Codon Worksheet Answers Key Genetics Made Easy
Unlocking the Secrets of Genetics: Codon Worksheet Answers Key
Genetics can be a complex and fascinating field, but understanding the basics of codons and how they work is essential for any aspiring geneticist or biologist. In this post, we’ll delve into the world of codons and provide answers to a codon worksheet, making genetics a little easier to grasp.
What are Codons?
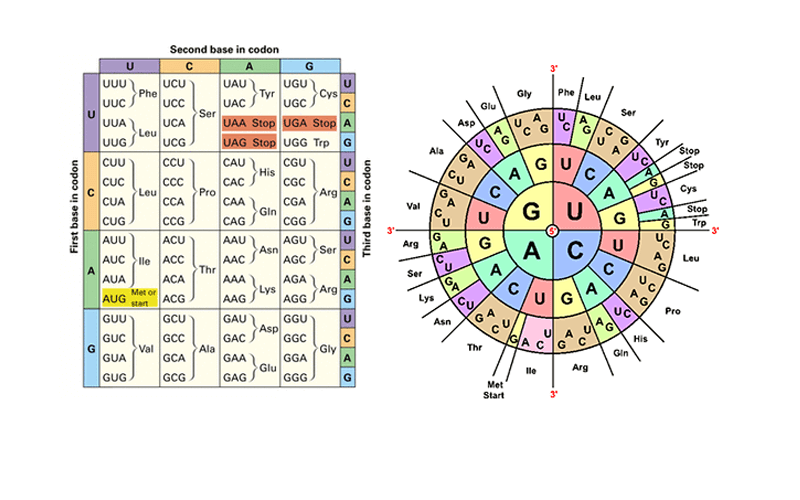
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides that correspond to a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis. The genetic code is made up of 64 possible codons, which are formed by combining the four nucleotide bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T).
Codon Table
Here’s a simplified codon table to help you understand how codons correspond to amino acids:
| Codon | Amino Acid |
|---|---|
| ATA | Isoleucine (Ile) |
| ATC | Isoleucine (Ile) |
| ATT | Isoleucine (Ile) |
| ATG | Methionine (Met) |
| ACA | Threonine (Thr) |
| ACC | Threonine (Thr) |
| ACG | Threonine (Thr) |
| ACT | Threonine (Thr) |
Codon Worksheet Answers Key
Here are the answers to a sample codon worksheet:
- What amino acid is encoded by the codon ATG?
Answer: Methionine (Met)
- Which codon corresponds to the amino acid Tryptophan (Trp)?
Answer: TGG
- What is the amino acid encoded by the codon CCG?
Answer: Proline (Pro)
- Which codon is a stop signal?
Answer: TAA
- What is the amino acid encoded by the codon GCT?
Answer: Alanine (Ala)
How to Read Codons
Reading codons can be a bit tricky, but here are some tips to help you:
- Start by identifying the first nucleotide of the codon.
- Move to the next nucleotide and identify the combination of the first two nucleotides.
- Finally, identify the third nucleotide and match it to the corresponding amino acid or stop signal.
Important Notes
📝 Note: The genetic code is degenerate, meaning that more than one codon can encode the same amino acid.
📝 Note: The start codon is usually AUG, which codes for Methionine (Met).
📝 Note: The stop signals are UAA, UAG, and UGA.
Conclusion
Mastering the basics of codons and the genetic code is essential for understanding how genes are expressed and how proteins are synthesized. With practice and patience, you’ll become more comfortable reading codons and understanding the complexities of genetics. Remember, genetics is a fascinating field, and with the right tools and resources, you can unlock its secrets.
What is the genetic code?
+The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) into proteins.
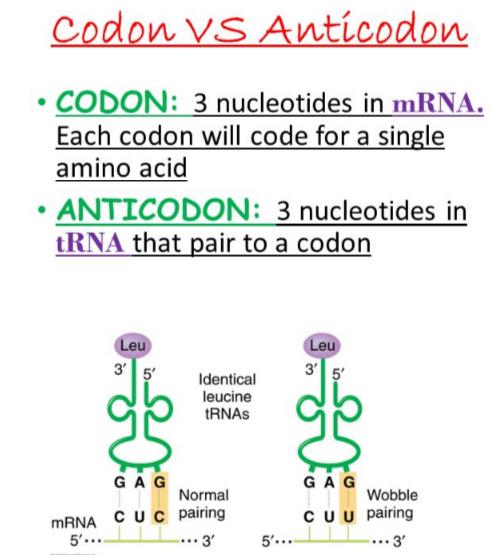
What is a codon?
+A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds to a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis.
What is the start codon?
+The start codon is usually AUG, which codes for Methionine (Met).
Related Terms:
- What codon means start
- Codon chart
- Protein synthesis worksheet