Charles Law Worksheet for Physics Students
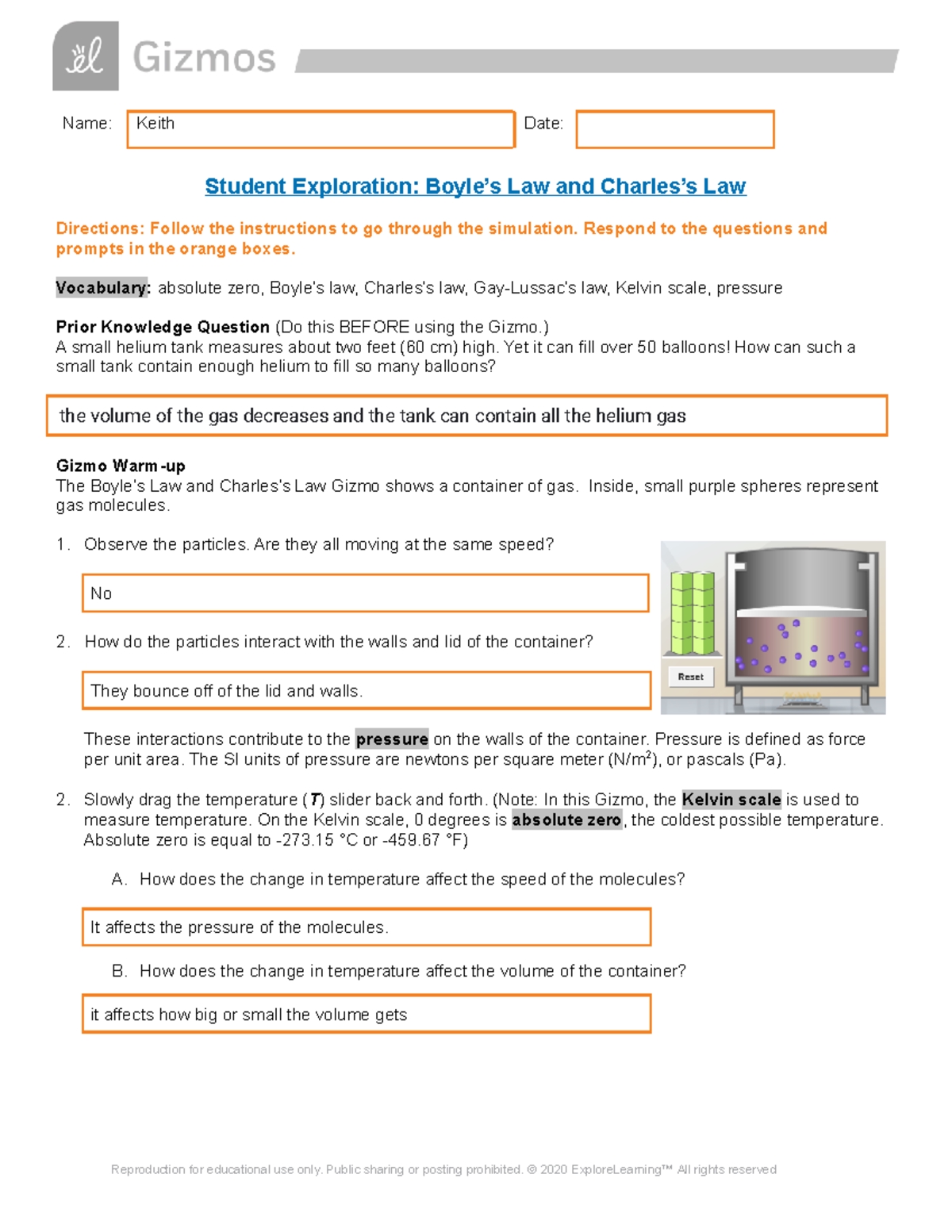
Understanding Charles Law: A Comprehensive Guide for Physics Students
Charles Law, also known as the Law of Volumes, is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas. In this guide, we will delve into the world of Charles Law, exploring its history, formula, applications, and providing a worksheet for physics students to practice and reinforce their understanding.
History of Charles Law
Jacques Charles, a French physicist, discovered Charles Law in 1787. Charles conducted a series of experiments, observing the behavior of gases at different temperatures. He found that, at constant pressure, the volume of a gas increases linearly with the temperature. This groundbreaking discovery laid the foundation for the development of modern physics and chemistry.
Charles Law Formula
The Charles Law formula is:
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
Where:
- V1 is the initial volume
- T1 is the initial temperature (in Kelvin)
- V2 is the final volume
- T2 is the final temperature (in Kelvin)
This formula demonstrates that the ratio of volume to temperature remains constant for a given amount of gas at constant pressure.
Understanding the Formula
To grasp the concept of Charles Law, let’s break down the formula:
- Volume (V): The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature (T). This means that as the temperature increases, the volume of the gas also increases, assuming constant pressure.
- Temperature (T): The temperature is measured in Kelvin (K). It’s essential to use Kelvin when applying Charles Law, as the formula is not valid for Celsius or Fahrenheit temperatures.
- Constant Pressure: Charles Law assumes that the pressure remains constant. If the pressure changes, the relationship between volume and temperature will not be linear.
Applications of Charles Law
Charles Law has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Physics and Chemistry: Understanding the behavior of gases is crucial in physics and chemistry. Charles Law helps scientists predict the volume of a gas at different temperatures, which is essential in various experiments and calculations.
- Engineering: Charles Law is applied in the design of engines, refrigeration systems, and air conditioning systems. Engineers use the law to calculate the volume of gases at different temperatures, ensuring efficient system performance.
- Aerospace: Charles Law is used in the development of aircraft and spacecraft. Understanding the behavior of gases at high altitudes and temperatures is critical for designing efficient propulsion systems and life support systems.
Charles Law Worksheet
Now that you’ve learned about Charles Law, it’s time to practice! Complete the following worksheet to reinforce your understanding:
Problem 1:
A gas has an initial volume of 2 liters at 250 K. If the temperature increases to 300 K, what is the new volume of the gas? Assume constant pressure.
Problem 2:
A sample of gas has a volume of 5 liters at 350 K. If the temperature decreases to 200 K, what is the new volume of the gas? Assume constant pressure.
Problem 3:
A balloon has a volume of 10 liters at 25°C. If the temperature increases to 50°C, what is the new volume of the balloon? Assume constant pressure.
Problem 4:
A gas has an initial volume of 3 liters at 400 K. If the temperature decreases to 250 K, what is the new volume of the gas? Assume constant pressure.
Problem 5:
A sample of gas has a volume of 8 liters at 500 K. If the temperature increases to 600 K, what is the new volume of the gas? Assume constant pressure.
📝 Note: Use the Charles Law formula to solve these problems. Make sure to convert temperatures to Kelvin (K) before applying the formula.
Additional Tips and Tricks
When working with Charles Law, keep the following tips in mind:
- Always convert temperatures to Kelvin (K) before applying the formula.
- Ensure that the pressure remains constant.
- Use the formula to calculate the new volume, not the temperature.
- Practice, practice, practice! The more you work with Charles Law, the more comfortable you’ll become with applying it to different problems.
What is Charles Law?
+Charles Law is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas.
What is the Charles Law formula?
+The Charles Law formula is V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, where V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes, and T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures in Kelvin.
What are the applications of Charles Law?
+Charles Law has numerous applications in physics, chemistry, engineering, and aerospace.
In conclusion, Charles Law is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas. By understanding the formula and applying it to different problems, you’ll become proficient in using Charles Law to solve a wide range of problems. Remember to practice regularly and use the tips and tricks provided to reinforce your understanding.



