Cell Membrane Structure And Function Worksheet Answer Key
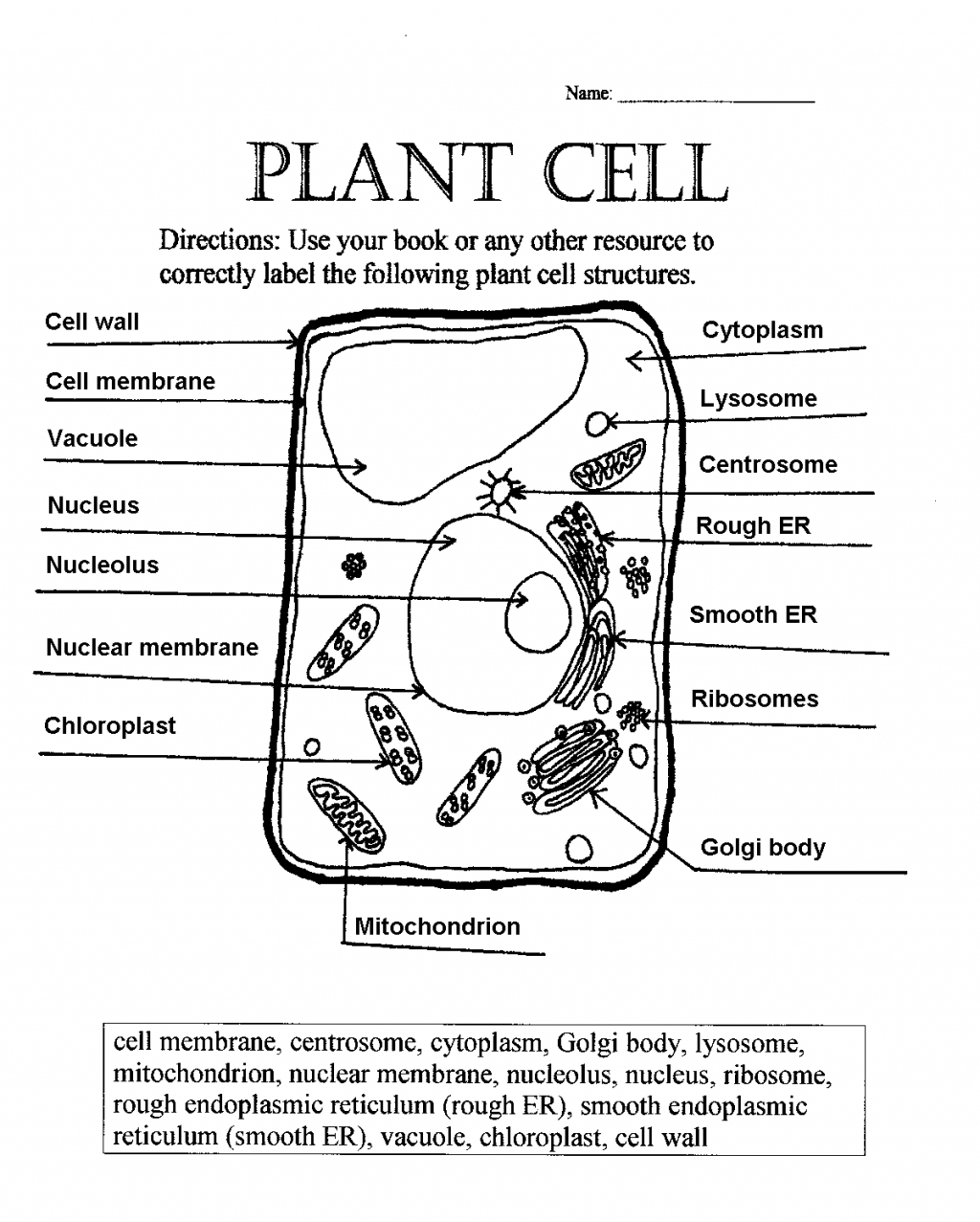
Cell Membrane Structure and Function
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. It is a semi-permeable membrane that allows certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
Components of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is composed of several key components, including:
- Phospholipid Bilayer: The main structure of the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, which is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules with their hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and their hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards.
- Proteins: Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and play a crucial role in the functioning of the cell membrane. They can act as channels, receptors, or enzymes.
- Cholesterol: Cholesterol molecules are also embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and help to maintain the fluidity of the membrane.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrate molecules are attached to the surface of the cell membrane and play a role in cell-cell recognition and signaling.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane performs several important functions, including:
- Selective Permeability: The cell membrane allows certain substances to pass through while keeping others out. This is achieved through the use of transport proteins and the selective permeability of the phospholipid bilayer.
- Cell Signaling: The cell membrane plays a crucial role in cell signaling, allowing cells to communicate with each other through the use of signaling molecules.
- Cell Recognition: The cell membrane allows cells to recognize and interact with other cells and molecules.
- Regulation of Cell Growth: The cell membrane helps to regulate cell growth by controlling the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
Types of Cell Membrane Transport
There are several types of cell membrane transport, including:
- Passive Transport: Passive transport involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This can occur through diffusion or osmosis.
- Active Transport: Active transport involves the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This requires energy and is often achieved through the use of transport proteins.
- Endocytosis: Endocytosis involves the uptake of molecules or particles into the cell through the formation of vesicles.
- Exocytosis: Exocytosis involves the release of molecules or particles from the cell through the formation of vesicles.
Cell Membrane Structure and Function Worksheet Answer Key
Section 1: Multiple Choice
- What is the main structure of the cell membrane? a) Phospholipid bilayer b) Protein layer c) Carbohydrate layer d) Nucleic acid layer
Answer: a) Phospholipid bilayer
- Which component of the cell membrane helps to maintain its fluidity? a) Cholesterol b) Protein c) Carbohydrate d) Phospholipid
Answer: a) Cholesterol
- What is the primary function of the cell membrane? a) To provide structure to the cell b) To regulate cell growth c) To control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell d) To produce energy for the cell
Answer: c) To control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell
Section 2: Short Answer
- Describe the structure of the phospholipid bilayer.
Answer: The phospholipid bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules with their hydrophilic heads facing outwards and their hydrophobic tails facing inwards.
- What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
Answer: Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and play a crucial role in the functioning of the cell membrane. They can act as channels, receptors, or enzymes.
Section 3: Essay
- Describe the functions of the cell membrane and explain how it regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
Answer: The cell membrane performs several important functions, including selective permeability, cell signaling, cell recognition, and regulation of cell growth. The cell membrane regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell through the use of transport proteins and the selective permeability of the phospholipid bilayer. This allows certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
🔍 Note: This answer key provides sample answers to a cell membrane structure and function worksheet. It is not intended to be a comprehensive or definitive answer key.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to control the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
What is the structure of the phospholipid bilayer?
+The phospholipid bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules with their hydrophilic heads facing outwards and their hydrophobic tails facing inwards.
What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
+Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and play a crucial role in the functioning of the cell membrane. They can act as channels, receptors, or enzymes.