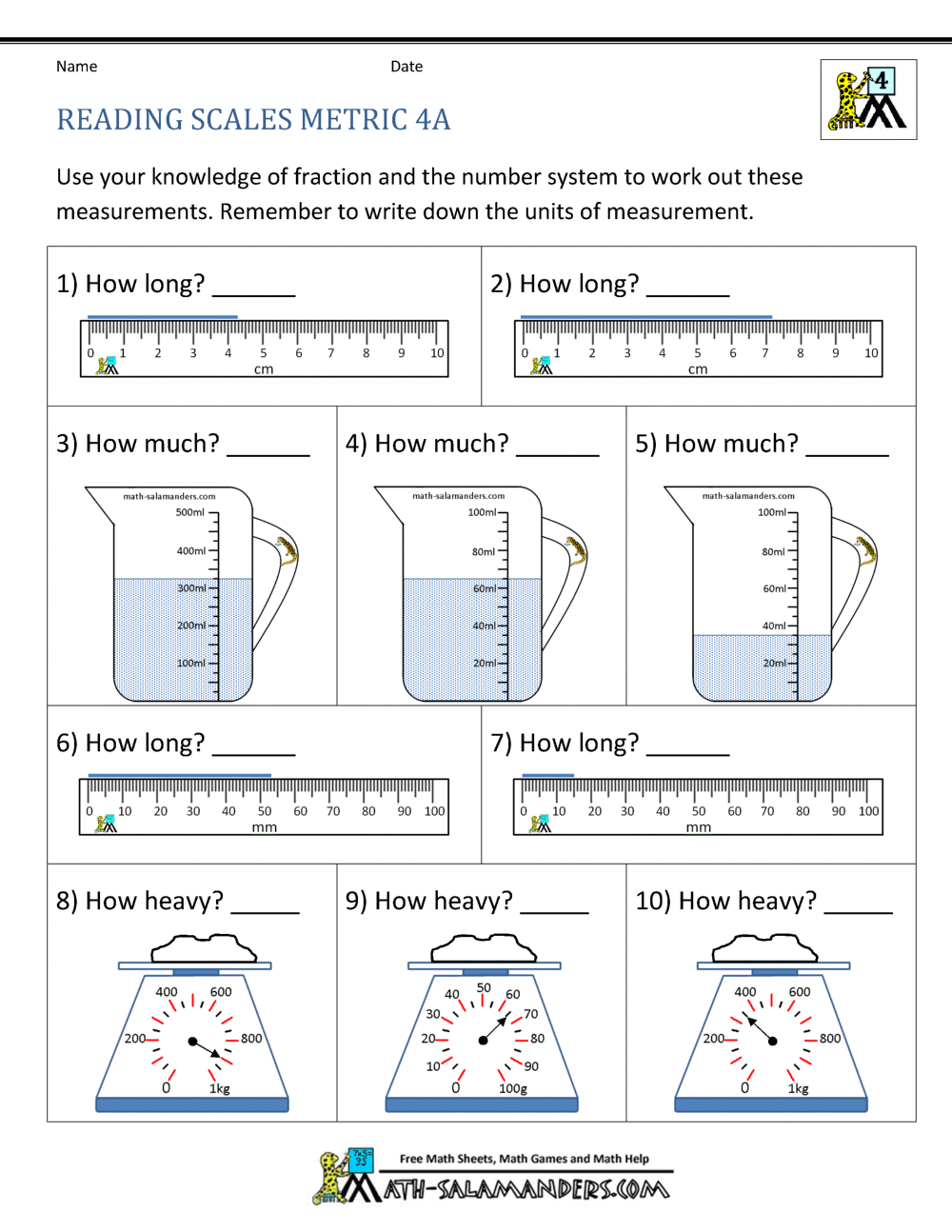
Understanding Business Expansion Strategies
When it comes to expanding a business, there are two primary strategies that companies consider: horizontal integration and vertical integration. Both strategies have their own set of benefits and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between them is crucial for making informed business decisions. In this article, we’ll break down the concepts of horizontal and vertical integration, explore their advantages and disadvantages, and provide examples to illustrate each strategy.
What is Horizontal Integration?
Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with another company that operates at the same level of the supply chain. In other words, two or more companies that produce the same products or offer the same services join forces to increase market share, reduce competition, and improve efficiency.
Benefits of Horizontal Integration:
- Increased Market Share: By merging with a competitor, a company can expand its customer base and increase its market share.
- Improved Efficiency: Horizontal integration can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency, as redundant operations and resources are eliminated.
- Enhanced Negotiating Power: A larger company can negotiate better deals with suppliers and vendors.
Examples of Horizontal Integration:
- Procter & Gamble’s acquisition of Gillette in 2005
- Exxon’s merger with Mobil in 1999
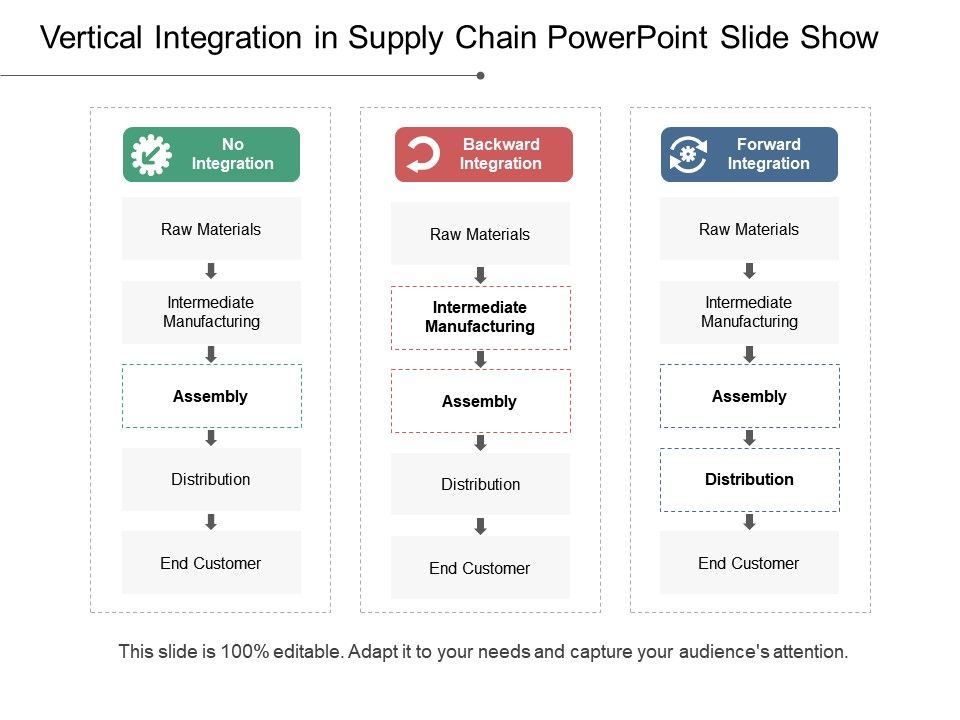
What is Vertical Integration?
Vertical integration occurs when a company expands its operations by acquiring or controlling another company that operates at a different level of the supply chain. This can include acquiring a supplier, a manufacturer, or a distributor.
Benefits of Vertical Integration:
- Improved Control: By controlling more stages of the supply chain, a company can improve its control over quality, cost, and delivery.
- Increased Efficiency: Vertical integration can lead to cost savings and improved efficiency, as companies can eliminate intermediaries and reduce transaction costs.
- Enhanced Innovation: By controlling more stages of the supply chain, a company can innovate more easily and bring new products to market faster.
Examples of Vertical Integration:
- Apple’s acquisition of chip manufacturer PA Semi in 2008
- Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods Market in 2017
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Integration

| Horizontal Integration | Vertical Integration | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Merging with a competitor at the same level of the supply chain | Acquiring or controlling a company at a different level of the supply chain |
| Benefits | Increased market share, improved efficiency, enhanced negotiating power | Improved control, increased efficiency, enhanced innovation |
| Examples | Procter & Gamble’s acquisition of Gillette, Exxon’s merger with Mobil | Apple’s acquisition of PA Semi, Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods Market |
Challenges and Risks of Integration
While integration can bring numerous benefits, it also involves significant challenges and risks. These can include:
- Cultural Integration: Integrating different corporate cultures can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Regulatory Issues: Integrations may be subject to regulatory scrutiny and approval.
- Financial Risks: Integrations can be costly and involve significant financial risks.
🚨 Note: Integration is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Companies should carefully consider the potential benefits and risks before embarking on an integration strategy.
Conclusion
Horizontal and vertical integration are two distinct business expansion strategies that offer different benefits and drawbacks. By understanding the differences between these strategies, companies can make informed decisions about which approach is best for their business. Whether through horizontal or vertical integration, companies can expand their operations, improve efficiency, and increase market share. However, integration also involves significant challenges and risks, and companies must carefully consider these factors before making a decision.
What is the main difference between horizontal and vertical integration?
+The main difference between horizontal and vertical integration is the level of the supply chain at which the integration occurs. Horizontal integration involves merging with a competitor at the same level of the supply chain, while vertical integration involves acquiring or controlling a company at a different level of the supply chain.
What are the benefits of horizontal integration?
+The benefits of horizontal integration include increased market share, improved efficiency, and enhanced negotiating power.
What are the risks of integration?
+The risks of integration include cultural integration challenges, regulatory issues, and financial risks.