5 Ways to Master pH and pOH Calculations
Understanding pH and pOH: A Crucial Aspect of Chemistry
In chemistry, the pH and pOH scales are essential concepts that help us understand the nature of solutions. pH measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, while pOH measures the concentration of hydroxide ions. Mastering pH and pOH calculations is crucial for chemists, biologists, and environmental scientists, as it helps them understand and predict the behavior of various substances in different environments. In this article, we will explore five ways to master pH and pOH calculations.
Method 1: Understanding the pH and pOH Scales
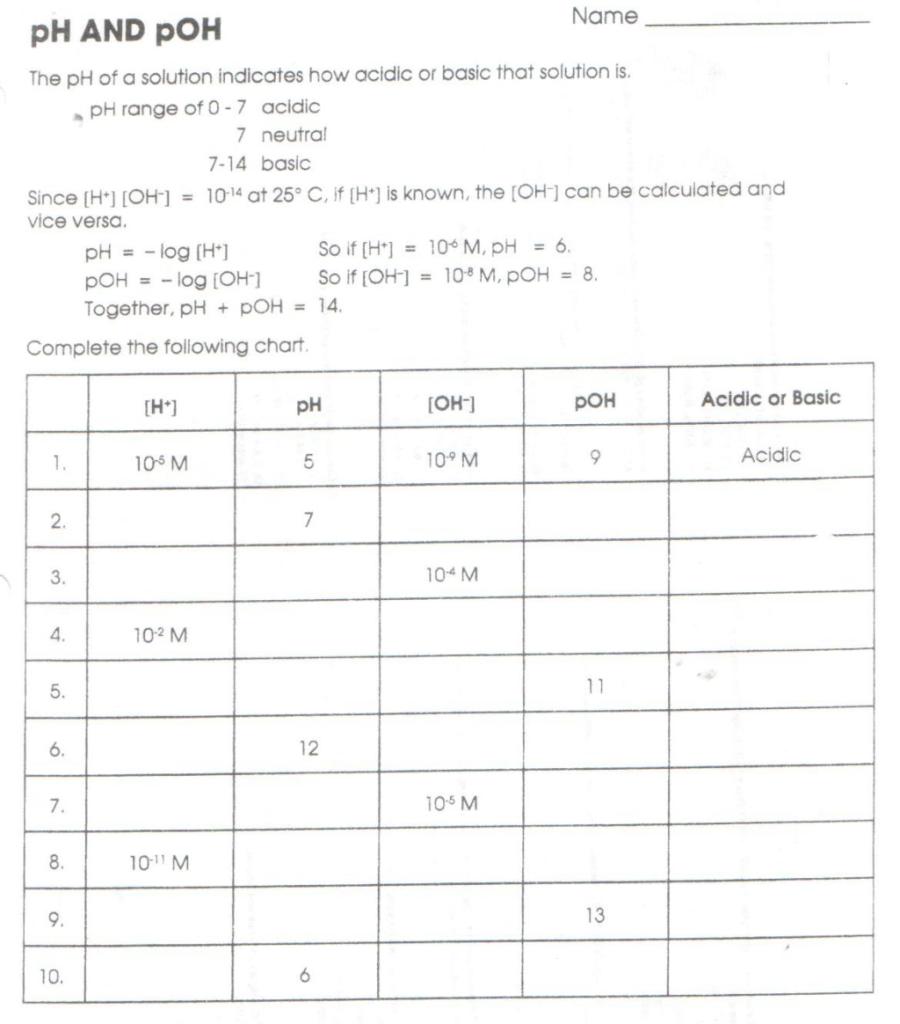
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with a pH of 7 being neutral. A pH less than 7 is acidic, while a pH greater than 7 is basic. The pOH scale, on the other hand, ranges from 0 to 14, with a pOH of 7 being neutral. A pOH less than 7 is basic, while a pOH greater than 7 is acidic.
To calculate pH and pOH, you need to understand the relationship between the two scales. The pH and pOH of a solution are related by the following equation:
pH + pOH = 14
This equation shows that as the pH of a solution increases, the pOH decreases, and vice versa.
📝 Note: It's essential to remember that the pH and pOH scales are logarithmic, meaning that a small change in pH or pOH represents a significant change in the concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions.
Method 2: Using the pH and pOH Formulas
To calculate the pH of a solution, you can use the following formula:
pH = -log[H+]
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per liter (M).
To calculate the pOH of a solution, you can use the following formula:
pOH = -log[OH-]
where [OH-] is the concentration of hydroxide ions in moles per liter (M).
These formulas can be used to calculate the pH and pOH of a solution if you know the concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions.
Method 3: Using the Kw Expression
The Kw expression is a useful tool for calculating the pH and pOH of a solution. Kw is the ion product constant for water, which is equal to 1.0 x 10^-14 at 25°C.
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10^-14
You can use the Kw expression to calculate the pH and pOH of a solution if you know the concentration of either hydrogen or hydroxide ions.
📝 Note: The Kw expression is temperature-dependent, so make sure to use the correct value for the temperature at which you are working.
Method 4: Using pH and pOH Tables
pH and pOH tables are useful tools for quickly calculating the pH and pOH of a solution. These tables provide the pH and pOH values for a range of hydrogen and hydroxide ion concentrations.
You can use pH and pOH tables to calculate the pH and pOH of a solution if you know the concentration of hydrogen or hydroxide ions.
Method 5: Practicing with Sample Problems
The best way to master pH and pOH calculations is to practice with sample problems. Here are a few examples:
- What is the pH of a solution with a hydrogen ion concentration of 1.0 x 10^-5 M?
- What is the pOH of a solution with a hydroxide ion concentration of 1.0 x 10^-9 M?
- What is the pH and pOH of a solution with a Kw value of 1.0 x 10^-14?
By practicing with sample problems, you can develop your skills and become proficient in calculating pH and pOH values.
📝 Note: Make sure to check your answers with a pH and pOH calculator or table to ensure accuracy.
In conclusion, mastering pH and pOH calculations is crucial for chemists, biologists, and environmental scientists. By understanding the pH and pOH scales, using the pH and pOH formulas, using the Kw expression, using pH and pOH tables, and practicing with sample problems, you can become proficient in calculating pH and pOH values.
What is the relationship between pH and pOH?
+
The pH and pOH of a solution are related by the equation pH + pOH = 14.
How do I calculate the pH of a solution?
+
You can calculate the pH of a solution using the formula pH = -log[H+], where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per liter (M).
What is the Kw expression?
+
The Kw expression is the ion product constant for water, which is equal to 1.0 x 10^-14 at 25°C.
Related Terms:
- Calculating pH Worksheet answers
- pH and pOH exercise
- pH Worksheet pdf



