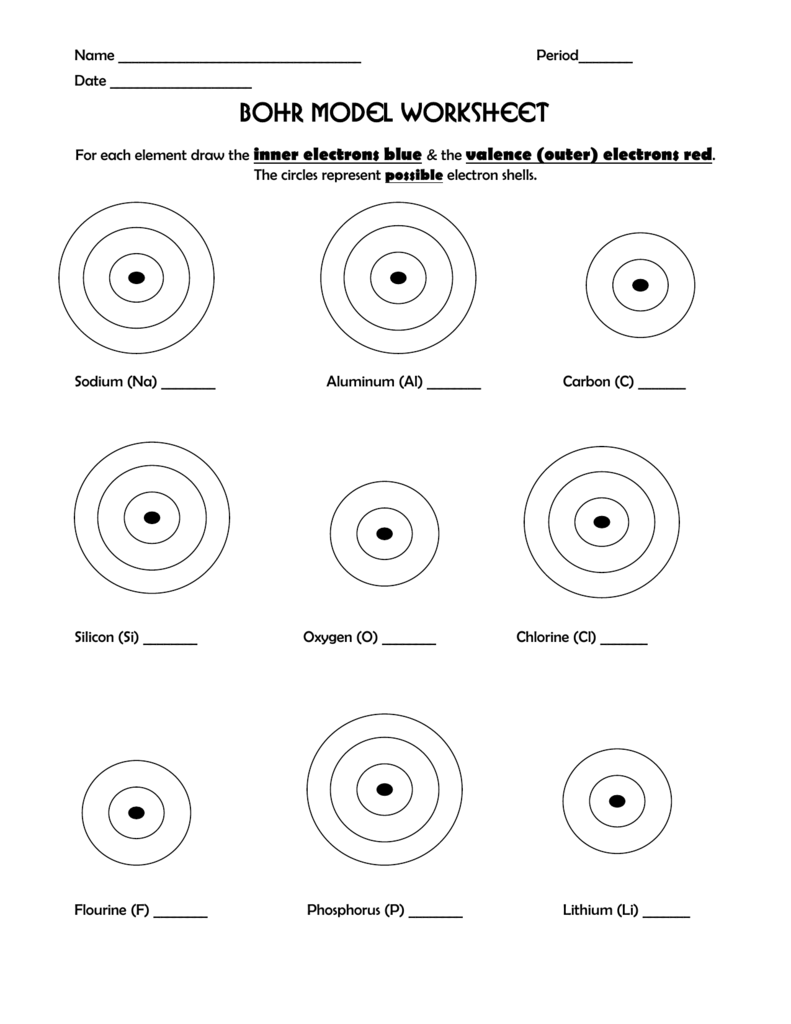
Bohr Models Worksheet Answers and Study Guide
Understanding the Bohr Model
The Bohr model, developed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a simplified model of an atom that depicts the arrangement of electrons in a concentric circle around the nucleus. This model is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, and it’s essential to understand its principles to grasp the behavior of atoms and molecules.
Key Components of the Bohr Model
- Nucleus: The central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells.
- Energy Levels: Concentric circles around the nucleus where electrons are found.
- Principal Energy Levels: The main energy levels, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.).
How the Bohr Model Works
In the Bohr model, electrons occupy specific energy levels, and each energy level has a limited capacity. The electrons in an atom tend to occupy the lowest available energy level, and they jump to higher energy levels when energy is absorbed.
🔹 Note: The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom, and it's not entirely accurate. However, it's still a useful tool for understanding the basic principles of atomic structure.
Bohr Models Worksheet Answers
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
- Who developed the Bohr model of the atom? a) Niels Bohr b) Ernest Rutherford c) J.J. Thomson d) Robert Millikan
Answer: a) Niels Bohr
- What is the central part of the atom called? a) Electron cloud b) Nucleus c) Proton d) Neutron
Answer: b) Nucleus
- What are the negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus? a) Protons b) Neutrons c) Electrons d) Alpha particles
Answer: c) Electrons
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the main components of the Bohr model.
Answer: The main components of the Bohr model are the nucleus, electrons, and energy levels. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while electrons occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus.
- What is the significance of the principal energy levels in the Bohr model?
Answer: The principal energy levels, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.), represent the main energy levels that electrons occupy. Each principal energy level has a limited capacity, and electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy level.
Section 3: Essay Questions
- Explain the limitations of the Bohr model.
Answer: The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom, and it has several limitations. It does not account for the electron’s spin, and it assumes that electrons occupy fixed energy levels. Additionally, the Bohr model does not explain the behavior of atoms with multiple electrons.
- Describe the significance of the Bohr model in understanding atomic structure.
Answer: The Bohr model is a fundamental concept in understanding atomic structure. It provides a simplified representation of the atom, highlighting the arrangement of electrons in energy levels around the nucleus. Although it has limitations, the Bohr model is still a useful tool for grasping the basic principles of atomic structure.
Study Guide
- Review the key components of the Bohr model, including the nucleus, electrons, and energy levels.
- Understand the significance of the principal energy levels and how electrons occupy them.
- Familiarize yourself with the limitations of the Bohr model and its significance in understanding atomic structure.

| Key Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | The central part of the atom, containing protons and neutrons. |
| Electrons | Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells. |
| Energy Levels | Concentric circles around the nucleus where electrons are found. |
| Principal Energy Levels | The main energy levels, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.). |
What is the Bohr model, and who developed it?
+The Bohr model is a simplified representation of the atom, developed by Niels Bohr in 1913. It depicts the arrangement of electrons in energy levels around the nucleus.
What are the limitations of the Bohr model?
+The Bohr model has several limitations, including not accounting for the electron’s spin and assuming that electrons occupy fixed energy levels. Additionally, it does not explain the behavior of atoms with multiple electrons.
What is the significance of the principal energy levels in the Bohr model?
+The principal energy levels, denoted by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.), represent the main energy levels that electrons occupy. Each principal energy level has a limited capacity, and electrons tend to occupy the lowest available energy level.
Related Terms:
- Momentum sudut
- Bilangan kuantum utama
- Konstanta Planck
- Pi
- Bohr Model Worksheet PDF
- Bohr model Worksheet with answers