7 Essential Cell Organelle Functions to Know
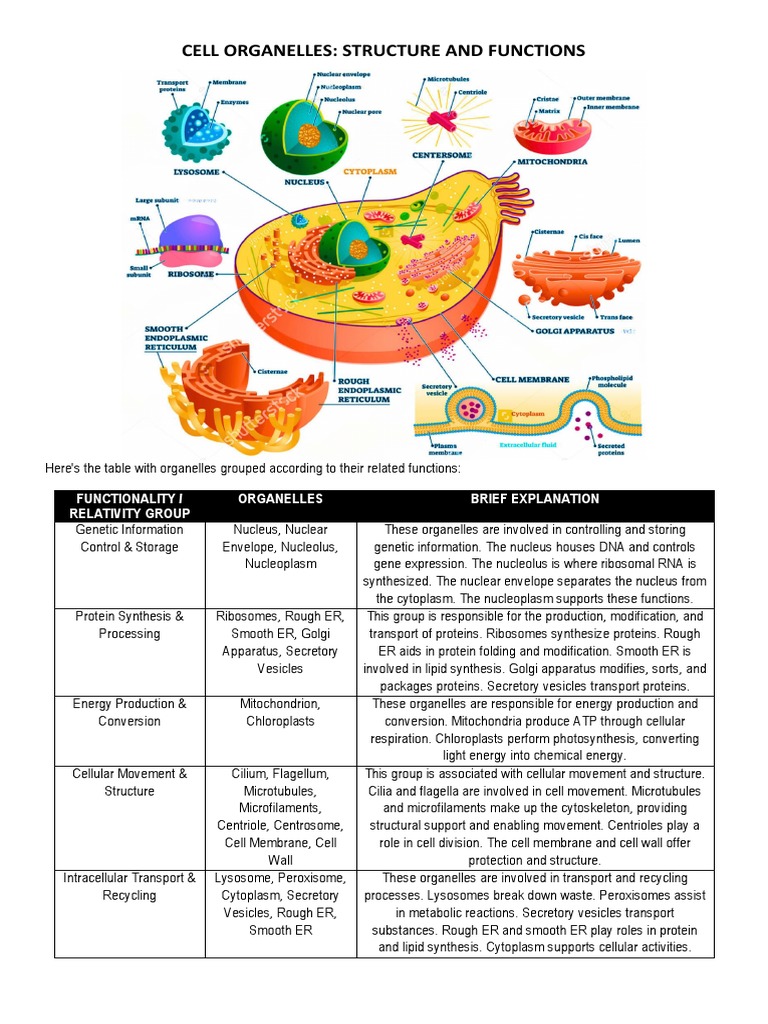
Understanding Cell Organelle Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms, and they are composed of various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and enable the cell to perform its functions. Each organelle has unique structures and functions that contribute to the overall functioning of the cell. In this article, we will explore 7 essential cell organelle functions that you should know.
1. Nucleus: The Control Center of the Cell
The nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell and serves as the control center, containing most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. The nucleus is responsible for:
- Storing genetic information: The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, which carries genetic instructions for the development and function of the cell.
- Regulating gene expression: The nucleus controls the expression of genes by transcribing DNA into RNA and regulating the translation of RNA into proteins.
- Cell division: The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell division, ensuring that the genetic material is replicated and distributed evenly between daughter cells.
📝 Note: The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus.
2. Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell
Mitochondria are organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, responsible for generating energy for the cell through the process of cellular respiration. The mitochondria:
- Produce ATP: Mitochondria generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of the cell, through the process of cellular respiration.
- Regulate energy metabolism: Mitochondria play a crucial role in regulating energy metabolism, ensuring that the cell has a constant supply of energy.
- Maintain cellular homeostasis: Mitochondria help maintain cellular homeostasis by regulating the levels of ATP, ADP, and other energy-related molecules.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Cellular Transport System
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that serves as a transport system for molecules within the cell. The ER:
- Transports molecules: The ER transports molecules, such as proteins and lipids, from the endoplasmic reticulum to other parts of the cell.
- Synthesizes proteins: The ER is involved in the synthesis of proteins, which are then transported to other parts of the cell.
- Regulates calcium levels: The ER helps regulate calcium levels within the cell, which is essential for various cellular processes.
4. Golgi Apparatus: The Cellular Packaging System
The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle that functions as a packaging and shipping system for the cell. The Golgi apparatus:
- Packages proteins and lipids: The Golgi apparatus packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell or for secretion outside the cell.
- Modifies proteins: The Golgi apparatus modifies proteins by adding carbohydrates and lipids to create glycoproteins and lipoproteins.
- Regulates cellular secretion: The Golgi apparatus regulates the secretion of molecules from the cell.
5. Lysosomes: The Cellular Digestive System
Lysosomes are organelles responsible for cellular digestion and recycling of macromolecules. The lysosomes:
- Digest macromolecules: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
- Recycle cellular waste: Lysosomes recycle cellular waste by breaking down and reusing macromolecules.
- Maintain cellular homeostasis: Lysosomes help maintain cellular homeostasis by regulating the levels of macromolecules within the cell.
6. Chloroplasts: The Photosynthetic Organelle
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some algae, responsible for photosynthesis. The chloroplasts:
- Absorb light energy: Chloroplasts absorb light energy from the sun, which is used to power photosynthesis.
- Convert light energy into chemical energy: Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- Produce glucose: Chloroplasts produce glucose through the process of photosynthesis.
7. Peroxisomes: The Cellular Detoxification System
Peroxisomes are organelles responsible for cellular detoxification and the breakdown of fatty acids. The peroxisomes:
- Break down fatty acids: Peroxisomes break down fatty acids into smaller molecules, which can be used for energy production.
- Detoxify the cell: Peroxisomes detoxify the cell by breaking down and removing toxic substances.
- Regulate cellular metabolism: Peroxisomes regulate cellular metabolism by controlling the levels of fatty acids and other molecules.
In conclusion, each cell organelle plays a unique and essential role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and enabling the cell to perform its functions. Understanding the functions of these organelles is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of cellular biology.
What is the main function of the nucleus?
+The main function of the nucleus is to store genetic information in the form of DNA and regulate gene expression.
What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
+Mitochondria generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) through the process of cellular respiration, which is the primary energy currency of the cell.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
+The Golgi apparatus packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell or for secretion outside the cell.



