Cladogram Worksheet Answers Key
Understanding Cladograms: A Comprehensive Guide
Cladograms are a fundamental tool in the field of phylogenetics, used to visually represent the evolutionary relationships between different species or organisms. A cladogram is a diagram that shows the relationships between organisms based on their shared characteristics, with the most closely related organisms grouped together. In this article, we will delve into the world of cladograms, explaining how to read and interpret them, and providing answers to common worksheet questions.
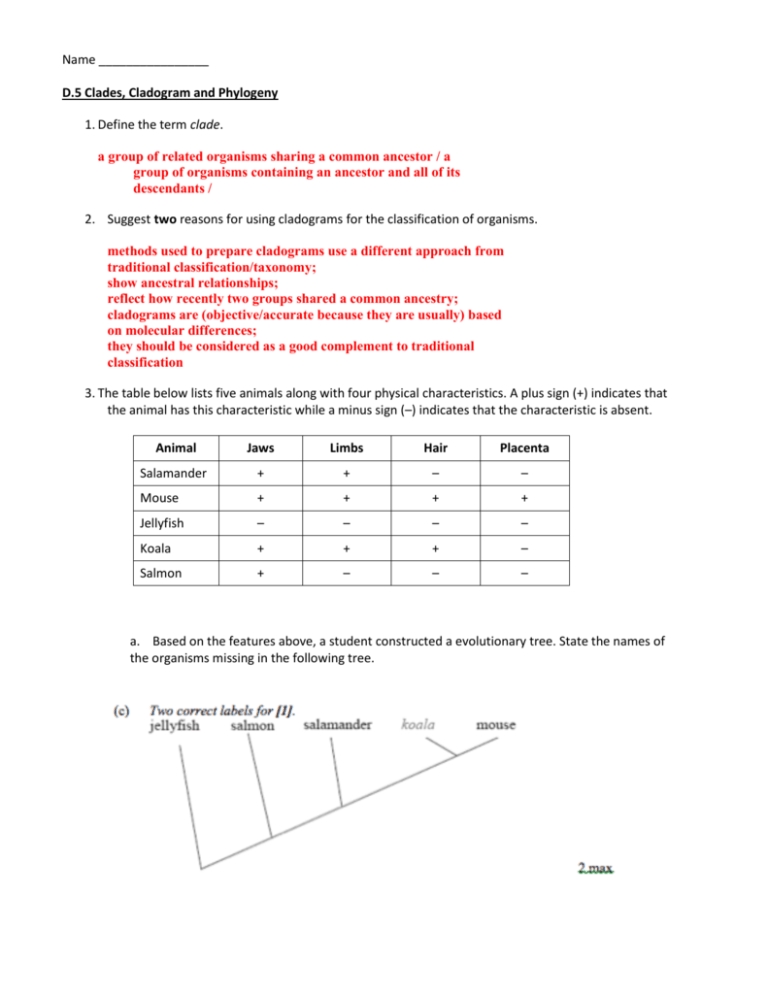
What is a Cladogram?
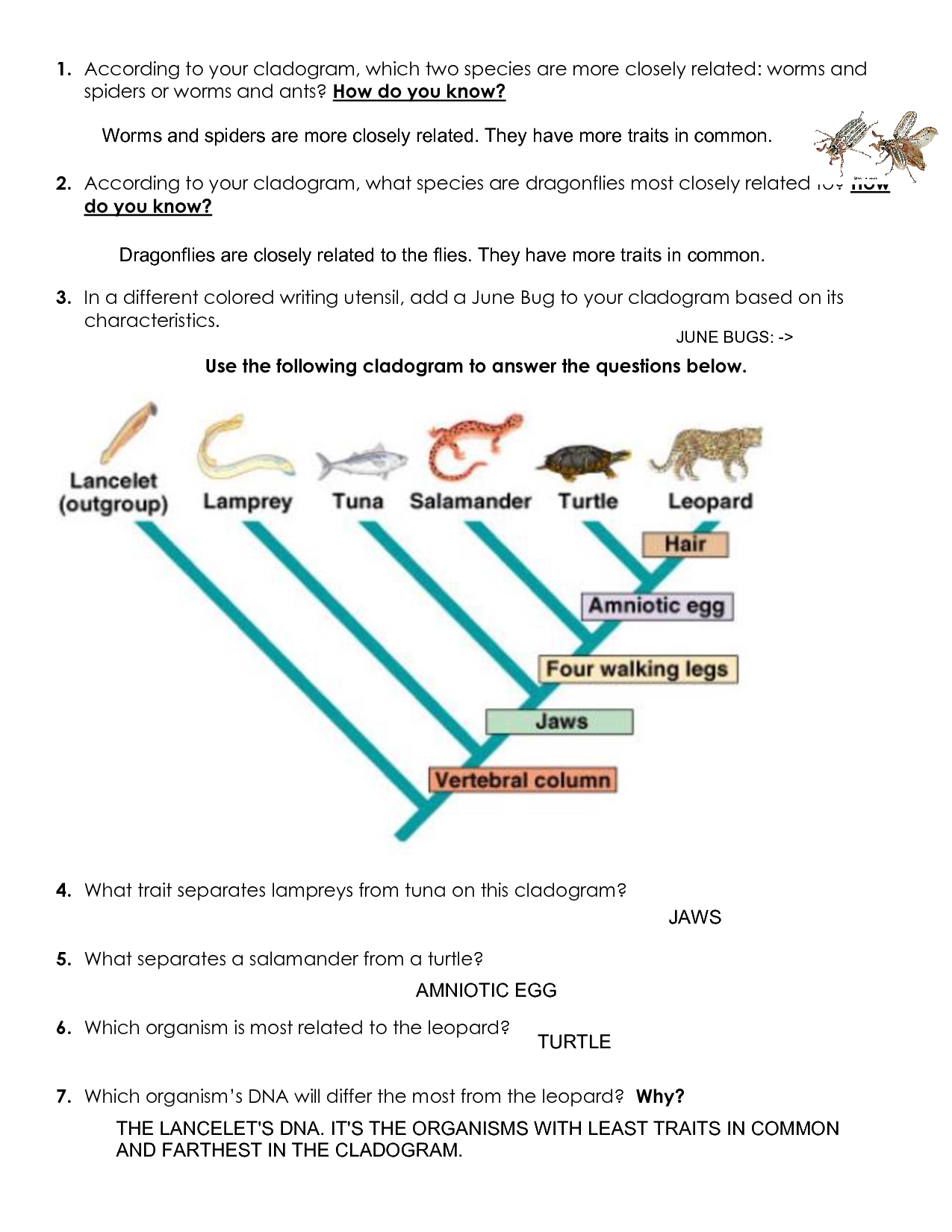
A cladogram is a type of tree-like diagram that illustrates the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. It is based on the principles of cladistics, which is a method of classifying organisms based on their shared characteristics. Cladograms are used to show the relationships between organisms in a way that is easy to understand and visualize.
How to Read a Cladogram
Reading a cladogram can seem daunting at first, but it is actually quite straightforward. Here are the steps to follow:
- Start at the bottom of the cladogram, where the most ancient organisms are typically represented.
- Work your way up the cladogram, following the branches as they split and merge.
- Each branch represents a group of organisms that share a common characteristic.
- The point where two branches meet is called a node, and it represents the point where the two groups of organisms diverged from a common ancestor.
- The length of the branches does not necessarily represent the amount of time that has passed, but rather the number of characteristics that have changed.
Types of Cladograms
There are several types of cladograms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few of the most common types:
- Rooted cladogram: This type of cladogram has a clear root, representing the most ancient organism.
- Unrooted cladogram: This type of cladogram does not have a clear root, and the relationships between organisms are shown relative to each other.
- Phylogram: This type of cladogram shows the relationships between organisms, as well as the amount of time that has passed between each node.
Answer Key to Common Cladogram Worksheet Questions
Here are the answers to some common cladogram worksheet questions:
- What is the most ancient organism in the cladogram?
- Answer: The organism at the bottom of the cladogram, where the branches first split.
- What is the point where two branches meet called?
- Answer: A node.
- What does the length of the branches represent?
- Answer: The number of characteristics that have changed, not necessarily the amount of time that has passed.
- What type of cladogram has a clear root?
- Answer: A rooted cladogram.
| Organism | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Human | Bipedalism, opposable thumbs |
| Chimpanzee | Bipedalism, opposable thumbs |
| Monkey | Prehensile tail, arboreal |
🔍 Note: This table shows the characteristics of three organisms, which can be used to construct a cladogram.
Constructing a Cladogram from a Table of Characteristics
Constructing a cladogram from a table of characteristics is a fun and interactive way to learn about phylogenetics. Here are the steps to follow:
- Start by identifying the organisms and their characteristics.
- Group the organisms based on their shared characteristics.
- Use the grouped organisms to construct a cladogram, with the most closely related organisms grouped together.
- Use the characteristics to identify the nodes and branches of the cladogram.
👍 Note: Remember to use the characteristics to identify the relationships between organisms, and to group the most closely related organisms together.
When constructing a cladogram, it is essential to use the characteristics to identify the relationships between organisms. By grouping the most closely related organisms together, you can create a diagram that accurately represents the evolutionary relationships between different species.
In conclusion, cladograms are a powerful tool for understanding the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. By learning how to read and interpret cladograms, you can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the history of life on Earth.
What is the difference between a rooted and unrooted cladogram?
+A rooted cladogram has a clear root, representing the most ancient organism, while an unrooted cladogram does not have a clear root, and the relationships between organisms are shown relative to each other.
What does the length of the branches represent in a cladogram?
+The length of the branches represents the number of characteristics that have changed, not necessarily the amount of time that has passed.
What is the point where two branches meet called in a cladogram?
+A node.



