10 Key Points on Cell Structure and Function
Understanding Cell Structure and Function: The Building Blocks of Life
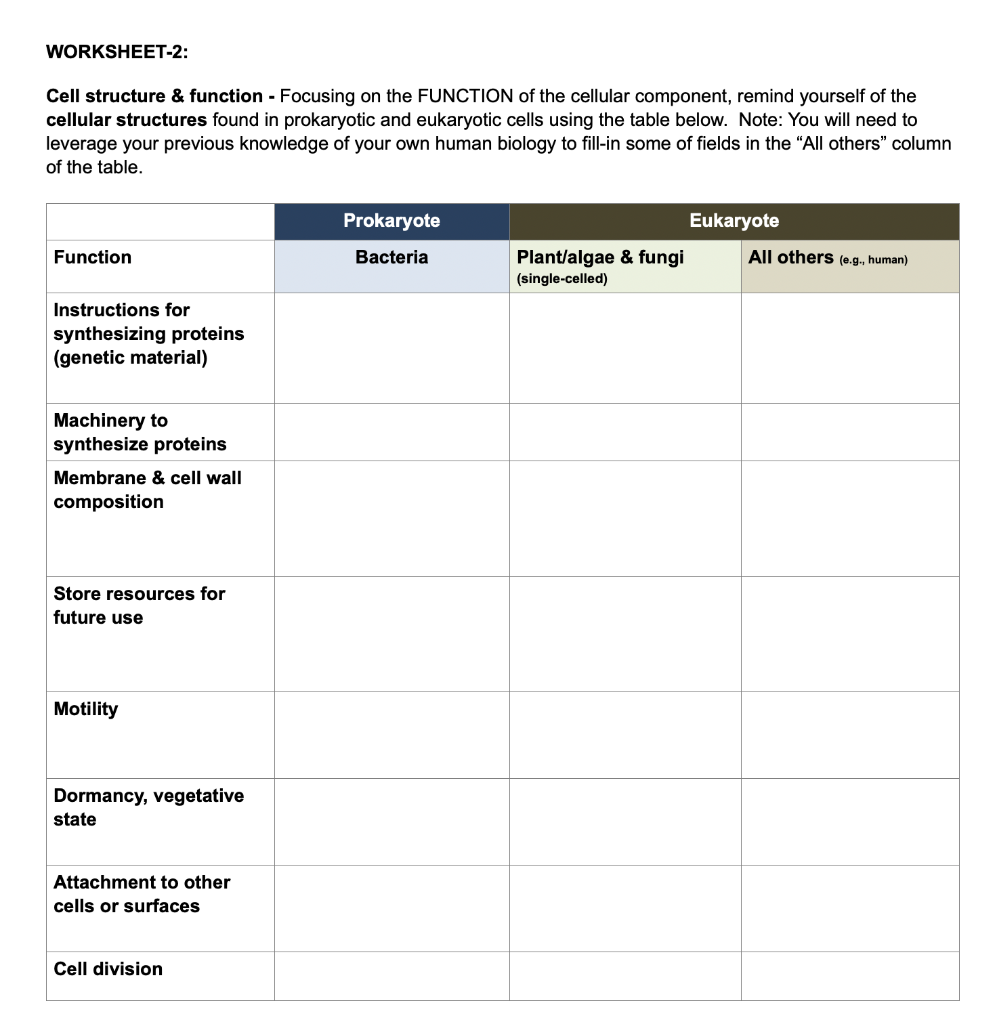
The cell is the fundamental unit of life, and its structure and function are crucial for understanding the intricacies of living organisms. The cell is a complex system that performs a variety of functions necessary for life, including growth, reproduction, and metabolism. In this article, we will delve into the 10 key points on cell structure and function, highlighting the essential components and processes that make life possible.
1. Cell Membrane: The Protective Barrier
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, semi-permeable lipid bilayer that surrounds the cell. It acts as a protective barrier, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is composed of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol, which work together to maintain cellular homeostasis.
💡 Note: The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while restricting others.
2. Cytoplasm: The Cellular Matrix
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell, comprising approximately 70% water. It is the medium in which many cellular processes take place, including metabolic reactions, protein synthesis, and cell signaling. Cytoplasm is a dynamic environment, with various organelles suspended within it, each performing specific functions.
3. Nucleus: The Control Center
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing most of the cell’s genetic material. It is a membrane-bound organelle that houses the chromosomes, which are made up of DNA and proteins. The nucleus regulates cellular activities, including growth, division, and differentiation.
4. Mitochondria: The Powerhouses
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). These organelles are found in the cytoplasm and have two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane. Mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular respiration, producing energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
💡 Note: Mitochondria have their own DNA, known as mtDNA, which is separate from the nuclear DNA.
5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Transport Network
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae within the cytoplasm. It is responsible for transporting materials throughout the cell, including proteins, lipids, and ions. The ER also plays a role in protein synthesis, folding, and modification.
6. Ribosomes: The Protein Factories
Ribosomes are small organelles found throughout the cytoplasm, responsible for protein synthesis. They read the genetic instructions encoded in the mRNA and assemble amino acids into proteins. Ribosomes can be free-floating or attached to the ER, and they play a crucial role in cellular growth and maintenance.
7. Lysosomes: The Cellular Recycling Centers
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes, responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances. They maintain cellular homeostasis by degrading damaged or dysfunctional cellular components.
8. Golgi Apparatus: The Protein Processing Center
The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle composed of flattened sacs and tubules. It is responsible for processing and modifying proteins synthesized by the ER, preparing them for secretion or transport to other parts of the cell.
9. Cytoskeleton: The Cellular Framework
The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that provides structural support and shape to the cell. It is composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which work together to maintain cellular integrity and facilitate cellular movements.
10. Cell Division: The Process of Reproduction
Cell division is the process by which a cell reproduces itself, resulting in two daughter cells. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the process of somatic cell division, resulting in two identical daughter cells. Meiosis is the process of reproductive cell division, resulting in four non-identical daughter cells.
In conclusion, understanding cell structure and function is essential for comprehending the intricacies of life. The cell is a complex system, with various organelles working together to maintain cellular homeostasis and facilitate growth, reproduction, and metabolism. By grasping these 10 key points, we can better appreciate the fascinating world of cellular biology.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
+Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through cellular respiration.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
+The Golgi apparatus is responsible for processing and modifying proteins synthesized by the ER, preparing them for secretion or transport to other parts of the cell.
Related Terms:
- Cell structure and function PDF